Valuation using discounted cash flows
Encyclopedia
Valuation using discounted cash flows is a method for determining the current value of a company using future cash flows adjusted for time value. The future cash flow
set is made up of the cash flows within the determined forecast period
and a continuing value that represents the cash flow stream after the forecast period.
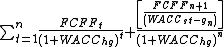
where
Example:
‘MedICT’ is a medical ICT startup that has just finished their business plan. Their goal is to provide medical professionals with software solutions for doing their own bookkeeping. Their only investor is required to wait for 5 years before making an exit. Therefore MedICT is using a forecast period of 5 years.
Example:
MedICT has chosen to use only operational cash flow
s in determining their estimated yearly cash flow:
In thousand €
Example:
MedICT has chosen their discount rates based upon their company maturity.
.
Example:
Total current value = 62.14
Example:
MedICT has chosen the perpetuity
growth model to calculate the value of cash flows after the forecast period. They estimate that they will grow at about 6% for the rest of these years.
(182*1.06 / (0.25-0.06)) = 1015.34
This value however is a future value
that still needs to be discounted to a current value:
1015.34 * 1/(1.25)^5 = 332.72
Example:
MedICT doesn’t have any debt so it only needs to add up the current value of the continuing value and the current value of all cash flows during the forecast period:
62.14 + 332.72= 394.86
The equity value of MedICT : € 394.86
Cash flow
Cash flow is the movement of money into or out of a business, project, or financial product. It is usually measured during a specified, finite period of time. Measurement of cash flow can be used for calculating other parameters that give information on a company's value and situation.Cash flow...
set is made up of the cash flows within the determined forecast period
Forecast period (finance)
In finance, the forecast period is the time period in which the individual yearly cash flows are input to the discounted cash flow formula. Cash flows after the forecast period can only be represented by a fixed number such as the compound annual growth rate. There are no fixed rules for...
and a continuing value that represents the cash flow stream after the forecast period.
Basic formula for firm valuation using DCF model
value of firm =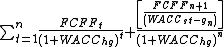
where
- FCFF is the Free Cash FlowFree cash flowIn corporate finance, free cash flow is cash flow available for distribution among all the securities holders of an organization. They include equity holders, debt holders, preferred stock holders, convertible security holders, and so on....
to the Firm (i.e. Operating cash flowOperating cash flowIn financial accounting, operating cash flow , cash flow provided by operations or cash flow from operating activities , refers to the amount of cash a company generates from the revenues it brings in, excluding costs associated with long-term investment on capital items or investment in securities...
minus capital expenditures) - WACC is the Weighted Average Cost of CapitalWeighted average cost of capitalThe weighted average cost of capital is the rate that a company is expected to pay on average to all its security holders to finance its assets....
- t is the time period
- n is the number of time periods
- g is the growth rate
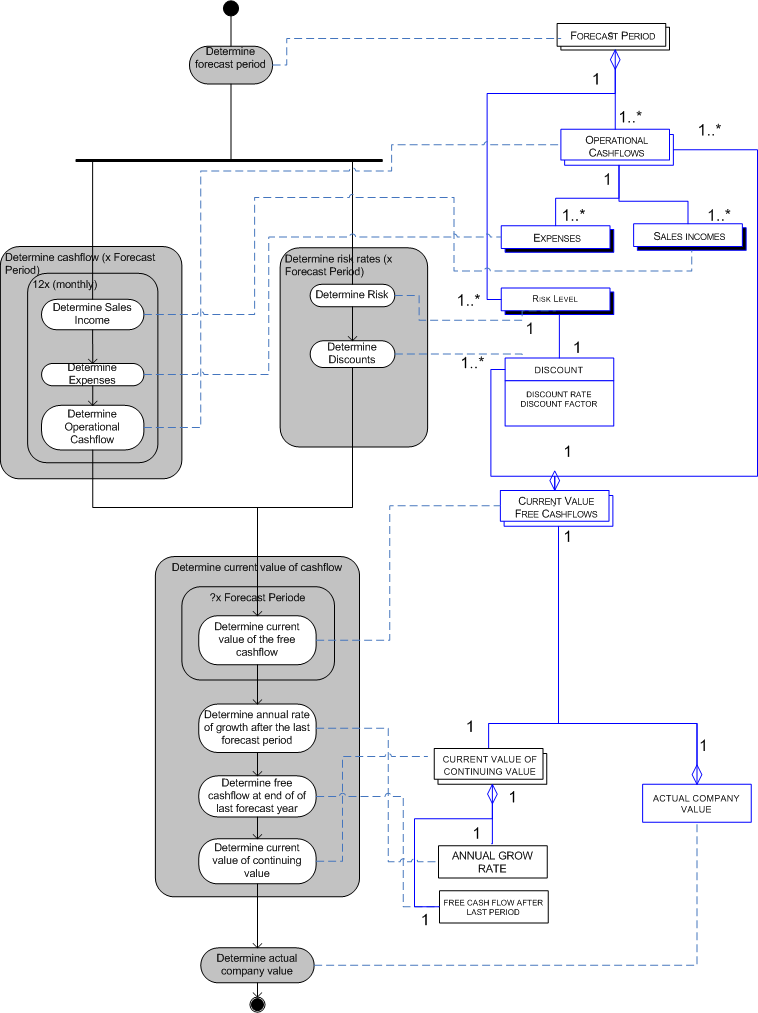
Process Data Diagram
The following diagram shows an overview of the process of company valuation. All activities in this model are explained in more detail in section 3: Using the DCF method.
