Télé Distribution Francaise
Encyclopedia
Télé Diffusion de France, or TDF, is a time signal
service, broadcast on longwave radio
by the French
"Laboratoire primaire du temps et des frequences" (LPTF). This time signal is generated by an extremely accurate caesium
fountain atomic clock
. The time signal is broadcast from Allouis
, France at the "Centre National d'Etudes des Télécommunications" with a power of 2 MW at 162 kHz.
The signal is phase-modulated on the 162 kHz carrier in a way that will not be audible to AM receivers
listening to the normal France Inter signal. It requires a more complex receiver than the popular DCF77
service, but the much more powerful transmitter (40 times DCF77's 50 kW) give it a much greater range.
The signal is almost continuous but there is a regularly scheduled interruption for maintenance from 01:00 to 05:00 every Tuesday.
longwave
radio station
, transmitting the programs of the France Inter
Network of Télédiffusion de France (TDF). Time signals are transmitted by phase-modulating
the carrier by ±1 radian
in 0.1 s every second except the 59th second of each minute. This modulation pattern is doubled to indicate a binary one.
The binary encoding of date and time data during seconds 15 through 59 is identical to that of DCF77
; the numbers of the minute, hour, day of the month, day of the week, month and year are transmitted each minute from the 21st to the 58th second, in accordance with the French legal time scale. The time transmitted is the local time of the upcoming minute.
Also like DCF77, bit 20 is always 1, bit 19 indicates an upcoming leap second at the end of the current hour, bit 18 indicates when the local time is 1 hour ahead of UTC (i.e. winter time), bit 17 indicates that the local time is 2 hours ahead of UTC (i.e. summer time), and bit 16 indicates that a change to local time is will take place at the end of the current hour. Bit 15 is reserved to indicate abnormal transmitter operation.
As extensions to the DCF77 code, bit 14 is set during public holidays (14 July, Christmas, etc.), and bit 13 is set the day before public holidays.
The relative uncertainty of the carrier frequency is 2 parts in 1012.
Both the average phase and the average frequency deviation are thus zero. Additional non-timing data is sent by phase modulation during the rest of each second. But the second marker (and data bit) is always preceded by 100 ms without any phase modulation. The signal is not phase-modulated at all during the 59th second past the minute.
Time signal
A time signal is a visible, audible, mechanical, or electronic signal used as a reference to determine the time of day.-Audible and visible time signals:...
service, broadcast on longwave radio
Allouis longwave transmitter
The Allouis longwave transmitter first entered service, as France's central longwave transmitter, in 1939. It is located near the village of Allouis....
by the French
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
"Laboratoire primaire du temps et des frequences" (LPTF). This time signal is generated by an extremely accurate caesium
Caesium
Caesium or cesium is the chemical element with the symbol Cs and atomic number 55. It is a soft, silvery-gold alkali metal with a melting point of 28 °C , which makes it one of only five elemental metals that are liquid at room temperature...
fountain atomic clock
Atomic clock
An atomic clock is a clock that uses an electronic transition frequency in the microwave, optical, or ultraviolet region of the electromagnetic spectrum of atoms as a frequency standard for its timekeeping element...
. The time signal is broadcast from Allouis
Allouis
Allouis is a commune in the Cher department of the Centre region of France.-Geography:An area of lakes, woods and farming comprising the village and several hamlets, situated in the valley of the river Yèvre, some northwest of Bourges at the junction of the D20, D79 and the D122...
, France at the "Centre National d'Etudes des Télécommunications" with a power of 2 MW at 162 kHz.
The signal is phase-modulated on the 162 kHz carrier in a way that will not be audible to AM receivers
Amplitude modulation
Amplitude modulation is a technique used in electronic communication, most commonly for transmitting information via a radio carrier wave. AM works by varying the strength of the transmitted signal in relation to the information being sent...
listening to the normal France Inter signal. It requires a more complex receiver than the popular DCF77
DCF77
DCF77 is a longwave time signal and standard-frequency radio station. Its primary and backup transmitter are located in Mainflingen, about 25 km south-east of Frankfurt am Main, Germany. It is operated by Media Broadcast GmbH , on behalf of the Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt, Germany's...
service, but the much more powerful transmitter (40 times DCF77's 50 kW) give it a much greater range.
