
Traffic intensity
Encyclopedia
In telecommunication
networks, traffic intensity is a measure of the average occupancy of a server or resource during a specified period of time
, normally a busy hour
.It is measured in traffic
units (erlangs) and defined as the ratio of the time during which a facility is cumulatively occupied to the time this facility is available for occupancy.
In a digital network, the traffic intensity is: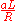
where
A traffic intensity greater than one erlang
means that the rate at which bits arrive exceeds the rate bits can be transmitted and queuing delay
will grow without bound (if the traffic intensity stays the same). If the traffic intensity is less than one erlang, then the router can handle more average traffic.
Telecommunication operators are vitally interested in traffic intensity, as it dictates the amount of equipment they must supply.
Telecommunication
Telecommunication is the transmission of information over significant distances to communicate. In earlier times, telecommunications involved the use of visual signals, such as beacons, smoke signals, semaphore telegraphs, signal flags, and optical heliographs, or audio messages via coded...
networks, traffic intensity is a measure of the average occupancy of a server or resource during a specified period of time
Time
Time is a part of the measuring system used to sequence events, to compare the durations of events and the intervals between them, and to quantify rates of change such as the motions of objects....
, normally a busy hour
Busy hour
Busy hour: In a communications system, the sliding 60-minute period during which occurs the maximum total traffic load in a given 24-hour period....
.It is measured in traffic
Traffic
Traffic on roads may consist of pedestrians, ridden or herded animals, vehicles, streetcars and other conveyances, either singly or together, while using the public way for purposes of travel...
units (erlangs) and defined as the ratio of the time during which a facility is cumulatively occupied to the time this facility is available for occupancy.
In a digital network, the traffic intensity is:
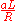
where
- a is the average arrival rate of packets (e.g. packets/sec)
- L is the average packet length (e.g. in bits), and
- R is the transmission rate (e.g. bits/sec)
A traffic intensity greater than one erlang
Erlang unit
The erlang is a dimensionless unit that is used in telephony as a statistical measure of offered load or carried load on service-providing elements such as telephone circuits or telephone switching equipment. It is named after the Danish telephone engineer A. K...
means that the rate at which bits arrive exceeds the rate bits can be transmitted and queuing delay
Queuing delay
In telecommunication and computer engineering, the queuing delay is the time a job waits in a queue until it can be executed. It is a key component of network delay....
will grow without bound (if the traffic intensity stays the same). If the traffic intensity is less than one erlang, then the router can handle more average traffic.
Telecommunication operators are vitally interested in traffic intensity, as it dictates the amount of equipment they must supply.

