
Recessional velocity
Encyclopedia
Recessional Velocity is a term used to describe the rate at which an object is moving away, typically from Earth
.
. The most common reason for the use of this term is Hubble's Law, which states that the redshift
is proportional to the distance between an inertial observer
and a distant galaxy
. The redshift is usually interpreted as due to Recessional Velocity which can be calculated according to the formula:
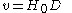
where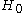 is the Hubble constant,
is the Hubble constant, 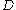 is the intervening distance, and
is the intervening distance, and  is the Recessional Velocity, generally measured in km/s.
is the Recessional Velocity, generally measured in km/s.
The recessional velocity of a galaxy is usually calculated from the redshift
observed in its emitted electromagnetic radiation
. The distance to the galaxy
is then estimated using Hubble's Law
.
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
.
Application to Cosmology
This term is generally only used in reference to distant GalaxiesGalaxy
A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a...
. The most common reason for the use of this term is Hubble's Law, which states that the redshift
Redshift
In physics , redshift happens when light seen coming from an object is proportionally increased in wavelength, or shifted to the red end of the spectrum...
is proportional to the distance between an inertial observer
Observation
Observation is either an activity of a living being, such as a human, consisting of receiving knowledge of the outside world through the senses, or the recording of data using scientific instruments. The term may also refer to any data collected during this activity...
and a distant galaxy
Galaxy
A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a...
. The redshift is usually interpreted as due to Recessional Velocity which can be calculated according to the formula:
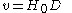
where
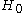 is the Hubble constant,
is the Hubble constant, 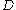 is the intervening distance, and
is the intervening distance, and  is the Recessional Velocity, generally measured in km/s.
is the Recessional Velocity, generally measured in km/s.The recessional velocity of a galaxy is usually calculated from the redshift
Redshift
In physics , redshift happens when light seen coming from an object is proportionally increased in wavelength, or shifted to the red end of the spectrum...
observed in its emitted electromagnetic radiation
Electromagnetic radiation
Electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy that exhibits wave-like behavior as it travels through space...
. The distance to the galaxy
Galaxy
A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a...
is then estimated using Hubble's Law
Hubble's law
Hubble's law is the name for the astronomical observation in physical cosmology that: all objects observed in deep space are found to have a doppler shift observable relative velocity to Earth, and to each other; and that this doppler-shift-measured velocity, of various galaxies receding from...
.

