
Proof-of-work system
Encyclopedia
A proof-of-work system (or protocol, or function) is an economic measure to deter denial of service attacks and other service abuses such as spam
on a network by requiring some work from the service requester, usually meaning processing time by a computer. A key feature of these schemes is their asymmetry: the work must be moderately hard (but feasible) on the requester side but easy to check for the service provider. This idea is also named Client Puzzle Protocol
(CPP). It is distinct from a CAPTCHA
, which is intended for a human to solve quickly, rather than a computer.
One popular system is Hashcash
, which uses partial hash inversions to prove that work was done, as a good-will token to send an e-mail
. For instance the following header represents about 240 hash computations to send a message to
X-Hashcash: 1:40:170319:hobbes@comics::eb9a45d0eac8b65a:159b56eb15c
It is verified with a single computation by checking that its SHA-1 hash begins with 40 binary zeros, that is 10 hexadecimal zeros: 00000000009f0b34697d40bf80d000a3a0646cd9
Whether POW systems can actually solve a particular denial-of-service issue such as the spam problem is subject to debate: on the one hand the system must make sending spams obtrusively unproductive for the spammer, but on the other hand it should not prevent legitimate users from sending their messages.
Moreover, the underlying functions used by these schemes may be:
Finally, some POW systems offer shortcut computations that allow participants who know a secret, typically a private key, to generate cheap POWs. The rationale is that mailing-list holders may generate stamps for every recipient without incurring a high cost. Whether such a feature is desirable depends on the usage scenario.
has built on the proof-of-work idea, yielding a system called reusable proof of work ("RPOW").
The easiest way to understand RPOW is to view it as a form of token money
. It is in fact the only form of digital token money invulnerable to inflation caused by greedy or untrustworthy mints issuing more tokens than they said they would issue.
In this aspect it resembles the gold
coin: an issuer of gold coins cannot unfairly profit by minting extra gold coins because in a well-run gold-coin currency, obtaining the gold to make the extra coins has a cost approximately equal to the revenue or benefit gained by the minting of the coins. Moreover, this cost (i.e., the price of gold) is knowable or predictable by anyone.
Just as a gold coin's value is in an important sense guaranteed by the value of the raw gold needed to make it, the value of an RPOW token is guaranteed by the value of a POW token. (In Finney's version of RPOW, that POW token is a piece of hashcash
.)
The property that makes the gold coin and the RPOW token invulnerable to cheating by the nominal issuer of the currency also of course makes it invulnerable to counterfeiting.
Since the cost of creating a POW token decreases as a function of time in a fairly predictable way, e.g., by a steady logarithm
ic decay sometimes called Moore's law
, it is impractical to hold onto a POW or RPOW token for years as a form of savings. Still, these tokens are quite useful and stable when used as a form of exchange.
An operator of a website
that offers some benefit or service that many people are highly motivated to use can demand a POW token in exchange for this benefit. In fact, there are often good reasons for doing so. The benefit almost always entails the consumption of certain resources, like bandwidth to the Internet
, computation or disk space that have a definite cost. Demanding a POW token prevents Internet users from making frivolous or excessive use of the service (and consequently of the resources underlying the service).
Parenthetically, most people do not yet have software installed on their computer to mint POW tokens, but this could easily change.
An RPOW system differs from a POW system in that after someone has "spent" a POW token at my web site, I have the option of exchanging that "spent" POW token for a new, unspent RPOW token, which I can then spend at some third party's web site (provided of course that that web site has been set up to accept RPOW tokens). This saves me the computational resources I would have otherwise needed to mint a POW token.
This third party can in turn exchange that spent RPOW for a new, unspent one of equal value.
The anti-counterfeit/anti-inflationary property of the RPOW token is guaranteed by a technique called remote attestation
. In particular, the RPOW server, the Internet server that exchanges a used POW or RPOW token for a new one of equal value, uses remote attestation to allow any sufficiently knowledgeable and interested party to verify what software is running on the RPOW server. Since the source code for this software has been published (under a BSD-like license), any sufficiently knowledgeable programmer can, by inspecting this source code, satisfy himself that the software and, by extension, the RPOW server never issue a new token except in exchange for a spent token of equal value.
Until recently, Finney's system is the only RPOW system to have been implemented so far, and it has not yet seen economically significant use. It is implemented as 12,000 lines of C code.
In 2009, the Bitcoin
network went online. Bitcoin is a proof-of-work crypto currency developed on top of a decentralized P2P network. Tokens are 'mined' by individual nodes and verified by the network. Approximately 6.4M of the ultimately 21M bitcoins have been mined as of 2011.
Spam (electronic)
Spam is the use of electronic messaging systems to send unsolicited bulk messages indiscriminately...
on a network by requiring some work from the service requester, usually meaning processing time by a computer. A key feature of these schemes is their asymmetry: the work must be moderately hard (but feasible) on the requester side but easy to check for the service provider. This idea is also named Client Puzzle Protocol
Client Puzzle Protocol
Client Puzzle Protocol is a computer algorithm for use in Internet communication, whose goal is to make abuse of server resources infeasible. It is an implementation of a proof-of-work system ....
