
Tiotropium
Encyclopedia
Tiotropium bromide is a long-acting, 24 hour, anticholinergic
bronchodilator
used in the management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
(COPD). Tiotropium bromide capsules for inhalation are co-promoted by Boehringer-Ingelheim
and Pfizer under the trade name Spiriva. It is also manufactured and marketed by Cipla
under trade name Tiova.
(COPD) which includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema. It is not however used for acute exacerbations
.
s (≥1% of patients) associated with tiotropium therapy include: dry mouth and/or throat irritation. Rarely (<0.1% of patients) treatment is associated with:urinary retention
, constipation, acute angle closure glaucoma, palpitations (notably supraventricular tachycardia
and atrial fibrillation
) and/or allergy (rash, angioedema
, anaphylaxis
).
Tiotropium and another member of its class ipratropium
were linked to increased risk of heart attacks, stroke and cardiovascular death. The FDA requested further trials which now complete they feel adequately resolve the previous safety concerns.
Tiotropium mist inhaler has been found to be associated with all cause mortality in people with COPD.
, often referred to as an antimuscarinic or anticholinergic
agent. Although it does not display selectivity for specific muscarinic receptors, on topical application it acts mainly on M3 muscarinic receptors located on smooth muscle cells and submucosal glands leading to a reduction in smooth muscle
contraction and mucus secretion, thus producing a bronchodilator
y effect.
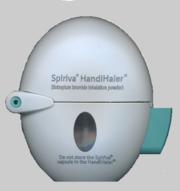
The capsule is manually pierced, and the medication is inhaled through the mouthpiece. It is recommended that inhalations are repeated 2 to 3 times to ensure all medication is drawn from the capsule. When properly done, the capsule will make a distinctive flutter or rattle, audible to the patient.
Once the powder capsules are removed from the blister pack, it should be taken immediately via the inhalation device. If a capsule is exposed to the air, it will rapidly degrade to the point the dose will become ineffective. Any previously exposed capsules should be discarded.
The capsules cannot be taken orally - they will not be effective as respiratory medication if absorbed through the gastrointestinal tract and may have side effects if absorbed via this route.
Anticholinergic
An anticholinergic agent is a substance that blocks the neurotransmitter acetylcholine in the central and the peripheral nervous system. An example of an anticholinergic is dicycloverine, and the classic example is atropine....
bronchodilator
Bronchodilator
A bronchodilator is a substance that dilates the bronchi and bronchioles, decreasing resistance in the respiratory airway and increasing airflow to the lungs. Bronchodilators may be endogenous , or they may be medications administered for the treatment of breathing difficulties...
used in the management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease , also known as chronic obstructive lung disease , chronic obstructive airway disease , chronic airflow limitation and chronic obstructive respiratory disease , is the co-occurrence of chronic bronchitis and emphysema, a pair of commonly co-existing diseases...
(COPD). Tiotropium bromide capsules for inhalation are co-promoted by Boehringer-Ingelheim
Boehringer-Ingelheim
C.H. Boehringer Sohn AG & Ko. KG is the parent company of Boehringer Ingelheim, which was founded in 1885 by Albert Boehringer in Ingelheim am Rhein. The Boehringer Ingelheim group is one of the world's 20 leading pharmaceutical companies. Headquartered in Ingelheim, Germany, it operates globally...
and Pfizer under the trade name Spiriva. It is also manufactured and marketed by Cipla
Cipla
Cipla Limited is a prominent Indian pharmaceutical company, best-known outside its home country for manufacturing low-cost anti-AIDS drugs for HIV-positive patients in developing countries...
under trade name Tiova.
Medical uses
Tiotropium is used for maintenance treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary diseaseChronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease , also known as chronic obstructive lung disease , chronic obstructive airway disease , chronic airflow limitation and chronic obstructive respiratory disease , is the co-occurrence of chronic bronchitis and emphysema, a pair of commonly co-existing diseases...
(COPD) which includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema. It is not however used for acute exacerbations
Acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
An acute exacerbation of COPD is a sudden worsening of COPD symptoms that typically lasts for several days. It may be triggered by an infection with bacteria or viruses or by environmental pollutants...
.
