
Pulmonary capillary wedge pressure
Encyclopedia
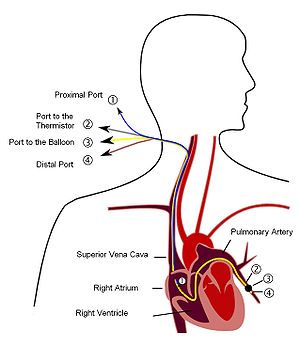
Physiologically, distinctions can be drawn among pulmonary venous pressure, pulmonary artery pressure, pulmonary capillary wedge pressure, and left atrial pressure, but not all of these can be measured in a clinical context.
Noninvasive estimation techniques have been proposed.
Clinical significance
Because of the large compliance of the pulmonary circulationPulmonary circulation
Pulmonary circulation is the half portion of the cardiovascular system which carries Oxygen-depleted Blood away from the heart, to the Lungs, and returns oxygenated blood back to the heart. Encyclopedic description and discovery of the pulmonary circulation is widely attributed to Doctor Ibn...
, it provides an indirect measure of the left atrial
Left atrium
The left atrium is one of the four chambers in the human heart. It receives oxygenated blood from the pulmonary veins, and pumps it into the left ventricle, via the mitral valve.-Foramen ovale:...
pressure.
For example, it is considered the gold standard for determining the cause of acute pulmonary edema; this is likely to be present at a PCWP of >20mmHg. It has also been used to diagnose severity of left ventricular failure and mitral stenosis
Calculating PCWP is also important in diagnosis of acute respiratory distress syndrome
Acute respiratory distress syndrome
Acute respiratory distress syndrome , also known as respiratory distress syndrome or adult respiratory distress syndrome is a serious reaction to various forms of injuries to the lung....
(ARDS).
Physiological pressure: 6–12 mm Hg.