The signal is almost continuous but there is a regularly scheduled interruption for maintenance from 01:00 to 05:00 every Tuesday.
Signal format
TDF is actually an amplitude modulatedAmplitude modulation
Amplitude modulation is a technique used in electronic communication, most commonly for transmitting information via a radio carrier wave. AM works by varying the strength of the transmitted signal in relation to the information being sent...
longwave
Longwave
In radio, longwave refers to parts of radio spectrum with relatively long wavelengths. The term is a historic one dating from the early 20th century, when the radio spectrum was considered to consist of long, medium and short wavelengths...
radio station
Radio station
Radio broadcasting is a one-way wireless transmission over radio waves intended to reach a wide audience. Stations can be linked in radio networks to broadcast a common radio format, either in broadcast syndication or simulcast or both...
, transmitting the programs of the France Inter
France Inter
France Inter is a major French public radio channel and part of Radio France. It is a "generalist" station, aiming to provide a wide national audience with a full service of news and intelligent spoken-word programming, both serious and entertaining, liberally punctuated with an eclectic mix of...
Network of Télédiffusion de France (TDF). Time signals are transmitted by phase-modulating
Phase modulation
Phase modulation is a form of modulation that represents information as variations in the instantaneous phase of a carrier wave.Unlike its more popular counterpart, frequency modulation , PM is not very widely used for radio transmissions...
the carrier by ±1 radian
Radian
Radian is the ratio between the length of an arc and its radius. The radian is the standard unit of angular measure, used in many areas of mathematics. The unit was formerly a SI supplementary unit, but this category was abolished in 1995 and the radian is now considered a SI derived unit...
in 0.1 s every second except the 59th second of each minute. This modulation pattern is doubled to indicate a binary one.
The binary encoding of date and time data during seconds 15 through 59 is identical to that of DCF77
DCF77
DCF77 is a longwave time signal and standard-frequency radio station. Its primary and backup transmitter are located in Mainflingen, about 25 km south-east of Frankfurt am Main, Germany. It is operated by Media Broadcast GmbH , on behalf of the Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt, Germany's...
; the numbers of the minute, hour, day of the month, day of the week, month and year are transmitted each minute from the 21st to the 58th second, in accordance with the French legal time scale. The time transmitted is the local time of the upcoming minute.
Also like DCF77, bit 20 is always 1, bit 19 indicates an upcoming leap second at the end of the current hour, bit 18 indicates when the local time is 1 hour ahead of UTC (i.e. winter time), bit 17 indicates that the local time is 2 hours ahead of UTC (i.e. summer time), and bit 16 indicates that a change to local time is will take place at the end of the current hour. Bit 15 is reserved to indicate abnormal transmitter operation.
As extensions to the DCF77 code, bit 14 is set during public holidays (14 July, Christmas, etc.), and bit 13 is set the day before public holidays.
The relative uncertainty of the carrier frequency is 2 parts in 1012.