(CPP). It is distinct from a CAPTCHA
CAPTCHA
A CAPTCHA is a type of challenge-response test used in computing as an attempt to ensure that the response is generated by a person. The process usually involves one computer asking a user to complete a simple test which the computer is able to generate and grade...
, which is intended for a human to solve quickly, rather than a computer.
One popular system is Hashcash
Hashcash
Hashcash is a proof-of-work system designed to limit email spam and denial-of-service attacks. It was proposed in March 1997 by Adam Back.-How it works:...
, which uses partial hash inversions to prove that work was done, as a good-will token to send an e-mail
E-mail
Electronic mail, commonly known as email or e-mail, is a method of exchanging digital messages from an author to one or more recipients. Modern email operates across the Internet or other computer networks. Some early email systems required that the author and the recipient both be online at the...
. For instance the following header represents about 240 hash computations to send a message to
hobbes@comics on March 19, 2017:X-Hashcash: 1:40:170319:hobbes@comics::eb9a45d0eac8b65a:159b56eb15c
It is verified with a single computation by checking that its SHA-1 hash begins with 40 binary zeros, that is 10 hexadecimal zeros: 00000000009f0b34697d40bf80d000a3a0646cd9
Whether POW systems can actually solve a particular denial-of-service issue such as the spam problem is subject to debate: on the one hand the system must make sending spams obtrusively unproductive for the spammer, but on the other hand it should not prevent legitimate users from sending their messages.
Proof-of-work variants
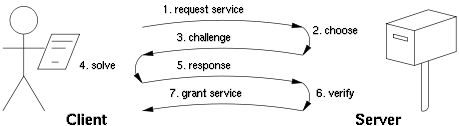
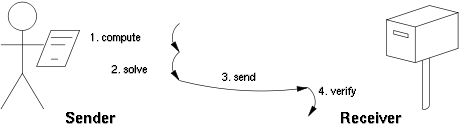
There are two classes of proof-of-work protocols.- Challenge-response protocols assume a direct interactive link between the requester and the provider. The provider chooses a challenge, say an item in a set with a property, the requester finds the relevant response in the set, which is sent back and checked by the provider. As the challenge is chosen on the spot by the provider, its difficulty can be adapted to its current load. The work on the requester side is bounded, and its varianceVarianceIn probability theory and statistics, the variance is a measure of how far a set of numbers is spread out. It is one of several descriptors of a probability distribution, describing how far the numbers lie from the mean . In particular, the variance is one of the moments of a distribution...
is low.

- Solution-verification protocols do not assume such a link: as a result the problem must be self-imposed before a solution is sought by the requester, and the provider must check both the problem choice and the found solution. Most such schemes are unbounded probabilistic iterative procedures with high varianceVarianceIn probability theory and statistics, the variance is a measure of how far a set of numbers is spread out. It is one of several descriptors of a probability distribution, describing how far the numbers lie from the mean . In particular, the variance is one of the moments of a distribution...
such as HashcashHashcashHashcash is a proof-of-work system designed to limit email spam and denial-of-service attacks. It was proposed in March 1997 by Adam Back.-How it works:...
.

Moreover, the underlying functions used by these schemes may be:
- CPU-bound where the computation runs at the speed of the processor, which greatly varies in timeMoore's LawMoore's law describes a long-term trend in the history of computing hardware: the number of transistors that can be placed inexpensively on an integrated circuit doubles approximately every two years....
, as well as from high-end server to low-end portable devices. - Memory-bound where the computation speed is bound by main memory accesses (either latency or bandwidth), the performance of which is expected to be less sensitive to hardware evolution.
- Network-bound if the client must performs few computations but must collect some tokens from various remote servers before querying the final service provider. In this sense the work is not actually performed by the requester, but it incurs delays anyway because of the latency to get the required tokens.
Finally, some POW systems offer shortcut computations that allow participants who know a secret, typically a private key, to generate cheap POWs. The rationale is that mailing-list holders may generate stamps for every recipient without incurring a high cost. Whether such a feature is desirable depends on the usage scenario.
List of proof-of-work functions
Here is a (preliminary) list of proof-of-work functions.- Integer square root modulo a large prime
- Weaken Fiat–Shamir signatures
- Ong–Schnorr–Shamir signature broken by Pollard
- Partial hash inversion as HashcashHashcashHashcash is a proof-of-work system designed to limit email spam and denial-of-service attacks. It was proposed in March 1997 by Adam Back.-How it works:...
- Hash sequences
- Puzzles
- Diffie–Hellman-based puzzle
- Moderate
- Mbound
- Hokkaido
- Merkle-tree based
- Guided tour puzzle protocolGuided tour puzzle protocolGuided tour puzzle protocol is a cryptographic protocol for mitigating application layer denial of service attacks. It aims to overcome the shortcoming of computation-based puzzle protocols, in which clients are required to compute hard CPU or memory-bound puzzles that favor clients with abundant...
Reusable proof-of-work
Computer scientist Hal FinneyHal Finney (cypherpunk)
Hal Finney is a developer for PGP Corporation, and was the 2nd developer hired after Phil Zimmerman. In his early career, he is credited as lead developer on several console games...
has built on the proof-of-work idea, yielding a system called reusable proof of work ("RPOW").
