
Stochastic Frontier Analysis
Encyclopedia
Stochastic frontier analysis (SFA) is a method of economic modeling
. It has its starting point in the stochastic
production frontier models simultaneously introduced by Aigner, Lovell and Schmidt (1977) and Meeusen and Van den Broeck (1977).
The production frontier model without random component can be written as:
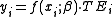
where yi is the observed scalar output of the producer i, i=1,..I, xi is a vector of N inputs used by the producer i, f(xi, β) is the production frontier, and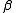 is a vector of technology parameters to be estimated.
is a vector of technology parameters to be estimated.
TEi denotes the technical efficiency defined as the ratio of observed output to maximum feasible output.
TEi = 1 shows that the i-th firm obtains the maximum feasible output, while TEi < 1 provides a measure of the shortfall of the observed output from maximum feasible output.
A stochastic component that describes random shocks affecting the production process is added. These shocks are not directly attributable to the producer or the underlying technology. These shocks may come from weather changes, economic adversities or plain luck. We denote these effects with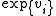 . Each producer is facing a different shock, but we assume the shocks are random and they are described by a common distribution.
. Each producer is facing a different shock, but we assume the shocks are random and they are described by a common distribution.
The stochastic production frontier will become:
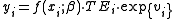
We assume that TEi is also a stochastic variable, with a specific distribution function, common to all producers.
We can also write it as an exponential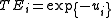 , where ui ≥ 0, since we required TEi ≤ 1. Thus, we obtain the following equation:
, where ui ≥ 0, since we required TEi ≤ 1. Thus, we obtain the following equation:
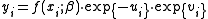
Now, if we also assume that f(xi, β) takes the log-linear Cobb-Douglas
form, the model can be written as:
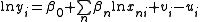
where vi is the “noise” component, which we will almost always consider as a two-sided normally distributed variable, and ui is the non-negative technical inefficiency component. Together they constitute a compound error term
, with a specific distribution to be determined, hence the name of “composed error model” as is often referred.
Model (economics)
In economics, a model is a theoretical construct that represents economic processes by a set of variables and a set of logical and/or quantitative relationships between them. The economic model is a simplified framework designed to illustrate complex processes, often but not always using...
. It has its starting point in the stochastic
Stochastic
Stochastic refers to systems whose behaviour is intrinsically non-deterministic. A stochastic process is one whose behavior is non-deterministic, in that a system's subsequent state is determined both by the process's predictable actions and by a random element. However, according to M. Kac and E...
production frontier models simultaneously introduced by Aigner, Lovell and Schmidt (1977) and Meeusen and Van den Broeck (1977).
The production frontier model without random component can be written as:
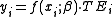
where yi is the observed scalar output of the producer i, i=1,..I, xi is a vector of N inputs used by the producer i, f(xi, β) is the production frontier, and
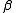 is a vector of technology parameters to be estimated.
is a vector of technology parameters to be estimated.TEi denotes the technical efficiency defined as the ratio of observed output to maximum feasible output.
TEi = 1 shows that the i-th firm obtains the maximum feasible output, while TEi < 1 provides a measure of the shortfall of the observed output from maximum feasible output.
A stochastic component that describes random shocks affecting the production process is added. These shocks are not directly attributable to the producer or the underlying technology. These shocks may come from weather changes, economic adversities or plain luck. We denote these effects with
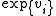 . Each producer is facing a different shock, but we assume the shocks are random and they are described by a common distribution.
. Each producer is facing a different shock, but we assume the shocks are random and they are described by a common distribution.The stochastic production frontier will become:
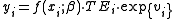
We assume that TEi is also a stochastic variable, with a specific distribution function, common to all producers.
We can also write it as an exponential
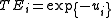 , where ui ≥ 0, since we required TEi ≤ 1. Thus, we obtain the following equation:
, where ui ≥ 0, since we required TEi ≤ 1. Thus, we obtain the following equation: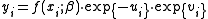
Now, if we also assume that f(xi, β) takes the log-linear Cobb-Douglas
Cobb-Douglas
In economics, the Cobb–Douglas functional form of production functions is widely used to represent the relationship of an output to inputs. Similar functions were originally used by Knut Wicksell , while the Cobb-Douglas form was developed and tested against statistical evidence by Charles Cobb and...
form, the model can be written as:
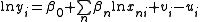
where vi is the “noise” component, which we will almost always consider as a two-sided normally distributed variable, and ui is the non-negative technical inefficiency component. Together they constitute a compound error term
Errors and residuals in statistics
In statistics and optimization, statistical errors and residuals are two closely related and easily confused measures of the deviation of a sample from its "theoretical value"...
, with a specific distribution to be determined, hence the name of “composed error model” as is often referred.