| Bit | Weight | Meaning | Bit | Weight | Meaning | Bit | Weight | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| :00 | M | Start of minute, always 0. | :20 | S | Start of encoded time, always 1. | :40 | 10 | Day of month (continued) |
| :01 | 0 | Unused, always 0 | :21 | 1 | Minutes 00–59 |
:41 | 20 | |
| :02 | 0 | :22 | 2 | :42 | 1 | Day of week Monday=1, Sunday=7 |
||
| :03 | 0 | :23 | 4 | :43 | 2 | |||
| :04 | 0 | :24 | 8 | :44 | 4 | |||
| :05 | 0 | :25 | 10 | :45 | 1 | Month number 01–12 |
||
| :06 | 0 | :26 | 20 | :46 | 2 | |||
| :07 | 0 | :27 | 40 | :47 | 4 | |||
| :08 | 0 | :28 | P1 | Even parity over minute bits 21–28. | :48 | 8 | ||
| :09 | 0 | :29 | 1 | Hours 0–23 |
:49 | 10 | ||
| :10 | 0 | :30 | 2 | :50 | 1 | Year within century 00–99 |
||
| :11 | 0 | :31 | 4 | :51 | 2 | |||
| :12 | 0 | :32 | 8 | :52 | 4 | |||
| :13 | Following day is a public holiday. | :33 | 10 | :53 | 8 | |||
| :14 | Current day is a public holiday. | :34 | 20 | :54 | 10 | |||
| :15 | R | Abnormal transmitter operation. | :35 | P2 | Even parity over hour bits 29–35. | :55 | 20 | |
| :16 | A1 | Summer time Daylight saving time Daylight saving time —also summer time in several countries including in British English and European official terminology —is the practice of temporarily advancing clocks during the summertime so that afternoons have more daylight and mornings have less... announcement. Set during hour before change. |
:36 | 1 | Day of month. 01–31 |
:56 | 40 | |
| :17 | Z1 | Set to 1 when CEST Central European Summer Time Central European Summer Time is one of the names of the Daylight saving time offset using the UTC offset of UTC+02:00, 2 hours ahead of Coordinated Universal Time. It is used as a summer daylight saving time in most European countries. During the winter, Central European Time is used... is in effect. |
:37 | 2 | :57 | 80 | ||
| :18 | Z2 | Set to 1 when CET Central European Time Central European Time , used in most parts of the European Union, is a standard time that is 1 hour ahead of Coordinated Universal Time . The time offset from UTC can be written as +01:00... is in effect. |
:38 | 4 | :58 | P3 | Even parity over date bits 36–58. | |
| :19 | A2 | Leap second Leap second A leap second is a positive or negative one-second adjustment to the Coordinated Universal Time time scale that keeps it close to mean solar time. UTC, which is used as the basis for official time-of-day radio broadcasts for civil time, is maintained using extremely precise atomic clocks... announcement. Set during hour before leap second. |
:39 | 8 | :59 | No bit transmitted during last second of each minute. | ||
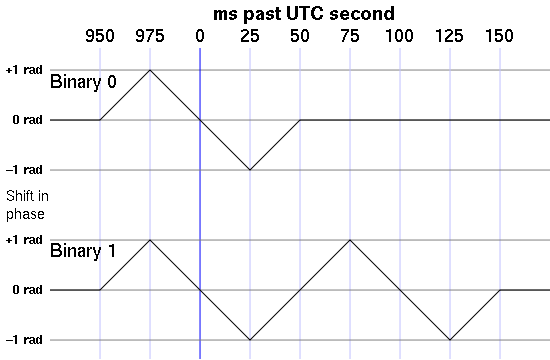
Phase modulation pattern
One signal element consists of the phase of the carrier shifted linearly by +1 rad in 25 ms (known as "ramp A"), then shifted linearly by −2 rad over 50 ms ("ramp B"), then shifted linearly again by +1 rad for another 25 ms ("ramp C"), returning the phase to zero. One signal element is always sent at each second between 0 and 58. Two signal elements are sent in sequence to represent a binary one; otherwise it is interpreted as binary zero. During ramp B of the initial signal element, the exact point the signal phase is at zero represents the top of the UTC second. Since the phase is the integral of the frequency, this triangular phase modulation corresponds to a square frequency modulation with an amplitude of about ±6 Hz.
Both the average phase and the average frequency deviation are thus zero. Additional non-timing data is sent by phase modulation during the rest of each second. But the second marker (and data bit) is always preceded by 100 ms without any phase modulation. The signal is not phase-modulated at all during the 59th second past the minute.
See also
- Allouis longwave transmitterAllouis longwave transmitterThe Allouis longwave transmitter first entered service, as France's central longwave transmitter, in 1939. It is located near the village of Allouis....
, the facility used for its transmission. - TéléDiffusion de France (also known as the TDF GroupTDF GroupTDF is a French company which provides radio and television transmission services, services for telecoms operators, and other multimedia services: digitization of content, encoding, storage, etc.Its headquarters are located in Paris.It is the dominant partner in the HDRR WiMAX consortium...
)