Determine Forecast Period
The forecast period is the time period for which the individual yearly cash flows are input to the DCF formula. Cash flows after the forecast period can only be represented by a fixed number such as annual growth rates. There are no fixed rules for determining the duration of the forecast period.Example:
‘MedICT’ is a medical ICT startup that has just finished their business plan. Their goal is to provide medical professionals with software solutions for doing their own bookkeeping. Their only investor is required to wait for 5 years before making an exit. Therefore MedICT is using a forecast period of 5 years.
Determine the yearly Cash Flow
Cash flow is the difference between the amount of cash flowing in and out a company. Make sure to consistently include the different types of cash flows.Example:
MedICT has chosen to use only operational cash flow
Cash flow
Cash flow is the movement of money into or out of a business, project, or financial product. It is usually measured during a specified, finite period of time. Measurement of cash flow can be used for calculating other parameters that give information on a company's value and situation.Cash flow...
s in determining their estimated yearly cash flow:
In thousand €
|
|
|
Year 1 |
Year 2 |
Year 3 |
Year 4 |
Year 5 |
| Revenues |
|
+30 |
+100 |
+160 |
+330 |
+460 |
| Personnel |
|
-30 |
-80 |
-110 |
-160 |
-200 |
| Car Lease |
|
-6 |
-12 |
-12 |
-18 |
-18 |
| Marketing |
|
-10 |
-10 |
-10 |
-25 |
-30 |
| IT |
|
-20 |
-20 |
-20 |
-25 |
-30 |
| Cash Flow |
|
-36 |
-22 |
+8 |
+102 |
+182 |
Determine Discount Factor / Rate
Determine the appropriate discount rate and discount factor for each year of the forecast period based on the risk level associated with the company and its market.Example:
MedICT has chosen their discount rates based upon their company maturity.
|
|
|
Year 1 |
Year 2 |
Year 3 |
Year 4 |
Year 5 |
| Risk Group |
|
Seeking Money |
Early Startup |
Late Start Up |
Mature |
|
| Risk Rate |
|
50 - 100 |
40 – 60 |
30 – 50% |
10- 25% |
|
| Discount Rate |
|
65% |
55% |
45% |
35% |
25% |
| Discount Factor |
|
0.61 |
0.42 |
0.33 |
0.30 |
0.33 |
Determine Current Value
Calculate the current value of the future cash flows by multiplying each yearly cash flow by the discount factor for the year in question. This is known as the time value of moneyTime value of money
The time value of money is the value of money figuring in a given amount of interest earned over a given amount of time. The time value of money is the central concept in finance theory....
.
Example:
|
|
|
Year 1 |
Year 2 |
Year 3 |
Year 4 |
Year 5 |
| Cash Flow |
|
-36 |
-22 |
+8 |
+102 |
+182 |
| Discount Factor |
|
0.61 |
0.42 |
0.33 |
0.30 |
0.33 |
| Current Value |
|
€ -21.96 |
€ -9.24 |
€ 2.64 |
€30.6 |
€60.1 |
Total current value = 62.14
Determine the Continuing Value
Calculating cash flows after the forecast period is much more difficult as uncertainty, and therefore the risk factor, rises with each additional year into the future. The continuing value, or terminal value, is a solution that represents the cash flows after the forecast period.Example:
MedICT has chosen the perpetuity
Perpetuity
A perpetuity is an annuity that has no end, or a stream of cash payments that continues forever. There are few actual perpetuities in existence...
growth model to calculate the value of cash flows after the forecast period. They estimate that they will grow at about 6% for the rest of these years.
(182*1.06 / (0.25-0.06)) = 1015.34
This value however is a future value
Future value
Future value is the value of an asset at a specific date. It measures the nominal future sum of money that a given sum of money is "worth" at a specified time in the future assuming a certain interest rate, or more generally, rate of return; it is the present value multiplied by the accumulation...
that still needs to be discounted to a current value:
1015.34 * 1/(1.25)^5 = 332.72
Determining Equity Value
The value of the equity can be calculated by subtracting any outstanding debts from the total of all discounted cash flows.Example:
MedICT doesn’t have any debt so it only needs to add up the current value of the continuing value and the current value of all cash flows during the forecast period:
62.14 + 332.72= 394.86
The equity value of MedICT : € 394.86
Literature
- Kubr, Marchesi, Ilar, Kienhuis. 1998. Starting Up. Mckinsey & Company
- Pablo Fernandez. 2004. Equivalence of ten different discounted cash flow valuation methods. IESE Research Papers. D549
- Ruback, R. S., 1995, An Introduction to Cash Flow Valuation Methods, Harvard Business School Case # 295-155.
- Keck, T., E. Levengood, and A. Longfield, 1998, Using Discounted Cash Flow Analysis in an International Setting: A Survey of Issues in Modeling the Cost of Capital, Journal of Applied Corporate Finance, Fall, pp. 82–99.
- Aswath DamodaranAswath DamodaranAswath Damodaran is a Professor of Finance at the Stern School of Business at New York University , where he teaches corporate finance and equity valuation...
2001 Investment Valuation: Tools and Techniques for Determining Value. Wiley - McKinsey & Co., Tim Koller, Marc Goedhart, David Wessels. 2005. Valuation: Measuring and Managing the Value of Companies. John Wiley & Sons.
External links
- Selected Moments in the History of Discounted Present Value, Prof. Eric Kirzner Rotman School of ManagementRotman School of ManagementThe Joseph L. Rotman School of Management commonly known as Rotman School of Management is the University of Toronto's business school, located in St. George Street in Downtown Toronto. The school, named after Joseph L...
- Formulating the Imputed Cost of Equity Capital, Federal Reserve Bank of New York. Includes a review of basic valuation models, including DCF and CAPMCapital asset pricing modelIn finance, the capital asset pricing model is used to determine a theoretically appropriate required rate of return of an asset, if that asset is to be added to an already well-diversified portfolio, given that asset's non-diversifiable risk...
.

