
Soil resistivity
Encyclopedia
Soil resistivity
is a measure of how much the soil resists the flow of electricity. It is a critical factor in design of systems that rely on passing current through the Earth's surface. Knowledge of the soil resitivity and how it varies with depth in the soil is necessary to design the grounding system in an electrical substation
. It is needed for design of grounding (earthing) electrodes for High-voltage direct current
transmission systems. In single wire earth return
power transmission systems, the earth itself is used as the path of conduction from the end customers (the power consumers) back to the transmission facility.
The soil resistivity value is subject to great variation, due to moisture, temperature and chemical content. Typical values are:
The SI
unit of resistivity is the Ohm-meter (Ωm); in the United States
the Ohm-centimeter (Ωcm) is often used instead.
A wide range typical soil resistivity
values can be found in literature.
Several methods of resistivity measurement are frequently employed:
Using the Wenner method, the apparent soil resistivity value is:
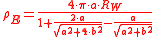
where
ρE = measured apparent soil resistivity (Ωm)
a = electrode spacing (m)
b = depth of the electrodes (m)
RW = Wenner resistance measured as “V/I” in Figure (Ω)
If a is small compared to b , as is the case of probes penetrating the ground only for a short distance (as normally happens), the previous equation can be reduced to:

Using the Schlumberger method, if b is small compared to a and c, and c>2a, the apparent soil resistivity value is:
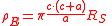
where
ρE = measured apparent soil resistivity (Ωm)
a = electrode spacing (m)
c = depth of the electrodes (m)
RS = Wenner resistance measured as “V/I” in Figure (Ω)
The current tends to flow near the surface for small probe spacing, whereas more current penetrates deeper soils for large spacing. Thus, it is usually a reasonable approximation to assume that the resistivity measured for a given current probe spacing represents the apparent resistivity of the soil to a depth of when soil layer resistivity contrasts are not excessive.
If the apparent soil resistivity measured with Schlumberger method ρE (with the corresponding electrode spacing aS and c) is given, assuming that the soil resistivity are referred to a volume as in the figure aside with a=L/3 follows:
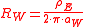
with

where:
RW = equivalent Wenner resistance
(Ω)
aW = equivalent electrode spacing with Wenner method (m)
aS = electrode
spacing between voltages probe with Schlumberger method (m)
c = electrode
spacing between voltages and currents probe with Schlumberger method (m)
If the measured Schlumberger resistance
is given, before to the calculate the and values, the apparent soil resistivity
has to be calculate as follows:
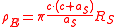
The Wenner method is more laborious than the Schlumberger method because it requires many time, long measure cables, large free space, and for big electrode spacing one person per electrode is necessary to complete the survey in a reasonable time. However, the Wenner four-pin method is the most efficient in terms of the ratio of received voltage per unit of transmitted current.
The soil resistivity
measurements have not to be affected by existing grounded electrodes. Buried conductive objects in contact with the soil can invalidate readings made by the methods described if they are close enough to alter the test current
flow pattern. This is particularly true for large or long objects.
Because of the variability of soil resistivity, IEC
standards require that the seasonal variation in resistivity be accounted for in transmission system design. For practical purposes, when there are no other available information, in very cold regions, during the winter, a resistivity
scale factor of 5 to 6 times the “summer” value would be an adequate average.
by the British Standard BS-1377 as follow:
Resistivity
Electrical resistivity is a measure of how strongly a material opposes the flow of electric current. A low resistivity indicates a material that readily allows the movement of electric charge. The SI unit of electrical resistivity is the ohm metre...
is a measure of how much the soil resists the flow of electricity. It is a critical factor in design of systems that rely on passing current through the Earth's surface. Knowledge of the soil resitivity and how it varies with depth in the soil is necessary to design the grounding system in an electrical substation
Substation
Substation can refer to:*Electrical substation*Police substation, a mini police station with limited services*The Substation, a Singaporean contemporary arts centre*SubStation Alpha, a subtitle file format...
. It is needed for design of grounding (earthing) electrodes for High-voltage direct current
High-voltage direct current
A high-voltage, direct current electric power transmission system uses direct current for the bulk transmission of electrical power, in contrast with the more common alternating current systems. For long-distance transmission, HVDC systems may be less expensive and suffer lower electrical losses...
transmission systems. In single wire earth return
Single wire earth return
Single wire earth return or single wire ground return is a single-wire transmission line for supplying single-phase electrical power from an electrical grid to remote areas at low cost...
power transmission systems, the earth itself is used as the path of conduction from the end customers (the power consumers) back to the transmission facility.
The soil resistivity value is subject to great variation, due to moisture, temperature and chemical content. Typical values are:
- Usual values: from 10 up to 1000 (Ωm)
- Exceptional values: from 1 up to 10000 (Ωm)
The SI
Si
Si, si, or SI may refer to :- Measurement, mathematics and science :* International System of Units , the modern international standard version of the metric system...
unit of resistivity is the Ohm-meter (Ωm); in the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
the Ohm-centimeter (Ωcm) is often used instead.
A wide range typical soil resistivity
Resistivity
Electrical resistivity is a measure of how strongly a material opposes the flow of electric current. A low resistivity indicates a material that readily allows the movement of electric charge. The SI unit of electrical resistivity is the ohm metre...
values can be found in literature.
Measurement
Because soil quality may vary greatly with depth and over a wide lateral area, estimation of soil resistivity based on soil classification provide only a rough approximation. Actual resistivity measurements are required to fully qualify the resistivity and its affects on the overall transmission system.Several methods of resistivity measurement are frequently employed:
Wenner method
The Wenner four-pin method, as shown in figure above, is the most commonly used technique for soil resistivity measurements.Using the Wenner method, the apparent soil resistivity value is:
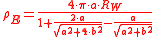
where
ρE = measured apparent soil resistivity (Ωm)
a = electrode spacing (m)
b = depth of the electrodes (m)
RW = Wenner resistance measured as “V/I” in Figure (Ω)
If a is small compared to b , as is the case of probes penetrating the ground only for a short distance (as normally happens), the previous equation can be reduced to:

