
Tube lemma
Encyclopedia
In mathematics
, particularly topology
, the tube lemma is a useful tool in order to prove that the finite product of compact space
s is compact. It is in general, a concept of point-set topology.
Tube Lemma: Let X and Y be topological spaces with Y compact, and consider the product space
X × Y. If N is an open set containing a slice in X × Y, then there exists a tube in X × Y containing this slice and contained in N.
Using the concept of closed maps, this can be rephrased concisely as follows: if X is any topological space and Y a compact space, then the projection map X × Y → X is closed.
Generalized Tube Lemma: Let X and Y be topological spaces and consider the product space X × Y. Let A be a compact subset of X and B be a compact subset of Y. If N is an open set containing A × B, then there exists U open in X and V open in Y such that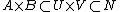 .
.
2. The tube lemma can be used to prove that if X and Y are compact topological spaces, then X × Y is compact as follows:
Let {Ga} be an open cover of X × Y; for each x belonging to X, cover the slice {x} × Y by finitely many elements of {Ga} (this is possible since {x} × Y is compact being homeomorphic
to Y). Call the union of these finitely many elements Nx. By the tube lemma, there is an open set of the form Wx × Y containing {x} × Y and contained in Nx. The collection of all Wx for x belonging to X is an open cover of X and hence has a finite subcover Wx1 ∪ ... ∪ Wxn. Then for each xi, Wxi × Y is contained in Nxi. Using the fact that each Nxi is the finite union of elements of Ga and that the finite collection (Wx1 × Y) ∪ ... ∪ (Wxn × Y) covers X × Y, the collection Nx1 ∪ ... ∪ Nxn is a finite subcover of X × Y.
3. By example 2 and induction, one can show that the finite product of compact spaces is compact.
4. The tube lemma cannot be used to prove the Tychonoff theorem, which generalizes the above to infinite products.
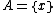 and
and 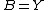 . It therefore suffices to prove the generalized tube lemma. By the definition of the product topology, for each
. It therefore suffices to prove the generalized tube lemma. By the definition of the product topology, for each 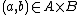 there are open sets
there are open sets 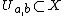 and
and 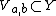 such that
such that 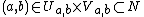 . Fix some
. Fix some 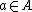 . Then
. Then 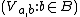 is an open cover of
is an open cover of 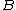 . Since
. Since 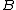 is compact, this cover has a finite subcover; namely, there is a finite
is compact, this cover has a finite subcover; namely, there is a finite 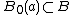 such that
such that 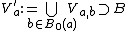 . Set
. Set 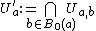 . Since
. Since 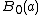 is finite,
is finite, 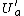 is open. Also
is open. Also 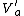 is open. Moreover, the construction of
is open. Moreover, the construction of 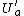 and
and 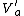 implies that
implies that 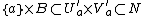 . We now essentially repeat the argument to drop the dependence on
. We now essentially repeat the argument to drop the dependence on  . Let
. Let 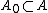 be a finite subset such that
be a finite subset such that 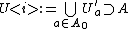 and set
and set 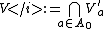 . It then follows by the above reasoning that
. It then follows by the above reasoning that 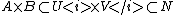 and
and 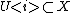 and
and 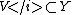 are open, which completes the proof.
are open, which completes the proof.
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
, particularly topology
Topology
Topology is a major area of mathematics concerned with properties that are preserved under continuous deformations of objects, such as deformations that involve stretching, but no tearing or gluing...
, the tube lemma is a useful tool in order to prove that the finite product of compact space
Compact space
In mathematics, specifically general topology and metric topology, a compact space is an abstract mathematical space whose topology has the compactness property, which has many important implications not valid in general spaces...
s is compact. It is in general, a concept of point-set topology.
Tube lemma
Before giving the lemma, one notes the following terminology:- If X and Y are topological spaces and X × Y is the product space, a slice in X × Y is a set of the form {x} × Y for x ∈ X
- A tube in X × Y is just a basis elementBase (topology)In mathematics, a base B for a topological space X with topology T is a collection of open sets in T such that every open set in T can be written as a union of elements of B. We say that the base generates the topology T...
