
Slope stability
Encyclopedia
Geomorphology
Geomorphology is the scientific study of landforms and the processes that shape them...
to determine relative slope stability based simply on site observations.
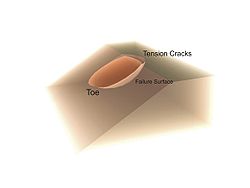
As seen in Figure 1, earthen slopes can develop a cut-spherical weakness area. The probability of this happening can be calculated in advance using a simple 2-D circular analysis package. A primary difficulty with analysis is locating the most-probable slip plane for any given situation. Many landslides have only been analyzed after the fact. More recently slope stability radar
Slope stability radar
The Slope Stability Radar is a new application for the monitoring of slope stability at open-cut mines. It is a system currently in use across the global mining and civil industries....
technology has been employed, particularly in the mining industry, to gather real time data and assist in pro-actively determining the likelihood of slope failure.
Real life failures
Real life failures in naturally deposited mixed soils are not necessarily circular, but prior to computers, it was far easier to analyse such a simplified geometry. Nevertheless, failures in 'pure' clay can be quite close to circular. Such slips often occur after a period of heavy rain, when the pore water pressure at the slip surface increases, reducing the effective normal stress and thus diminishing the restraining friction along the slip line. This is combined with increased soil weight due to the added groundwater. A 'shrinkage' crack (formed during prior dry weather) at the top of the slip may also fill with rain water, pushing the slip forward. At the other extreme, slab-shaped slips on hillsides can remove a layer of soil from the top of the underlying bedrock. Again, this is usually initiated by heavy rain, sometimes combined with increased loading from new buildings or removal of support at the toe (resulting from road widening or other construction work). Stability can thus be significantly improved by installing drainage paths to reduce the destabilising forces. Once the slip has occurred, however, a weakness along the slip circle remains, which may then recur at the next monsoon.Slope stability issues can be seen with almost any walk down a ravine
Ravine
A ravine is a landform narrower than a canyon and is often the product of streamcutting erosion. Ravines are typically classified as larger in scale than gullies, although smaller than valleys. A ravine is generally a fluvial slope landform of relatively steep sides, on the order of twenty to...
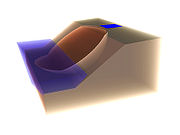
in an urban setting. An example is shown in Figure 3, where a river is eroding the toe of a slope, and there is a swimming pool near the top of the slope. If the toe is eroded too far, or the swimming pool begins to leak, the forces driving a slope failure will exceed those resisting failure, and a landslide
Landslide
A landslide or landslip is a geological phenomenon which includes a wide range of ground movement, such as rockfalls, deep failure of slopes and shallow debris flows, which can occur in offshore, coastal and onshore environments...
will develop, possibly quite suddenly.
Analysis methods
Factor of safety
Factor of safety , also known as safety factor , is a term describing the structural capacity of a system beyond the expected loads or actual loads. Essentially, how much stronger the system is than it usually needs to be for an intended load...
is calculated by dividing the forces resisting movement by the forces driving movement. In earthquake-prone areas, the analysis is typically run for static conditions and pseudo-static conditions, where the seismic forces from an earthquake are assumed to add static loads to the analysis.
Method of slices
The method of slices is a method for analyzing the stability of a slope in two dimensions. The sliding mass above the failure surface is divided into a number of slices. The forces acting on each slice are obtained by considering the mechanical equilibrium for the slices.Bishop's method
The Modified (or Simplified) Bishop's Method is a method for calculating the stability of slopes. It is an extension of the Method of Slices. By making some simplifying assumptions, the problem becomes statically determinate and suitable for hand calculations:- forces on the sides of each slice are horizontal
The method has been shown to produce factor of safety values within a few percent of the "correct" values.
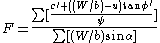
where
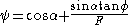
- c' is the effective cohesion
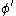 is the effective internal angle of internal friction
is the effective internal angle of internal friction - b is the width of each slice, assuming that all slices have the same width
- W is the weight of each slice
- u is the water pressure at the base of each slice
Sarma method
The Sarma methodSarma method
The Sarma method is a method used primarily to assess the stability of soil slopes under seismic conditions. Using appropriate assumptions the method can also be employed for static slope stability analysis. It was proposed by Sarada K...
, proposed by Sarada K. Sarma
Sarada K. Sarma
Dr Sarada Kanta Sarma, BTech PhD DIC MASCE is a Geotechnical Engineer, Emeritus Reader of Engineering Seismology and Senior Research Investigator at Imperial College London...
is a Limit equilibrium technique used to assess the stability of slopes under seismic conditions. It may also be used for static conditions if the value of the horizontal load is taken as zero. The method can analyse a wide range of slope failures as it may accommodate a multi-wedge failure mechanism and therefore it is not restricted to planar or circular failure surfaces. It may provide information about the factor of safety or about the critical acceleration required to cause collapse.
Lorimer's method
Lorimer's Method is a technique for evaluating slope stability in cohesive soils. It differs from Bishop's Method in that it uses a clothoid slip surface in place of a circle. This mode of failure was determined experimentally to account for effects of particle cementation.The method was developed in the 1930s by Gerhardt Lorimer (Dec 20, 1894-Oct 19, 1961), a student of geotechnical pioneer Karl von Terzaghi
Karl von Terzaghi
Karl von Terzaghi was an Austrian civil engineer and geologist, called the father of soil mechanics.-Early life:...
.
See also
- Slope stability radarSlope stability radarThe Slope Stability Radar is a new application for the monitoring of slope stability at open-cut mines. It is a system currently in use across the global mining and civil industries....
- Slope stability analysisSlope stability analysisThe slope stability analyses are performed to assess the safe and economic design of a human-made or natural slopes and the equilibrium conditions. The term slope stability may be defined as the resistance of inclined surface to failure by sliding or collapsing...
- Mass wastingMass wastingMass wasting, also known as slope movement or mass movement, is the geomorphic process by which soil, regolith, and rock move downslope under the force of gravity. Types of mass wasting include creep, slides, flows, topples, and falls, each with its own characteristic features, and taking place...
- Mohr-Coulomb theoryMohr-Coulomb theoryMohr–Coulomb theory is a mathematical model describing the response of brittle materials such as concrete, or rubble piles, to shear stress as well as normal stress. Most of the classical engineering materials somehow follow this rule in at least a portion of their shear failure envelope...
- Discontinuity layout optimizationDiscontinuity layout optimizationDiscontinuity layout optimization is an engineering analysis procedure which can be used to directly establish the amount of load that can be carried by a solid or structure prior to collapse...

