
White test
Encyclopedia
In statistics
, the White test is a statistical test that establishes whether the residual
variance
of a variable in a regression model is constant: that is for homoscedasticity
.
This test, and an estimator for heteroscedasticity-consistent standard errors
, were proposed by Halbert White
in 1980. These methods have become extremely widely used, making this paper one of the most cited articles in economics.
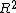 . The LM test statistic is the product of the R2 value and sample size:
. The LM test statistic is the product of the R2 value and sample size: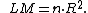
This follows a chi-squared distribution, with degrees of freedom equal to the number of estimated parameters (in the auxiliary regression) minus one.
An alternative to the White test is the Breusch–Pagan test.
If homoscedasticity is rejected one can use a GARCH model.
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
, the White test is a statistical test that establishes whether the residual
Errors and residuals in statistics
In statistics and optimization, statistical errors and residuals are two closely related and easily confused measures of the deviation of a sample from its "theoretical value"...
variance
Variance
In probability theory and statistics, the variance is a measure of how far a set of numbers is spread out. It is one of several descriptors of a probability distribution, describing how far the numbers lie from the mean . In particular, the variance is one of the moments of a distribution...
of a variable in a regression model is constant: that is for homoscedasticity
Homoscedasticity
In statistics, a sequence or a vector of random variables is homoscedastic if all random variables in the sequence or vector have the same finite variance. This is also known as homogeneity of variance. The complementary notion is called heteroscedasticity...
.
This test, and an estimator for heteroscedasticity-consistent standard errors
Heteroscedasticity-consistent standard errors
The topic of heteroscedasticity-consistent standard errors arises in statistics and econometrics in the context of linear regression and also time series analysis...
, were proposed by Halbert White
Halbert White
Halbert White is the Chancellor’s Associates Distinguished Professor of Economics at the University of California, San Diego and has via his 1980 paper on robust standard errors become noted for having written the most cited paper within economics over the recent past.In 1999, Dr...
in 1980. These methods have become extremely widely used, making this paper one of the most cited articles in economics.
Testing constant variance
To test for constant variance one undertakes an auxiliary regression analysis: this regresses the squared residuals from the original regression model onto a set of regressors that contain the original regressors, the cross-products of the regressors and the squared regressors. One then inspects the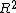 . The LM test statistic is the product of the R2 value and sample size:
. The LM test statistic is the product of the R2 value and sample size: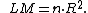
This follows a chi-squared distribution, with degrees of freedom equal to the number of estimated parameters (in the auxiliary regression) minus one.
An alternative to the White test is the Breusch–Pagan test.
If homoscedasticity is rejected one can use a GARCH model.

