Wenker synthesis
Encyclopedia
The Wenker synthesis is an organic reaction
converting a beta amino alcohol
to an aziridine
with the aid of sulfuric acid
.
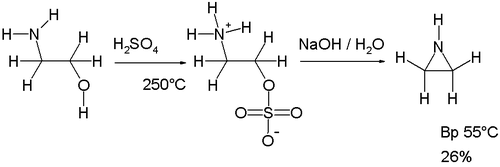 The original Wenker synthesis of aziridine itself takes place in two steps. In the first step ethanolamine
The original Wenker synthesis of aziridine itself takes place in two steps. In the first step ethanolamine
is reacted with sulfuric acid
at high temperatures (250°C) to the sulfonate
salt, This salt is then reacted with sodium hydroxide in the second step forming aziridine. The base
abstracts an amine proton enabling it to displace the sulfonate group. A modification of this reaction involving lower reaction temperatures (140 - 180°C) and therefore reduced charring increases the yield of the intermediate.
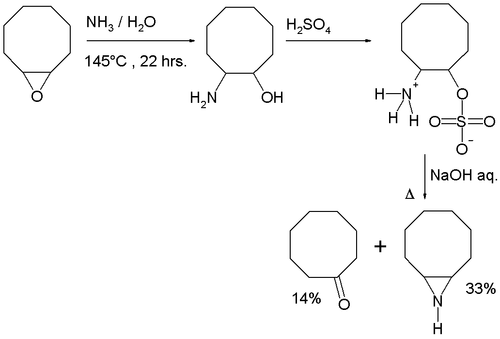
Starting from cyclooctene oxide
, trans-2-Aminocyclooctanol gives a mixture of Cycloöctenimine and of cyclooctanone as a result of competing Hofmann elimination
.
Organic reaction
Organic reactions are chemical reactions involving organic compounds. The basic organic chemistry reaction types are addition reactions, elimination reactions, substitution reactions, pericyclic reactions, rearrangement reactions, photochemical reactions and redox reactions. In organic synthesis,...
converting a beta amino alcohol
Amino alcohol
Amino alcohols are organic compounds that contain both an amine functional group and an alcohol functional group.-Common amino alcohols:* Ethanolamines* Heptaminol* Isoetarine* Norepinephrine* Propanolamines* Sphingosine...
to an aziridine
Aziridine
Aziridines are organic compounds containing the aziridine functional group, a three-membered heterocycle with one amine group and two methylene groups...
with the aid of sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid is a strong mineral acid with the molecular formula . Its historical name is oil of vitriol. Pure sulfuric acid is a highly corrosive, colorless, viscous liquid. The salts of sulfuric acid are called sulfates...
.

Ethanolamine
Ethanolamine, also called 2-aminoethanol or monoethanolamine , is an organic chemical compound that is both a primary amine and a primary alcohol . Like other amines, monoethanolamine acts as a weak base...
is reacted with sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid is a strong mineral acid with the molecular formula . Its historical name is oil of vitriol. Pure sulfuric acid is a highly corrosive, colorless, viscous liquid. The salts of sulfuric acid are called sulfates...
at high temperatures (250°C) to the sulfonate
Sulfonate
A sulfonate is a salt or ester of a sulfonic acid. It contains the functional group R-SO2O-.- Sulfonate salts:Anions with the general formula RSO2O− are called sulfonates. They are the conjugate bases of sulfonic acids with formula RSO2OH. As sulfonic acids tend to be strong acids, the...
salt, This salt is then reacted with sodium hydroxide in the second step forming aziridine. The base
Base (chemistry)
For the term in genetics, see base A base in chemistry is a substance that can accept hydrogen ions or more generally, donate electron pairs. A soluble base is referred to as an alkali if it contains and releases hydroxide ions quantitatively...
abstracts an amine proton enabling it to displace the sulfonate group. A modification of this reaction involving lower reaction temperatures (140 - 180°C) and therefore reduced charring increases the yield of the intermediate.
Starting from cyclooctene oxide
Epoxide
An epoxide is a cyclic ether with three ring atoms. This ring approximately defines an equilateral triangle, which makes it highly strained. The strained ring makes epoxides more reactive than other ethers. Simple epoxides are named from the parent compound ethylene oxide or oxirane, such as in...
, trans-2-Aminocyclooctanol gives a mixture of Cycloöctenimine and of cyclooctanone as a result of competing Hofmann elimination
Hofmann elimination
Hofmann elimination is a process where an amine is reacted to create a tertiary amine and an alkene by treatment with excess methyl iodide followed by treatment with silver oxide, water, and heat.After the first step, a quaternary ammonium iodide salt is created...
.


