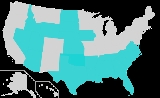
Right-to-work law
Overview
U.S. state
A U.S. state is any one of the 50 federated states of the United States of America that share sovereignty with the federal government. Because of this shared sovereignty, an American is a citizen both of the federal entity and of his or her state of domicile. Four states use the official title of...
s, mostly in the southern or western U.S., allowed under provisions of the federal Taft–Hartley Act, which prohibit agreements between labor unions and employers that make membership, payment of union dues
Union dues
Union dues are a regular payment of money made by members of unions. Dues are the cost of membership; they are used to fund the various activities which the union engages in...
, or fees a condition of employment, either before or after hiring, which would require the workplace to be a closed shop
Closed shop
A closed shop is a form of union security agreement under which the employer agrees to hire union members only, and employees must remain members of the union at all times in order to remain employed....
.
Prior to the passage of the Taft–Hartley Act by Congress over President Harry S Truman's veto in 1947, unions and employers covered by the National Labor Relations Act
National Labor Relations Act
The National Labor Relations Act or Wagner Act , is a 1935 United States federal law that limits the means with which employers may react to workers in the private sector who create labor unions , engage in collective bargaining, and take part in strikes and other forms of concerted activity in...
could lawfully agree to a closed shop
Closed shop
A closed shop is a form of union security agreement under which the employer agrees to hire union members only, and employees must remain members of the union at all times in order to remain employed....
, in which employees at unionized workplaces must be members of the union as a condition of employment.
Discussions