Schlumberger method
In the Schlumberger method the distance between the voltages probe is a and the distances from voltages probe and currents probe are c (see figure above).Using the Schlumberger method, if b is small compared to a and c, and c>2a, the apparent soil resistivity value is:
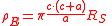
where
ρE = measured apparent soil resistivity (Ωm)
a = electrode spacing (m)
c = depth of the electrodes (m)
RS = Wenner resistance measured as “V/I” in Figure (Ω)
Conversion between measures using Schlumberger and Wenner
The conversion between values measured using the Schlumberger and Wenner methods is possible only in an approximate way. In any cases, for both Wenner and Schlumberger methods the electrode spacing between the currents probe corresponds to the depth of soil investigation and the measured apparent soil resistivity is referred to a soil volume as in figure aside.The current tends to flow near the surface for small probe spacing, whereas more current penetrates deeper soils for large spacing. Thus, it is usually a reasonable approximation to assume that the resistivity measured for a given current probe spacing represents the apparent resistivity of the soil to a depth of when soil layer resistivity contrasts are not excessive.
If the apparent soil resistivity measured with Schlumberger method ρE (with the corresponding electrode spacing aS and c) is given, assuming that the soil resistivity are referred to a volume as in the figure aside with a=L/3 follows:
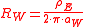
with

where:
RW = equivalent Wenner resistance
Electrical resistance
The electrical resistance of an electrical element is the opposition to the passage of an electric current through that element; the inverse quantity is electrical conductance, the ease at which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with the mechanical...
(Ω)
aW = equivalent electrode spacing with Wenner method (m)
aS = electrode
Electrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit...
spacing between voltages probe with Schlumberger method (m)
c = electrode
Electrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit...
spacing between voltages and currents probe with Schlumberger method (m)
If the measured Schlumberger resistance
Electrical resistance
The electrical resistance of an electrical element is the opposition to the passage of an electric current through that element; the inverse quantity is electrical conductance, the ease at which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with the mechanical...
is given, before to the calculate the and values, the apparent soil resistivity
Resistivity
Electrical resistivity is a measure of how strongly a material opposes the flow of electric current. A low resistivity indicates a material that readily allows the movement of electric charge. The SI unit of electrical resistivity is the ohm metre...
has to be calculate as follows:
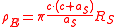
The Wenner method is more laborious than the Schlumberger method because it requires many time, long measure cables, large free space, and for big electrode spacing one person per electrode is necessary to complete the survey in a reasonable time. However, the Wenner four-pin method is the most efficient in terms of the ratio of received voltage per unit of transmitted current.
The soil resistivity
Resistivity
Electrical resistivity is a measure of how strongly a material opposes the flow of electric current. A low resistivity indicates a material that readily allows the movement of electric charge. The SI unit of electrical resistivity is the ohm metre...
measurements have not to be affected by existing grounded electrodes. Buried conductive objects in contact with the soil can invalidate readings made by the methods described if they are close enough to alter the test current
Current
- Science and Mathematics :* Electric current* Current , including** Ocean currents** Air currents** Current - currents in rivers and streams* Current density, mathematical concept unifying electric current, fluid current, and others...
flow pattern. This is particularly true for large or long objects.
Soil resistivity variability
Electrical conduction in soil is essentially electrolytic and for this reason the soil resistivity depends on:- moisture content
- salt content
- temperature (above the freezing point 0 °C)
Because of the variability of soil resistivity, IEC
IEC
-Organisations:* Independent Electoral Commission * Independent Electrical Contractors, a U.S. national trade association.* Institut d'Estudis Catalans , a Catalan academic institution....
standards require that the seasonal variation in resistivity be accounted for in transmission system design. For practical purposes, when there are no other available information, in very cold regions, during the winter, a resistivity
Resistivity
Electrical resistivity is a measure of how strongly a material opposes the flow of electric current. A low resistivity indicates a material that readily allows the movement of electric charge. The SI unit of electrical resistivity is the ohm metre...
scale factor of 5 to 6 times the “summer” value would be an adequate average.
Corrosion
Soil resistivity is one of the driving factors determining the corrosiveness of soil. The soil corrosiveness is classified based on soil electrical resistivityResistivity
Electrical resistivity is a measure of how strongly a material opposes the flow of electric current. A low resistivity indicates a material that readily allows the movement of electric charge. The SI unit of electrical resistivity is the ohm metre...
by the British Standard BS-1377 as follow:
- ρE > 100 Ωm: slightly corrosive
- 50 < ρE < 100 Ωm: moderately corrosive
- 10 < ρE < 50 Ωm: corrosive
- ρE < 10 Ωm: severe

