
Virial stress
Encyclopedia
Virial stress is a measure of mechanical stress
on an atomic scale. It is given by
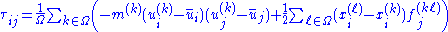
where
At zero kelvin
, all velocities are zero so we have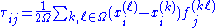 .
.
This can be thought of as follows. The τ11 component of stress is the force in the x1-direction divided by the area of a plane perpendicular to that direction. Consider two adjacent volumes separated by such a plane. The 11-component of stress on that interface is the sum of all pairwise forces between atoms on the two sides.
Stress (physics)
In continuum mechanics, stress is a measure of the internal forces acting within a deformable body. Quantitatively, it is a measure of the average force per unit area of a surface within the body on which internal forces act. These internal forces are a reaction to external forces applied on the body...
on an atomic scale. It is given by
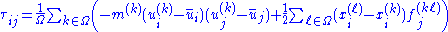
where
-
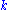 and
and 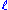 are atoms in the domain,
are atoms in the domain, -
 is the volume of the domain,
is the volume of the domain, -
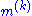 is the mass of atom k,
is the mass of atom k, -
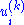 is the ith component of the velocity of atom k,
is the ith component of the velocity of atom k, -
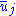 is the jth component of the average velocity of atoms in the volume,
is the jth component of the average velocity of atoms in the volume, -
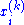 is the ith component of the position of atom k, and
is the ith component of the position of atom k, and -
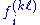 is the ith component of the force between atom
is the ith component of the force between atom 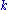 and
and 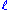 .
.
At zero kelvin
Absolute zero
Absolute zero is the theoretical temperature at which entropy reaches its minimum value. The laws of thermodynamics state that absolute zero cannot be reached using only thermodynamic means....
, all velocities are zero so we have
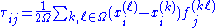 .
.This can be thought of as follows. The τ11 component of stress is the force in the x1-direction divided by the area of a plane perpendicular to that direction. Consider two adjacent volumes separated by such a plane. The 11-component of stress on that interface is the sum of all pairwise forces between atoms on the two sides.