Adverse effects
Adverse effects are mainly related to its antimuscarinic effects. Common adverse drug reactionAdverse drug reaction
An adverse drug reaction is an expression that describes harm associated with the use of given medications at a normal dosage. ADRs may occur following a single dose or prolonged administration of a drug or result from the combination of two or more drugs...
s (≥1% of patients) associated with tiotropium therapy include: dry mouth and/or throat irritation. Rarely (<0.1% of patients) treatment is associated with:urinary retention
Urinary retention
Urinary retention, also known as ischuria, is a lack of ability to urinate. It is a common complication of benign prostatic hyperplasia , although it can also be caused by nerve dysfunction, constipation, infection, or medications...
, constipation, acute angle closure glaucoma, palpitations (notably supraventricular tachycardia
Supraventricular tachycardia
Supraventricular tachycardia is a general term that refers to any rapid heart rhythm originating above the ventricular tissue. Supraventricular tachycardias can be contrasted to the potentially more dangerous ventricular tachycardias - rapid rhythms that originate within the ventricular...
and atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation is the most common cardiac arrhythmia . It is a common cause of irregular heart beat, identified clinically by taking a pulse. Chaotic electrical activity in the two upper chambers of the heart result in the muscle fibrillating , instead of achieving coordinated contraction...
) and/or allergy (rash, angioedema
Angioedema
Angioedema or Quincke's edema is the rapid swelling of the dermis, subcutaneous tissue, mucosa and submucosal tissues. It is very similar to urticaria, but urticaria, commonly known as hives, occurs in the upper dermis...
, anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis is defined as "a serious allergic reaction that is rapid in onset and may cause death". It typically results in a number of symptoms including throat swelling, an itchy rash, and low blood pressure...
).
Tiotropium and another member of its class ipratropium
Ipratropium
Ipratropium bromide is an anticholinergic drug used for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and acute asthma. It blocks the muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in the smooth muscles of the bronchi in the lungs, opening the bronchi...
were linked to increased risk of heart attacks, stroke and cardiovascular death. The FDA requested further trials which now complete they feel adequately resolve the previous safety concerns.
Tiotropium mist inhaler has been found to be associated with all cause mortality in people with COPD.
Mechanism of action
Tiotropium is a muscarinic receptor antagonistReceptor antagonist
A receptor antagonist is a type of receptor ligand or drug that does not provoke a biological response itself upon binding to a receptor, but blocks or dampens agonist-mediated responses...
, often referred to as an antimuscarinic or anticholinergic
Anticholinergic
An anticholinergic agent is a substance that blocks the neurotransmitter acetylcholine in the central and the peripheral nervous system. An example of an anticholinergic is dicycloverine, and the classic example is atropine....
agent. Although it does not display selectivity for specific muscarinic receptors, on topical application it acts mainly on M3 muscarinic receptors located on smooth muscle cells and submucosal glands leading to a reduction in smooth muscle
Smooth muscle
Smooth muscle is an involuntary non-striated muscle. It is divided into two sub-groups; the single-unit and multiunit smooth muscle. Within single-unit smooth muscle tissues, the autonomic nervous system innervates a single cell within a sheet or bundle and the action potential is propagated by...
contraction and mucus secretion, thus producing a bronchodilator
Bronchodilator
A bronchodilator is a substance that dilates the bronchi and bronchioles, decreasing resistance in the respiratory airway and increasing airflow to the lungs. Bronchodilators may be endogenous , or they may be medications administered for the treatment of breathing difficulties...
y effect.
Mode of delivery
The patient removes one tiotropium capsule from the blister pack, places it into the piercing chamber of the inhalation device and closes the mouthpiece.The capsule is manually pierced, and the medication is inhaled through the mouthpiece. It is recommended that inhalations are repeated 2 to 3 times to ensure all medication is drawn from the capsule. When properly done, the capsule will make a distinctive flutter or rattle, audible to the patient.
Once the powder capsules are removed from the blister pack, it should be taken immediately via the inhalation device. If a capsule is exposed to the air, it will rapidly degrade to the point the dose will become ineffective. Any previously exposed capsules should be discarded.
The capsules cannot be taken orally - they will not be effective as respiratory medication if absorbed through the gastrointestinal tract and may have side effects if absorbed via this route.
 |

