Private equity fund
Encyclopedia
A private equity fund is a collective investment scheme
used for making investments in various equity (and to a lesser extent debt) securities according to one of the investment strategies associated with private equity
.
Private equity funds are typically limited partnerships with a fixed term of 10 years (often with annual extensions). At inception, institutional investors make an unfunded commitment to the limited partnership, which is then drawn over the term of the fund.
A private equity fund is raised and managed by investment professionals of a specific private equity firm (the general partner
and investment advisor). Typically, a single private equity firm
will manage a series of distinct private equity funds and will attempt to raise a new fund every 3 to 5 years as the previous fund is fully invested.
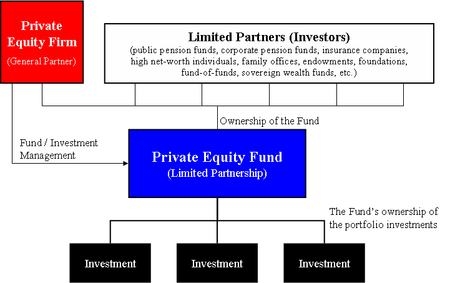 Most private equity funds are structured as limited partnerships and are governed by the terms set forth in the limited partnership agreement or LPA. Such funds have a general partner (GP), which raises capital from cash-rich institutional investors, such as pension plans, universities, insurance companies, foundations, endowments, and high net worth individuals, which invest as limited partners (LPs) in the fund. Among the terms set forth in the limited partnership agreement are the following:
Most private equity funds are structured as limited partnerships and are governed by the terms set forth in the limited partnership agreement or LPA. Such funds have a general partner (GP), which raises capital from cash-rich institutional investors, such as pension plans, universities, insurance companies, foundations, endowments, and high net worth individuals, which invest as limited partners (LPs) in the fund. Among the terms set forth in the limited partnership agreement are the following:
Term of the partnership: The partnership is usually a fixed-life investment vehicle that is typically 10 years plus some number of extensions.
Management fee
s: An annual payment made by the investors in the fund to the fund's manager to pay for the private equity firm's investment operations (typically 1 to 2% of the committed capital of the fund.
Carried interest
: A share of the profits of the fund's investments (typically up to 20%), paid to the private equity fund's management company as a performance incentive. The remaining 80% of the profits are paid to the fund's investors.
Hurdle rate
or preferred return: A minimum rate of return (e.g., 8–12%), which must be achieved before the fund manager can receive any carried interest payments.
Transfer of an interest in the fund: Private equity funds are not intended to be transferred or traded; however, they can be transferred to another investor. Typically, such a transfer must receive the consent of and is at the discretion of the fund's manager.
Restrictions on the General Partner: The fund's manager has significant discretion to make investments and control the affairs of the fund. However, the LPA does have certain restrictions and controls and is often limited in the type, size, or geographic focus of investments permitted, and how long the manager is permitted to make new investments.
Such LBO financing most often comes from commercial banks, although other financial institutions, such as hedge funds and mezzanine funds, may also provide financing. Since mid-2007, debt financing has become much more difficult to obtain for private equity funds than in previous years.
LBO funds commonly acquire most of the equity interests or assets of the portfolio company through a newly-created special purpose acquisition subsidiary controlled by the fund, and sometimes as a consortium of several like-minded funds.
). Private equity multiples are highly dependent on the portfolio company's industry, the size of the company, and the availability of LBO financing.
:
Substantial entry requirements: With most private equity funds requiring significant initial commitment (usually upwards of $1,000,000), which can be drawn at the manager's discretion over the first few years of the fund.
Limited liquidity: Investments in limited partnership interests (which is the dominant legal form of private equity investments) are referred to as "illiquid" investments, which should earn a premium over traditional securities, such as stocks and bonds. Once invested, it is very difficult to achieve liquidity before the manager realizes the investments in the portfolio as an investor's capital is locked-up in long-term investments, which can last for as long as twelve years. Distributions are made only as investments are converted to cash; limited partners typically have no right to demand that sales be made.
