
Tracking error
Encyclopedia
In finance
, tracking error is a measure of how closely a portfolio follows the index to which it is benchmarked. The most common measure is the root-mean-square of the difference between the portfolio and index returns.
Many portfolios are managed to a benchmark, normally an index. Some portfolios are expected to replicate, before trading and other costs, the returns of an index exactly (an index fund
), while others are expected to 'actively manage' the portfolio by deviating slightly from the index in order to generate active returns or to lower transaction costs. Tracking error (also called active risk
) is a measure of the deviation from the benchmark; the aforementioned index fund would have a tracking error close to zero, while an actively managed portfolio would normally have a higher tracking error. Dividing portfolio active return by portfolio tracking error gives the information ratio
, which is a risk adjusted performance metric.
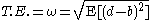
Nevertheless it is commonly calculated as Standard deviation of returns relative to benchmark:
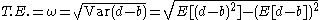
which in case of large portfolio deviations would lessen TE significantly and mislead its original meaning. This volatility definition makes sense, however, if the tracking error is to be used in an information ratio
.
where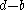 is the difference between the portfolio return and the index return for period i and N is the number of observations
is the difference between the portfolio return and the index return for period i and N is the number of observations
Finance
"Finance" is often defined simply as the management of money or “funds” management Modern finance, however, is a family of business activity that includes the origination, marketing, and management of cash and money surrogates through a variety of capital accounts, instruments, and markets created...
, tracking error is a measure of how closely a portfolio follows the index to which it is benchmarked. The most common measure is the root-mean-square of the difference between the portfolio and index returns.
Many portfolios are managed to a benchmark, normally an index. Some portfolios are expected to replicate, before trading and other costs, the returns of an index exactly (an index fund
Index fund
An index fund or index tracker is a collective investment scheme that aims to replicate the movements of an index of a specific financial market, or a set of rules of ownership that are held constant, regardless of market conditions.-Tracking:Tracking can be achieved by trying to hold all of the...
), while others are expected to 'actively manage' the portfolio by deviating slightly from the index in order to generate active returns or to lower transaction costs. Tracking error (also called active risk
Active Risk
In finance, active risk refers to that segment of risk in an investment portfolio that is due to active management decisions made by the portfolio manager. It does not include any risk that is merely a function of the market's movement...
) is a measure of the deviation from the benchmark; the aforementioned index fund would have a tracking error close to zero, while an actively managed portfolio would normally have a higher tracking error. Dividing portfolio active return by portfolio tracking error gives the information ratio
Information ratio
The Information ratio is a measure of the risk-adjusted return of a financial security . It is also known as Appraisal ratio and is defined as expected active return divided by tracking error, where active return is the difference between the return of the security and the return of a selected...
, which is a risk adjusted performance metric.
Definition
If tracking error is measured historically, it is called 'realised' or 'ex post' tracking error. If a model is used to predict tracking error, it is called 'ex ante' tracking error. The former is more useful for reporting performance, whereas ex ante is generally used by portfolio managers to control risk. Various types of ex-ante tracking error models exist, from simple equity models which use beta as a primary determinant to more complicated multi-factor fixed income models.Formulas
The ex-post Tracking Error formula is the deviation of the active returns, given by: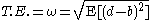
Nevertheless it is commonly calculated as Standard deviation of returns relative to benchmark:
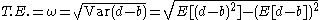
which in case of large portfolio deviations would lessen TE significantly and mislead its original meaning. This volatility definition makes sense, however, if the tracking error is to be used in an information ratio
Information ratio
The Information ratio is a measure of the risk-adjusted return of a financial security . It is also known as Appraisal ratio and is defined as expected active return divided by tracking error, where active return is the difference between the return of the security and the return of a selected...
.
where
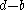 is the difference between the portfolio return and the index return for period i and N is the number of observations
is the difference between the portfolio return and the index return for period i and N is the number of observationsExamples
- Index fundIndex fundAn index fund or index tracker is a collective investment scheme that aims to replicate the movements of an index of a specific financial market, or a set of rules of ownership that are held constant, regardless of market conditions.-Tracking:Tracking can be achieved by trying to hold all of the...
s are expected to have minimal tracking errors. - Inverse exchange-traded fundInverse exchange-traded fundAn inverse exchange-traded fund is an exchange-traded fund , traded on a public stock market, which is designed to perform as the inverse of whatever index or benchmark it is designed to track...
s are designed to perform as the inverse of an index or other benchmark, and thus reflect tracking errors relative to short positions in the underlying index or benchmark.

