Similarity Enhanced Transfer
Encyclopedia
Similarity-Enhanced Transfer (SET) is a technique for improving the speed at which peer-to-peer
Peer-to-peer
Peer-to-peer computing or networking is a distributed application architecture that partitions tasks or workloads among peers. Peers are equally privileged, equipotent participants in the application...
file sharing
File sharing
File sharing is the practice of distributing or providing access to digitally stored information, such as computer programs, multimedia , documents, or electronic books. It may be implemented through a variety of ways...
and content distribution systems can share data. Similarity-Enhanced Transfer (SET) works by spotting chunks of identical data in files that are an exact or near match to the one needed and transferring this data to the client if the 'exact' data is not present.
Method
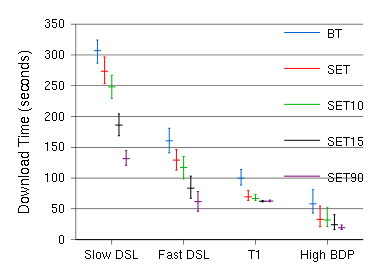
SET uses a technique called handprinting - which is based on earlier techniques known as "Shingling" that have been used to filter junk e-mails - to seek out files that contain some of the data needed by the one a file-sharing program has requested. The SET system computes a handprint for each file, and can take chunks of data from files which are both identical and similar to the one being searched for. The lower similarity ranking that SET searches for, the more sources for that data are likely to be found. The extra overhead of locating these sources does not out-weigh the benefit of using them to help saturate the recipient's available bandwidth. Indeed, exploiting similar sources can significantly improve download time.In tests, SET improved the transfer time of an MP3 music file by 71% and a 55Mb movie trailer went 30% faster using the researchers' techniques to draw from movie trailers that were 47% similar. SET could help most with less popular files, but it is not believed to improve transfer rates much for popular data, where there is already a huge set of people downloading it. Experiments suggest that in the other cases, SET can help a lot.
History
SET was developed by Professor David Andersen of Carnegie Mellon UniversityCarnegie Mellon University
Carnegie Mellon University is a private research university in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States....
, Ph.D student Himabindu Pucha, Purdue University
Purdue University
Purdue University, located in West Lafayette, Indiana, U.S., is the flagship university of the six-campus Purdue University system. Purdue was founded on May 6, 1869, as a land-grant university when the Indiana General Assembly, taking advantage of the Morrill Act, accepted a donation of land and...
and Dr. Michael Kaminsky, Intel Research Pittsburgh. Andersen believes that this technique could be immediately used by developers and applied to the BitTorrent file sharing system.
Application areas
SET could be used to improve the speed of:- peer-to-peerPeer-to-peerPeer-to-peer computing or networking is a distributed application architecture that partitions tasks or workloads among peers. Peers are equally privileged, equipotent participants in the application...
file sharingFile sharingFile sharing is the practice of distributing or providing access to digitally stored information, such as computer programs, multimedia , documents, or electronic books. It may be implemented through a variety of ways... - content distribution systems
- cooperative web cachingWeb cacheA web cache is a mechanism for the temporary storage of web documents, such as HTML pages and images, to reduce bandwidth usage, server load, and perceived lag...
External links
- David Andersen Prof. David Andersen's Home Page.
- How to Speed Up Movie Downloads, Technology Review, 2007-04-19
- BitTorrent BitTorrent website.

