
Volume of fluid method
Encyclopedia
In computational fluid dynamics
, the volume of fluid method (or in short VOF method) is a numerical technique for tracking and locating the free surface
(or fluid-fluid interface). It belongs to the class of Eulerian methods which are characterized by a mesh
that is either stationary or is moving in a certain prescribed manner to accommodate the evolving shape of the interface. As such, VOF is an advection scheme—a numerical recipe that allows the programmer to track the shape and position of the interface, but it is not a standalone flow solving algorithm. The Navier-Stokes equations
describing the motion of the flow have to be solved separately. The same applies for all other advection algorithms.
(MAC) methods. First accounts of what is now known as VOF have been given by Noh & Woodward (1976), where fraction function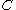 (see below) appeared, although first publication in a Journal was by Hirt & Nichols (1981). Since VOF method surpassed MAC by lowering computer storage requirements, it quickly became popular. Early applications include Torrey et al. from Los Alamos, who created VOF codes for NASA (1985,1987). First implementations of VOF suffered from imperfect interface description, which was later remedied by introducing a Piecewise-Linear Interface Calculation (PLIC) scheme . Using VOF with PLIC is a contemporary standard, used in number of computer codes , including ANSYS Fluent.
(see below) appeared, although first publication in a Journal was by Hirt & Nichols (1981). Since VOF method surpassed MAC by lowering computer storage requirements, it quickly became popular. Early applications include Torrey et al. from Los Alamos, who created VOF codes for NASA (1985,1987). First implementations of VOF suffered from imperfect interface description, which was later remedied by introducing a Piecewise-Linear Interface Calculation (PLIC) scheme . Using VOF with PLIC is a contemporary standard, used in number of computer codes , including ANSYS Fluent.
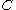 . It is defined as the integral
. It is defined as the integral
of fluid's characteristic function
in the control volume
(namely, volume of a computational grid
cell). Basically, when the cell is empty, with no traced fluid inside. the value of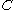 is zero; when the cell is full,
is zero; when the cell is full, 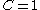 ; and when the interphasal interface cuts the cell, then
; and when the interphasal interface cuts the cell, then 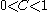 .
. 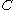 is a discontinuous function, its value jumps from 0 to 1 when the argument moves into interior of traced phase.
is a discontinuous function, its value jumps from 0 to 1 when the argument moves into interior of traced phase.
The fraction function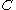 is a scalar function, and while the fluid moves with velocity
is a scalar function, and while the fluid moves with velocity  (in three-dimensional space
(in three-dimensional space 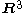 ) every fluid particle retains its identity, i.e. when a particle is a given phase, it doesn't change the phase - like a particle of air, that is a part of air bubble in water remains air particle, regardless of the bubble movement (actually, for this to hold, we have to disregard processes such as dissolving of air in water). If that is so, then the substantial derivative of fraction function
) every fluid particle retains its identity, i.e. when a particle is a given phase, it doesn't change the phase - like a particle of air, that is a part of air bubble in water remains air particle, regardless of the bubble movement (actually, for this to hold, we have to disregard processes such as dissolving of air in water). If that is so, then the substantial derivative of fraction function 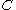 needs to be equal to zero:
needs to be equal to zero:
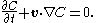
This is actually the same equation that has to be fulfilled by the level set
distance function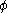 .
.
This equation cannot be easily solved directly, since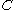 is discontinuous, but such attempts have been performed. But the most popular approach to the equation is the so called geometrical reconstruction, originating in the works of Hirt and B. D. Nichols.
is discontinuous, but such attempts have been performed. But the most popular approach to the equation is the so called geometrical reconstruction, originating in the works of Hirt and B. D. Nichols.
The VOF method is known for its ability to conserve the "mass" of the traced fluid, also, when fluid interface changes its topology
, this change is traced easily, so the interfaces can for example join, or break apart.
Computational fluid dynamics
Computational fluid dynamics, usually abbreviated as CFD, is a branch of fluid mechanics that uses numerical methods and algorithms to solve and analyze problems that involve fluid flows. Computers are used to perform the calculations required to simulate the interaction of liquids and gases with...
, the volume of fluid method (or in short VOF method) is a numerical technique for tracking and locating the free surface
Free surface
In physics, a free surface is the surface of a fluid that is subject to constant perpendicular normal stress and zero parallel shear stress,such as the boundary between two homogenous fluids,for example liquid water and the air in the Earth's atmosphere...
(or fluid-fluid interface). It belongs to the class of Eulerian methods which are characterized by a mesh
Polygon mesh
A polygon mesh or unstructured grid is a collection of vertices, edges and faces that defines the shape of a polyhedral object in 3D computer graphics and solid modeling...
that is either stationary or is moving in a certain prescribed manner to accommodate the evolving shape of the interface. As such, VOF is an advection scheme—a numerical recipe that allows the programmer to track the shape and position of the interface, but it is not a standalone flow solving algorithm. The Navier-Stokes equations
Navier-Stokes equations
In physics, the Navier–Stokes equations, named after Claude-Louis Navier and George Gabriel Stokes, describe the motion of fluid substances. These equations arise from applying Newton's second law to fluid motion, together with the assumption that the fluid stress is the sum of a diffusing viscous...
describing the motion of the flow have to be solved separately. The same applies for all other advection algorithms.
