
Sound energy density
Encyclopedia
The sound energy density or sound density (symbol E or w) is an adequate measure to describe the sound field at a given point as a sound energy value. The letter "lower case w" sign 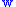 is easily mixed with the sign
is easily mixed with the sign 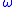 (omega), therefore we choose the letter E.
(omega), therefore we choose the letter E.
In opposite to the sound intensity
I, which gives the sound power per area A, the sound energy density E (also: sound density) describes the time medium value of the sound energy per volume unit; it gives information about the sound energy which is at a defined place in the room.
The sound energy density E (or w) for an even-proceeding sound wave is: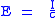 ,
,
where I is the sound intensity in W/m2 and c is the sound speed in m/s.
The sound energy density is given in J/m3, where the joule J = W·s = N·m.
You will find also W·s/m3 or N·m/m3.
The unit of measurement for sound energy density is N/m2, also known as pascal
s, the same as the units of sound pressure.
The terms instantaneous energy density, maximum energy density, and peak energy density have meanings analogous to the related terms used for sound pressure. In speaking of average energy density, it is necessary to distinguish between the space average (at a given instant) and the time average (at a given point).
More formulas for sound energy density for even proceeding sound waves: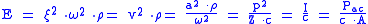
where:
For digits of the sound energy density the RMS
value will be given.
But you get also the level in dB
. See sound energy density level
.
 is easily mixed with the sign
is easily mixed with the sign  (omega), therefore we choose the letter E.
(omega), therefore we choose the letter E.In opposite to the sound intensity
Sound intensity
Sound intensity or acoustic intensity is defined as the sound power Pac per unit area A. The usual context is the noise measurement of sound intensity in the air at a listener's location.-Acoustic intensity:...
I, which gives the sound power per area A, the sound energy density E (also: sound density) describes the time medium value of the sound energy per volume unit; it gives information about the sound energy which is at a defined place in the room.
The sound energy density E (or w) for an even-proceeding sound wave is:
 ,
,where I is the sound intensity in W/m2 and c is the sound speed in m/s.
The sound energy density is given in J/m3, where the joule J = W·s = N·m.
You will find also W·s/m3 or N·m/m3.
The unit of measurement for sound energy density is N/m2, also known as pascal
Pascal (unit)
The pascal is the SI derived unit of pressure, internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus and tensile strength, named after the French mathematician, physicist, inventor, writer, and philosopher Blaise Pascal. It is a measure of force per unit area, defined as one newton per square metre...
s, the same as the units of sound pressure.
The terms instantaneous energy density, maximum energy density, and peak energy density have meanings analogous to the related terms used for sound pressure. In speaking of average energy density, it is necessary to distinguish between the space average (at a given instant) and the time average (at a given point).
More formulas for sound energy density for even proceeding sound waves:
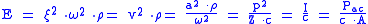
where:
| Symbol | Units | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| p | pascal Pascal (unit) The pascal is the SI derived unit of pressure, internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus and tensile strength, named after the French mathematician, physicist, inventor, writer, and philosopher Blaise Pascal. It is a measure of force per unit area, defined as one newton per square metre... s |
sound pressure Sound pressure Sound pressure or acoustic pressure is the local pressure deviation from the ambient atmospheric pressure caused by a sound wave. Sound pressure can be measured using a microphone in air and a hydrophone in water... |
| f | hertz Hertz The hertz is the SI unit of frequency defined as the number of cycles per second of a periodic phenomenon. One of its most common uses is the description of the sine wave, particularly those used in radio and audio applications.... |
frequency Frequency Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency... |
| ξ | m, meters | particle displacement Particle displacement Particle displacement or particle amplitude is a measurement of distance of the movement of a particle from its equilibrium position in a medium as it transmits a wave.... |
| c | m/s Second The second is a unit of measurement of time, and is the International System of Units base unit of time. It may be measured using a clock.... |
speed of sound Speed of sound The speed of sound is the distance travelled during a unit of time by a sound wave propagating through an elastic medium. In dry air at , the speed of sound is . This is , or about one kilometer in three seconds or approximately one mile in five seconds.... |
| v | m/s | particle velocity Particle velocity Particle velocity is the velocity v of a particle in a medium as it transmits a wave. In many cases this is a longitudinal wave of pressure as with sound, but it can also be a transverse wave as with the vibration of a taut string.... |
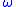 = 2 · = 2 ·  · f · f |
radians/s Second The second is a unit of measurement of time, and is the International System of Units base unit of time. It may be measured using a clock.... |
