
Velocity obstacle
Encyclopedia
In robotics
and motion planning
, a velocity obstacle, commonly abbreviated VO, is the set of all velocities
of a robot
that will result in a collision
with another robot at some moment in time, assuming that the other robot maintains its current velocity. If the robot chooses a velocity inside the velocity obstacle then the two robots will eventually collide, if it chooses a velocity outside the velocity obstacle, such a collision is guaranteed not to occur.
This algorithm for robot collision avoidance has been repeatedly rediscovered and published under different names:
in 1989 as a maneuvering-board approach,
in 1993 it was first introduced as the "velocity obstacle",
in 1998 as collision cones,
and in 2009 as forbidden velocity maps.
The same algorithm has been used in maritime port navigation since at least 1903.
The velocity obstacle for a robot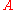 induced by a robot
induced by a robot 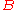 may be formally written as
may be formally written as
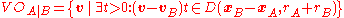
where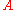 has position
has position 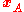 and radius
and radius
 , and
, and 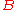 has position
has position 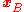 , radius
, radius 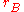 , and velocity
, and velocity 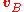 . The notation
. The notation 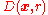 represents a disc
represents a disc
with center
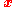 and radius
and radius  .
.
Variations include common velocity obstacles (CVO),, finite-time-interval velocity obstacles (FVO), generalized
velocity obstacles (GVO), hybrid reciprocal velocity obstacles (HRVO), nonlinear velocity obstacles (NLVO), reciprocal velocity obstacles (RVO), and recursive
probabilistic
velocity obstacles (PVO).
Robotics
Robotics is the branch of technology that deals with the design, construction, operation, structural disposition, manufacture and application of robots...
and motion planning
Motion planning
Motion planning is a term used in robotics for the process of detailing a task into discrete motions....
, a velocity obstacle, commonly abbreviated VO, is the set of all velocities
Velocity
In physics, velocity is speed in a given direction. Speed describes only how fast an object is moving, whereas velocity gives both the speed and direction of the object's motion. To have a constant velocity, an object must have a constant speed and motion in a constant direction. Constant ...
of a robot
Robot
A robot is a mechanical or virtual intelligent agent that can perform tasks automatically or with guidance, typically by remote control. In practice a robot is usually an electro-mechanical machine that is guided by computer and electronic programming. Robots can be autonomous, semi-autonomous or...
that will result in a collision
Collision
A collision is an isolated event which two or more moving bodies exert forces on each other for a relatively short time.Although the most common colloquial use of the word "collision" refers to accidents in which two or more objects collide, the scientific use of the word "collision" implies...
with another robot at some moment in time, assuming that the other robot maintains its current velocity. If the robot chooses a velocity inside the velocity obstacle then the two robots will eventually collide, if it chooses a velocity outside the velocity obstacle, such a collision is guaranteed not to occur.
This algorithm for robot collision avoidance has been repeatedly rediscovered and published under different names:
in 1989 as a maneuvering-board approach,
in 1993 it was first introduced as the "velocity obstacle",
in 1998 as collision cones,
and in 2009 as forbidden velocity maps.
The same algorithm has been used in maritime port navigation since at least 1903.
The velocity obstacle for a robot
 induced by a robot
induced by a robot  may be formally written as
may be formally written as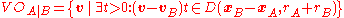
where
 has position
has position 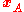 and radius
and radiusRadius
In classical geometry, a radius of a circle or sphere is any line segment from its center to its perimeter. By extension, the radius of a circle or sphere is the length of any such segment, which is half the diameter. If the object does not have an obvious center, the term may refer to its...
 , and
, and  has position
has position 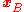 , radius
, radius 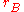 , and velocity
, and velocity 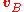 . The notation
. The notation 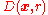 represents a disc
represents a discDisk (mathematics)
In geometry, a disk is the region in a plane bounded by a circle.A disk is said to be closed or open according to whether or not it contains the circle that constitutes its boundary...
with center
Centroid
In geometry, the centroid, geometric center, or barycenter of a plane figure or two-dimensional shape X is the intersection of all straight lines that divide X into two parts of equal moment about the line. Informally, it is the "average" of all points of X...
 and radius
and radius  .
.Variations include common velocity obstacles (CVO),, finite-time-interval velocity obstacles (FVO), generalized
Generalization
A generalization of a concept is an extension of the concept to less-specific criteria. It is a foundational element of logic and human reasoning. Generalizations posit the existence of a domain or set of elements, as well as one or more common characteristics shared by those elements. As such, it...
velocity obstacles (GVO), hybrid reciprocal velocity obstacles (HRVO), nonlinear velocity obstacles (NLVO), reciprocal velocity obstacles (RVO), and recursive
Recursion
Recursion is the process of repeating items in a self-similar way. For instance, when the surfaces of two mirrors are exactly parallel with each other the nested images that occur are a form of infinite recursion. The term has a variety of meanings specific to a variety of disciplines ranging from...
probabilistic
Probability
Probability is ordinarily used to describe an attitude of mind towards some proposition of whose truth we arenot certain. The proposition of interest is usually of the form "Will a specific event occur?" The attitude of mind is of the form "How certain are we that the event will occur?" The...
velocity obstacles (PVO).

