
Respiratory minute volume
Encyclopedia
Respiratory minute volume (or minute ventilation) is the volume
of gas inhaled
(inhaled minute volume) or exhaled
(exhaled minute volume) from a person's lung
s in one minute. It is an important parameter in respiratory medicine due to its relationship with blood carbon dioxide levels. It can be measured with devices such as a Wright respirometer, or can be calculated from other known respiratory parameters. Note that although its name implies that it is a volume, minute volume is actually a flow (it represents a volume change over time).
Several symbols can be used to represent minute volume. They include: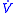 , MV, and VE.
, MV, and VE.
(VT) and respiratory rate
(ƒ or RR) are known, minute volume can calculated by multiplying the two values.
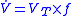
) should demonstrate a lower blood carbon dioxide level. The healthy human body will alter minute volume in an attempt to maintain physiologic homeostasis. A normal minute volume while resting is about 5–8 liter
s per minute in humans. Minute volume generally decreases when at rest, and increases with exercise. For example, during light activities minute volume may be around 12 litres per minute. Driving a bicycle increases minute ventilation by a factor of 2 to 4 depending on the level of exercise involved. Minute ventilation during moderate exercise may be between 40 and 60 litres per minute.
Hyperventilation
is the term for having a minute ventilation higher than physiologically appropriate. Hypoventilation
describes a minute volume less than physiologically appropriate.
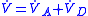
where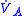 is alveolar ventilation, and
is alveolar ventilation, and 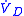 represents dead space ventilation.
represents dead space ventilation.
Volume
Volume is the quantity of three-dimensional space enclosed by some closed boundary, for example, the space that a substance or shape occupies or contains....
of gas inhaled
Inhalation
Inhalation is the movement of air from the external environment, through the air ways, and into the alveoli....
(inhaled minute volume) or exhaled
Exhalation
Exhalation is the movement of air out of the bronchial tubes, through the airways, to the external environment during breathing....
(exhaled minute volume) from a person's lung
Lung
The lung is the essential respiration organ in many air-breathing animals, including most tetrapods, a few fish and a few snails. In mammals and the more complex life forms, the two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart...
s in one minute. It is an important parameter in respiratory medicine due to its relationship with blood carbon dioxide levels. It can be measured with devices such as a Wright respirometer, or can be calculated from other known respiratory parameters. Note that although its name implies that it is a volume, minute volume is actually a flow (it represents a volume change over time).
Several symbols can be used to represent minute volume. They include:
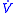 , MV, and VE.
, MV, and VE.Determination of minute volume
Minute volume can either be measured directly or calculated from other known parameters.Measurement of minute volume
Minute volume is the amount of gas inhaled or exhaled from a person's lungs in one minute. It can be measured by a Wright respirometer or other device capable of cumulatively measuring gas flow, such as mechanical ventilators.Calculation of minute volume
If both tidal volumeTidal volume
Tidal volume is the lung volume representing the normal volume of air displaced between normal inspiration and expiration when extra effort is not applied.Typical values are around 500ml or 7ml/kg bodyweight.-Mechanical Ventilation:...
(VT) and respiratory rate
Respiratory rate
Respiratory rate is also known by respiration rate, pulmonary ventilation rate, ventilation rate, or breathing frequency is the number of breaths taken within a set amount of time, typically 60 seconds....
(ƒ or RR) are known, minute volume can calculated by multiplying the two values.
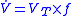
Physiological significance of minute volume
Blood carbon dioxide (PaCO2) levels generally vary inversely with minute volume. For example, a person with increased minute volume (e.g. due to hyperventilationHyperventilation
Hyperventilation or overbreathing is the state of breathing faster or deeper than normal, causing excessive expulsion of circulating carbon dioxide. It can result from a psychological state such as a panic attack, from a physiological condition such as metabolic acidosis, can be brought about by...
) should demonstrate a lower blood carbon dioxide level. The healthy human body will alter minute volume in an attempt to maintain physiologic homeostasis. A normal minute volume while resting is about 5–8 liter
Litér
- External links :*...
s per minute in humans. Minute volume generally decreases when at rest, and increases with exercise. For example, during light activities minute volume may be around 12 litres per minute. Driving a bicycle increases minute ventilation by a factor of 2 to 4 depending on the level of exercise involved. Minute ventilation during moderate exercise may be between 40 and 60 litres per minute.
Hyperventilation
Hyperventilation
Hyperventilation or overbreathing is the state of breathing faster or deeper than normal, causing excessive expulsion of circulating carbon dioxide. It can result from a psychological state such as a panic attack, from a physiological condition such as metabolic acidosis, can be brought about by...
is the term for having a minute ventilation higher than physiologically appropriate. Hypoventilation
Hypoventilation
In medicine, hypoventilation occurs when ventilation is inadequate to perform needed gas exchange...
describes a minute volume less than physiologically appropriate.
Relationship to other physiological rates
Minute volume comprises the sum of alveolar ventilation and dead space ventilation. That is: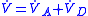
where
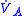 is alveolar ventilation, and
is alveolar ventilation, and 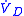 represents dead space ventilation.
represents dead space ventilation.
