
Vivification
Encyclopedia
Vivification is an operation on a description logic
knowledge base to improve performance of a semantic reasoner
. Vivification replaces a disjunction
of concepts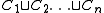 by the least common subsumer of the concepts
by the least common subsumer of the concepts 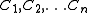 .
.
The goal of this operation is to improve the performance of the reasoner by replacing a complex set of concepts with a single concept which subsumes the original concepts.
For example, consider the example given in (Cohen 92): Suppose we have the concept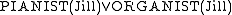 . This concept can be vivified into a simpler concept
. This concept can be vivified into a simpler concept 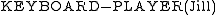 . This summarization leads to an approximation that may not be exactly equivalent to the original.
. This summarization leads to an approximation that may not be exactly equivalent to the original.
vivification is not necessarily exact. If the reasoner is operating under the open world assumption
we may get surprising results. In the previous example, if we replace the disjunction with the vivified concept, we will arrive at a surprising results.
First, we find that the reasoner will no longer classify Jill as either a pianist or an organist. Even though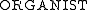 and
and 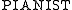 are the only two sub-classes, under the OWA we can no longer classify Jill as playing one or the other. The reason is that there may be another keyboard instrument (e.g. a harpsichord) that Jill plays but which does not have a specific subclass.
are the only two sub-classes, under the OWA we can no longer classify Jill as playing one or the other. The reason is that there may be another keyboard instrument (e.g. a harpsichord) that Jill plays but which does not have a specific subclass.
Description logic
Description logic is a family of formal knowledge representation languages. It is more expressive than propositional logic but has more efficient decision problems than first-order predicate logic....
knowledge base to improve performance of a semantic reasoner
Semantic reasoner
A semantic reasoner, reasoning engine, rules engine, or simply a reasoner, is a piece of software able to infer logical consequences from a set of asserted facts or axioms. The notion of a semantic reasoner generalizes that of an inference engine, by providing a richer set of mechanisms to work with...
. Vivification replaces a disjunction
Logical disjunction
In logic and mathematics, a two-place logical connective or, is a logical disjunction, also known as inclusive disjunction or alternation, that results in true whenever one or more of its operands are true. E.g. in this context, "A or B" is true if A is true, or if B is true, or if both A and B are...
of concepts
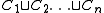 by the least common subsumer of the concepts
by the least common subsumer of the concepts 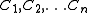 .
.The goal of this operation is to improve the performance of the reasoner by replacing a complex set of concepts with a single concept which subsumes the original concepts.
For example, consider the example given in (Cohen 92): Suppose we have the concept
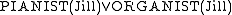 . This concept can be vivified into a simpler concept
. This concept can be vivified into a simpler concept 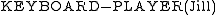 . This summarization leads to an approximation that may not be exactly equivalent to the original.
. This summarization leads to an approximation that may not be exactly equivalent to the original.An approximation
Knowledge baseKnowledge base
A knowledge base is a special kind of database for knowledge management. A Knowledge Base provides a means for information to be collected, organised, shared, searched and utilised.-Types:...
vivification is not necessarily exact. If the reasoner is operating under the open world assumption
Open World Assumption
In formal logic, the open world assumption is the assumption that the truth-value of a statement is independent of whether or not it is known by any single observer or agent to be true. It is the opposite of the closed world assumption, which holds that any statement that is not known to be true is...
we may get surprising results. In the previous example, if we replace the disjunction with the vivified concept, we will arrive at a surprising results.
First, we find that the reasoner will no longer classify Jill as either a pianist or an organist. Even though
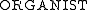 and
and 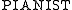 are the only two sub-classes, under the OWA we can no longer classify Jill as playing one or the other. The reason is that there may be another keyboard instrument (e.g. a harpsichord) that Jill plays but which does not have a specific subclass.
are the only two sub-classes, under the OWA we can no longer classify Jill as playing one or the other. The reason is that there may be another keyboard instrument (e.g. a harpsichord) that Jill plays but which does not have a specific subclass.