, K × Y, in X × Y containing a slice in X × Y
Tube Lemma: Let X and Y be topological spaces with Y compact, and consider the product space
Product topology
In topology and related areas of mathematics, a product space is the cartesian product of a family of topological spaces equipped with a natural topology called the product topology...
X × Y. If N is an open set containing a slice in X × Y, then there exists a tube in X × Y containing this slice and contained in N.
Using the concept of closed maps, this can be rephrased concisely as follows: if X is any topological space and Y a compact space, then the projection map X × Y → X is closed.
Generalized Tube Lemma: Let X and Y be topological spaces and consider the product space X × Y. Let A be a compact subset of X and B be a compact subset of Y. If N is an open set containing A × B, then there exists U open in X and V open in Y such that
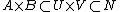 .
.Examples and properties
1. Consider R × R in the product topology, that is the Euclidean plane, and the open set N = { (x, y) : |x·y| < 1 }. The open set N contains {0} × R, but contains no tube, so in this case the tube lemma fails. Indeed, if W × R is a tube containing {0} × R and contained in N, W must be a subset of (−1/x, +1/x) for all positive integers x which means W = {0} contradicting the fact that W is open in R (because W × R is a tube). This shows that the compactness assumption is essential.2. The tube lemma can be used to prove that if X and Y are compact topological spaces, then X × Y is compact as follows:
Let {Ga} be an open cover of X × Y; for each x belonging to X, cover the slice {x} × Y by finitely many elements of {Ga} (this is possible since {x} × Y is compact being homeomorphic
Homeomorphism
In the mathematical field of topology, a homeomorphism or topological isomorphism or bicontinuous function is a continuous function between topological spaces that has a continuous inverse function. Homeomorphisms are the isomorphisms in the category of topological spaces—that is, they are...
to Y). Call the union of these finitely many elements Nx. By the tube lemma, there is an open set of the form Wx × Y containing {x} × Y and contained in Nx. The collection of all Wx for x belonging to X is an open cover of X and hence has a finite subcover Wx1 ∪ ... ∪ Wxn. Then for each xi, Wxi × Y is contained in Nxi. Using the fact that each Nxi is the finite union of elements of Ga and that the finite collection (Wx1 × Y) ∪ ... ∪ (Wxn × Y) covers X × Y, the collection Nx1 ∪ ... ∪ Nxn is a finite subcover of X × Y.
3. By example 2 and induction, one can show that the finite product of compact spaces is compact.
4. The tube lemma cannot be used to prove the Tychonoff theorem, which generalizes the above to infinite products.
Proofs
The tube lemma follows from the generalized tube lemma by taking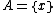 and
and 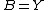 . It therefore suffices to prove the generalized tube lemma. By the definition of the product topology, for each
. It therefore suffices to prove the generalized tube lemma. By the definition of the product topology, for each 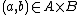 there are open sets
there are open sets 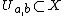 and
and 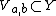 such that
such that 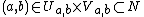 . Fix some
. Fix some 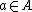 . Then
. Then 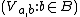 is an open cover of
is an open cover of 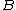 . Since
. Since 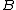 is compact, this cover has a finite subcover; namely, there is a finite
is compact, this cover has a finite subcover; namely, there is a finite 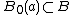 such that
such that 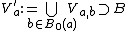 . Set
. Set 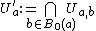 . Since
. Since 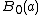 is finite,
is finite, 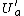 is open. Also
is open. Also 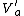 is open. Moreover, the construction of
is open. Moreover, the construction of 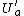 and
and 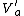 implies that
implies that 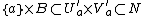 . We now essentially repeat the argument to drop the dependence on
. We now essentially repeat the argument to drop the dependence on  . Let
. Let 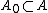 be a finite subset such that
be a finite subset such that 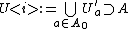 and set
and set 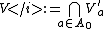 . It then follows by the above reasoning that
. It then follows by the above reasoning that 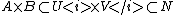 and
and 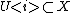 and
and 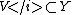 are open, which completes the proof.
are open, which completes the proof.

