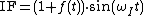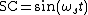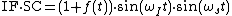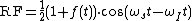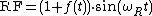Superheterodyne transmitter
Encyclopedia
Superheterodyne transmitter is a radio
or TV transmitter which uses an intermediate frequency signal in addition to radio frequency signal.
, video (VF) etc.) modulates the radio frequency (RF)
signal. These direct modulation transmitters are relatively simple transmitters.
In more complicated transmitters which are called superheterodyne, the information signal modulates an intermediate frequency (IF)
signal. After stages for correction, equalization and sometimes amplification, the IF signal is converted to an RF signal by a stage named frequency mixer
or frequency converter. Superheterodyne transmitters are more complex than direct modulation transmitters.
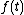 be the information signal
be the information signal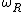 be the angular RF,
be the angular RF, be the angular IF and
be the angular IF and be the angular subcarrier frequency.
be the angular subcarrier frequency.
In direct modulation transmitter the information signal modulates the RF carrier. If the type of modulation is conventional amplitude modulation
the RF output is,
Likewise in superheterodyne transmitter the modulated IF is;
This signal is applied to a frequency mixer. The other input to the mixer is a high frequency subcarrier signal.
The two signals are multiplied to give;
Applying well known rules of trigonometry
;
A filter at the output of the mixer filters out one of the terms at the right (usually the summation) leaving RF
Here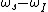 is the required angular RF; i.e.,
is the required angular RF; i.e., 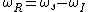
After phase and amplitude equalization,
Radio
Radio is the transmission of signals through free space by modulation of electromagnetic waves with frequencies below those of visible light. Electromagnetic radiation travels by means of oscillating electromagnetic fields that pass through the air and the vacuum of space...
or TV transmitter which uses an intermediate frequency signal in addition to radio frequency signal.
Types of transmitters
There are two types of transmitters. In some transmitters, the information signal (audio (AF)Audio signal
An audio signal is an analog representation of sound, typically as an electrical voltage. Audio signals may be synthesized directly, or may originate at a transducer such as a microphone, musical instrument pickup, phonograph cartridge, or tape head. Loudspeakers or headphones convert an electrical...
, video (VF) etc.) modulates the radio frequency (RF)
Radio frequency
Radio frequency is a rate of oscillation in the range of about 3 kHz to 300 GHz, which corresponds to the frequency of radio waves, and the alternating currents which carry radio signals...
signal. These direct modulation transmitters are relatively simple transmitters.
In more complicated transmitters which are called superheterodyne, the information signal modulates an intermediate frequency (IF)
Intermediate frequency
In communications and electronic engineering, an intermediate frequency is a frequency to which a carrier frequency is shifted as an intermediate step in transmission or reception. The intermediate frequency is created by mixing the carrier signal with a local oscillator signal in a process called...
signal. After stages for correction, equalization and sometimes amplification, the IF signal is converted to an RF signal by a stage named frequency mixer
Frequency mixer
In electronics a mixer or frequency mixer is a nonlinear electrical circuit that creates new frequencies from two signals applied to it. In its most common application, two signals at frequencies f1 and f2 are applied to a mixer, and it produces new signals at the sum f1 + f2 and difference f1 -...
or frequency converter. Superheterodyne transmitters are more complex than direct modulation transmitters.
Mathematical approach
Let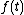 be the information signal
be the information signal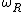 be the angular RF,
be the angular RF, be the angular IF and
be the angular IF and be the angular subcarrier frequency.
be the angular subcarrier frequency.In direct modulation transmitter the information signal modulates the RF carrier. If the type of modulation is conventional amplitude modulation
Amplitude modulation
Amplitude modulation is a technique used in electronic communication, most commonly for transmitting information via a radio carrier wave. AM works by varying the strength of the transmitted signal in relation to the information being sent...
the RF output is,
Likewise in superheterodyne transmitter the modulated IF is;
This signal is applied to a frequency mixer. The other input to the mixer is a high frequency subcarrier signal.
The two signals are multiplied to give;
Applying well known rules of trigonometry
Trigonometry
Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics that studies triangles and the relationships between their sides and the angles between these sides. Trigonometry defines the trigonometric functions, which describe those relationships and have applicability to cyclical phenomena, such as waves...
;
A filter at the output of the mixer filters out one of the terms at the right (usually the summation) leaving RF
Here
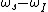 is the required angular RF; i.e.,
is the required angular RF; i.e., 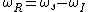
After phase and amplitude equalization,
Advantages of superheterodyne
- In transmitters several correction and equalization stages are used after modulation. In direct modulation these stages must be developed separatelly for each output RF (so called channel). On the other hand, in superheterodyne transmitters since a single intermediate frequency signal is used, only one type of stage for IF is developed. Thus the said stages are more reliable in superheterodyne. Also R&D is much easier for the designer.
- Operators may change the RF output of the transmitter. In direct modulation, it is very difficult to change the RF output. Because in this case, practically all stages need to be retuned for the new RF. On the other hand in superheterodyne only the output stages need to be retuned.
See also
- TV transmitters
- Superheterodyne receiverSuperheterodyne receiverIn electronics, a superheterodyne receiver uses frequency mixing or heterodyning to convert a received signal to a fixed intermediate frequency, which can be more conveniently processed than the original radio carrier frequency...
- TV transmitter topics