The easiest way to understand RPOW is to view it as a form of token money
Token money
Token money is money made from tokens of some form, as opposed to account money. Coins are token money, as are paper notes.Token money has a strong privacy feature in that it works as money without the intervention of any other party in each transaction between two parties. Privacy makes money...
. It is in fact the only form of digital token money invulnerable to inflation caused by greedy or untrustworthy mints issuing more tokens than they said they would issue.
In this aspect it resembles the gold
Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au and an atomic number of 79. Gold is a dense, soft, shiny, malleable and ductile metal. Pure gold has a bright yellow color and luster traditionally considered attractive, which it maintains without oxidizing in air or water. Chemically, gold is a...
coin: an issuer of gold coins cannot unfairly profit by minting extra gold coins because in a well-run gold-coin currency, obtaining the gold to make the extra coins has a cost approximately equal to the revenue or benefit gained by the minting of the coins. Moreover, this cost (i.e., the price of gold) is knowable or predictable by anyone.
Just as a gold coin's value is in an important sense guaranteed by the value of the raw gold needed to make it, the value of an RPOW token is guaranteed by the value of a POW token. (In Finney's version of RPOW, that POW token is a piece of hashcash
Hashcash
Hashcash is a proof-of-work system designed to limit email spam and denial-of-service attacks. It was proposed in March 1997 by Adam Back.-How it works:...
.)
The property that makes the gold coin and the RPOW token invulnerable to cheating by the nominal issuer of the currency also of course makes it invulnerable to counterfeiting.
Since the cost of creating a POW token decreases as a function of time in a fairly predictable way, e.g., by a steady logarithm
Logarithm
The logarithm of a number is the exponent by which another fixed value, the base, has to be raised to produce that number. For example, the logarithm of 1000 to base 10 is 3, because 1000 is 10 to the power 3: More generally, if x = by, then y is the logarithm of x to base b, and is written...
ic decay sometimes called Moore's law
Moore's Law
Moore's law describes a long-term trend in the history of computing hardware: the number of transistors that can be placed inexpensively on an integrated circuit doubles approximately every two years....
, it is impractical to hold onto a POW or RPOW token for years as a form of savings. Still, these tokens are quite useful and stable when used as a form of exchange.
An operator of a website
Website
A website, also written as Web site, web site, or simply site, is a collection of related web pages containing images, videos or other digital assets. A website is hosted on at least one web server, accessible via a network such as the Internet or a private local area network through an Internet...
that offers some benefit or service that many people are highly motivated to use can demand a POW token in exchange for this benefit. In fact, there are often good reasons for doing so. The benefit almost always entails the consumption of certain resources, like bandwidth to the Internet
Internet
The Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standard Internet protocol suite to serve billions of users worldwide...
, computation or disk space that have a definite cost. Demanding a POW token prevents Internet users from making frivolous or excessive use of the service (and consequently of the resources underlying the service).
Parenthetically, most people do not yet have software installed on their computer to mint POW tokens, but this could easily change.
An RPOW system differs from a POW system in that after someone has "spent" a POW token at my web site, I have the option of exchanging that "spent" POW token for a new, unspent RPOW token, which I can then spend at some third party's web site (provided of course that that web site has been set up to accept RPOW tokens). This saves me the computational resources I would have otherwise needed to mint a POW token.
This third party can in turn exchange that spent RPOW for a new, unspent one of equal value.
The anti-counterfeit/anti-inflationary property of the RPOW token is guaranteed by a technique called remote attestation
Trusted Computing
Trusted Computing is a technology developed and promoted by the Trusted Computing Group. The term is taken from the field of trusted systems and has a specialized meaning. With Trusted Computing, the computer will consistently behave in expected ways, and those behaviors will be enforced by...
. In particular, the RPOW server, the Internet server that exchanges a used POW or RPOW token for a new one of equal value, uses remote attestation to allow any sufficiently knowledgeable and interested party to verify what software is running on the RPOW server. Since the source code for this software has been published (under a BSD-like license), any sufficiently knowledgeable programmer can, by inspecting this source code, satisfy himself that the software and, by extension, the RPOW server never issue a new token except in exchange for a spent token of equal value.
Until recently, Finney's system is the only RPOW system to have been implemented so far, and it has not yet seen economically significant use. It is implemented as 12,000 lines of C code.
In 2009, the Bitcoin
Bitcoin
Bitcoin is a decentralized, peer-to-peer network over which users make transactions that are tracked and verified through this network. The word Bitcoin also refers to the digital currency implemented as the currency medium for user transactions over this network...
network went online. Bitcoin is a proof-of-work crypto currency developed on top of a decentralized P2P network. Tokens are 'mined' by individual nodes and verified by the network. Approximately 6.4M of the ultimately 21M bitcoins have been mined as of 2011.
External links
- Finney's system
- Bit gold. Describes a complete money system (including generation, storage, assay, and transfer) based on proof of work functions and the machine architecture problem raised by the use of these functions.