angular frequency Angular frequency In physics, angular frequency ω is a scalar measure of rotation rate. Angular frequency is the magnitude of the vector quantity angular velocity... |
| ρ | kg Kilogram The kilogram or kilogramme , also known as the kilo, is the base unit of mass in the International System of Units and is defined as being equal to the mass of the International Prototype Kilogram , which is almost exactly equal to the mass of one liter of water... /m3 |
density of air Density of air The density of air, ρ , is the mass per unit volume of Earth's atmosphere, and is a useful value in aeronautics and other sciences. Air density decreases with increasing altitude, as does air pressure. It also changes with variances in temperature or humidity... |
| Z = c · ρ | N·s Second The second is a unit of measurement of time, and is the International System of Units base unit of time. It may be measured using a clock.... /m³ |
acoustic impedance Acoustic impedance The acoustic impedance at a particular frequency indicates how much sound pressure is generated by a given air vibration at that frequency. The acoustic impedance Z is frequency dependent and is very useful, for example, for describing the behaviour of musical wind instruments... |
| a | m/s Second The second is a unit of measurement of time, and is the International System of Units base unit of time. It may be measured using a clock.... ² |
particle acceleration Particle acceleration In a compressible sound transmission medium - mainly air - air particles get an accelerated motion: the particle acceleration or sound acceleration with the symbol a in metre/second². In acoustics or physics, acceleration is defined as the rate of change of velocity. It is thus a vector... |
| I | W Watt The watt is a derived unit of power in the International System of Units , named after the Scottish engineer James Watt . The unit, defined as one joule per second, measures the rate of energy conversion.-Definition:... /m² |
sound intensity Sound intensity Sound intensity or acoustic intensity is defined as the sound power Pac per unit area A. The usual context is the noise measurement of sound intensity in the air at a listener's location.-Acoustic intensity:... |
| E | W Watt The watt is a derived unit of power in the International System of Units , named after the Scottish engineer James Watt . The unit, defined as one joule per second, measures the rate of energy conversion.-Definition:... ·s Second The second is a unit of measurement of time, and is the International System of Units base unit of time. It may be measured using a clock.... /m³ |
sound energy density |
| Pac | W, watt Watt The watt is a derived unit of power in the International System of Units , named after the Scottish engineer James Watt . The unit, defined as one joule per second, measures the rate of energy conversion.-Definition:... s |
sound power or acoustic power |
| A | m² | area Area Area is a quantity that expresses the extent of a two-dimensional surface or shape in the plane. Area can be understood as the amount of material with a given thickness that would be necessary to fashion a model of the shape, or the amount of paint necessary to cover the surface with a single coat... |
For digits of the sound energy density the RMS
Root mean square
In mathematics, the root mean square , also known as the quadratic mean, is a statistical measure of the magnitude of a varying quantity. It is especially useful when variates are positive and negative, e.g., sinusoids...
value will be given.
But you get also the level in dB
Decibel
The decibel is a logarithmic unit that indicates the ratio of a physical quantity relative to a specified or implied reference level. A ratio in decibels is ten times the logarithm to base 10 of the ratio of two power quantities...
. See sound energy density level
Sound energy density level
The sound energy density level gives the ratio of a sound incidence as a sound energy value in comparison to a reference level of 0 dB . It is a logarithmic measure of the ratio of two sound energy densities.- Definition :...
.
See also
- Particle displacementParticle displacementParticle displacement or particle amplitude is a measurement of distance of the movement of a particle from its equilibrium position in a medium as it transmits a wave....
- Sound velocity
- Particle accelerationParticle accelerationIn a compressible sound transmission medium - mainly air - air particles get an accelerated motion: the particle acceleration or sound acceleration with the symbol a in metre/second². In acoustics or physics, acceleration is defined as the rate of change of velocity. It is thus a vector...
- Sound pressureSound pressureSound pressure or acoustic pressure is the local pressure deviation from the ambient atmospheric pressure caused by a sound wave. Sound pressure can be measured using a microphone in air and a hydrophone in water...
- Sound intensitySound intensitySound intensity or acoustic intensity is defined as the sound power Pac per unit area A. The usual context is the noise measurement of sound intensity in the air at a listener's location.-Acoustic intensity:...
- Sound power
- Particle velocity level
- Sound intensity level
- Sound power level
- Sound energy density levelSound energy density levelThe sound energy density level gives the ratio of a sound incidence as a sound energy value in comparison to a reference level of 0 dB . It is a logarithmic measure of the ratio of two sound energy densities.- Definition :...