History
The Volume of Fluid method is based on earlier Marker-and-CellMarker-And-Cell
The Marker-And-Cell method is commonly used in computer graphics to discretize functions for fluid and other simulations. -External links:*, an explanation of fluid simulation...
(MAC) methods. First accounts of what is now known as VOF have been given by Noh & Woodward (1976), where fraction function
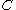 (see below) appeared, although first publication in a Journal was by Hirt & Nichols (1981). Since VOF method surpassed MAC by lowering computer storage requirements, it quickly became popular. Early applications include Torrey et al. from Los Alamos, who created VOF codes for NASA (1985,1987). First implementations of VOF suffered from imperfect interface description, which was later remedied by introducing a Piecewise-Linear Interface Calculation (PLIC) scheme . Using VOF with PLIC is a contemporary standard, used in number of computer codes , including ANSYS Fluent.
(see below) appeared, although first publication in a Journal was by Hirt & Nichols (1981). Since VOF method surpassed MAC by lowering computer storage requirements, it quickly became popular. Early applications include Torrey et al. from Los Alamos, who created VOF codes for NASA (1985,1987). First implementations of VOF suffered from imperfect interface description, which was later remedied by introducing a Piecewise-Linear Interface Calculation (PLIC) scheme . Using VOF with PLIC is a contemporary standard, used in number of computer codes , including ANSYS Fluent.Specification
The method is based on the idea of so-called fraction function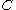 . It is defined as the integral
. It is defined as the integralIntegral
Integration is an important concept in mathematics and, together with its inverse, differentiation, is one of the two main operations in calculus...
of fluid's characteristic function
Characteristic function
In mathematics, characteristic function can refer to any of several distinct concepts:* The most common and universal usage is as a synonym for indicator function, that is the function* In probability theory, the characteristic function of any probability distribution on the real line is given by...
in the control volume
Control volume
In fluid mechanics and thermodynamics, a control volume is a mathematical abstraction employed in the process of creating mathematical models of physical processes. In an inertial frame of reference, it is a volume fixed in space or moving with constant velocity through which the fluid flows...
(namely, volume of a computational grid
Grid
Grid or The Grid may refer to:In entertainment and media:* The Grid, an electronic dance group* Kevorkian Death Cycle, a music group formerly called Grid* The Grid , a 2001 third person shooter...
cell). Basically, when the cell is empty, with no traced fluid inside. the value of
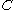 is zero; when the cell is full,
is zero; when the cell is full, 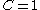 ; and when the interphasal interface cuts the cell, then
; and when the interphasal interface cuts the cell, then 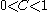 .
. 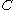 is a discontinuous function, its value jumps from 0 to 1 when the argument moves into interior of traced phase.
is a discontinuous function, its value jumps from 0 to 1 when the argument moves into interior of traced phase.The fraction function
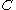 is a scalar function, and while the fluid moves with velocity
is a scalar function, and while the fluid moves with velocity  (in three-dimensional space
(in three-dimensional space 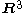 ) every fluid particle retains its identity, i.e. when a particle is a given phase, it doesn't change the phase - like a particle of air, that is a part of air bubble in water remains air particle, regardless of the bubble movement (actually, for this to hold, we have to disregard processes such as dissolving of air in water). If that is so, then the substantial derivative of fraction function
) every fluid particle retains its identity, i.e. when a particle is a given phase, it doesn't change the phase - like a particle of air, that is a part of air bubble in water remains air particle, regardless of the bubble movement (actually, for this to hold, we have to disregard processes such as dissolving of air in water). If that is so, then the substantial derivative of fraction function 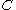 needs to be equal to zero:
needs to be equal to zero: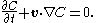
This is actually the same equation that has to be fulfilled by the level set
Level set
In mathematics, a level set of a real-valued function f of n variables is a set of the formthat is, a set where the function takes on a given constant value c....
distance function
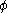 .
.This equation cannot be easily solved directly, since
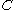 is discontinuous, but such attempts have been performed. But the most popular approach to the equation is the so called geometrical reconstruction, originating in the works of Hirt and B. D. Nichols.
is discontinuous, but such attempts have been performed. But the most popular approach to the equation is the so called geometrical reconstruction, originating in the works of Hirt and B. D. Nichols.The VOF method is known for its ability to conserve the "mass" of the traced fluid, also, when fluid interface changes its topology
Topology
Topology is a major area of mathematics concerned with properties that are preserved under continuous deformations of objects, such as deformations that involve stretching, but no tearing or gluing...
, this change is traced easily, so the interfaces can for example join, or break apart.