Investment Control: Nearly all investors in private equity are passive and rely on the manager to make investments and generate liquidity from those investments. Typically, governance rights for limited partners in private equity funds are minimal.
Unfunded Commitments: An investor's commitment to a private equity fund is drawn over time. If a private equity firm cannot find suitable investment opportunities, it will not draw on an investor's commitment, and an investor may potentially invest less than expected or committed.
Investment Risks: Given the risks associated with private equity investments, an investor can lose all of its investment. The risk of loss of capital is typically higher in venture capital
funds, which invest in companies during the earliest phases of their development or in companies with high amounts of financial leverage
. By their nature, investments in privately held companies tend to be riskier than investments in publicly traded companies.
High returns: Consistent with the risks outlined above, private equity can provide high returns, with the best private equity managers significantly outperforming the public markets.
For the above mentioned reasons, private equity fund investment is for those who can afford to have capital locked in for long periods of time and who are able to risk losing significant amounts of money. These disadvantages are offset by the potential benefits of annual returns, which range up to 30% for successful funds.
Collective investment scheme
A collective investment scheme is a way of investing money alongside other investors in order to benefit from the inherent advantages of working as part of a group...
used for making investments in various equity (and to a lesser extent debt) securities according to one of the investment strategies associated with private equity
Private equity
Private equity, in finance, is an asset class consisting of equity securities in operating companies that are not publicly traded on a stock exchange....
.
Private equity funds are typically limited partnerships with a fixed term of 10 years (often with annual extensions). At inception, institutional investors make an unfunded commitment to the limited partnership, which is then drawn over the term of the fund.
A private equity fund is raised and managed by investment professionals of a specific private equity firm (the general partner
General partner
General partner is a legal term used to describe a person who joins with at least one other person to form a business. A general partner has responsibility for the actions of the business, can legally bind the business and is personally liable for all the business's debts and obligations.General...
and investment advisor). Typically, a single private equity firm
Private equity firm
A private equity firm is an investment manager that makes investments in the private equity of operating companies through a variety of loosely affiliated investment strategies including leveraged buyout, venture capital, and growth capital...
will manage a series of distinct private equity funds and will attempt to raise a new fund every 3 to 5 years as the previous fund is fully invested.
Legal structure and terms

Term of the partnership: The partnership is usually a fixed-life investment vehicle that is typically 10 years plus some number of extensions.
Management fee
Management fee
In the investment advisory industry, a management fee is a periodic payment that is paid by investors in a pooled investment fund to the fund's investment adviser for investment and portfolio management services.-Mutual funds:...
s: An annual payment made by the investors in the fund to the fund's manager to pay for the private equity firm's investment operations (typically 1 to 2% of the committed capital of the fund.
Carried interest
Carried interest
Carried interest or carry, in finance, specifically in alternative investment management, is a share of the profits of a successful investment partnership that is paid to the investment manager of the partnership as a form of compensation that is designed as an incentive to the manager to maximize...
: A share of the profits of the fund's investments (typically up to 20%), paid to the private equity fund's management company as a performance incentive. The remaining 80% of the profits are paid to the fund's investors.
Hurdle rate
Carried interest
Carried interest or carry, in finance, specifically in alternative investment management, is a share of the profits of a successful investment partnership that is paid to the investment manager of the partnership as a form of compensation that is designed as an incentive to the manager to maximize...
or preferred return: A minimum rate of return (e.g., 8–12%), which must be achieved before the fund manager can receive any carried interest payments.
Transfer of an interest in the fund: Private equity funds are not intended to be transferred or traded; however, they can be transferred to another investor. Typically, such a transfer must receive the consent of and is at the discretion of the fund's manager.
Restrictions on the General Partner: The fund's manager has significant discretion to make investments and control the affairs of the fund. However, the LPA does have certain restrictions and controls and is often limited in the type, size, or geographic focus of investments permitted, and how long the manager is permitted to make new investments.
Private equity investments and financing
A private equity fund typically makes investments in companies (known as portfolio companies). These portfolio company investments are funded with the capital raised from LPs, and may be partially or substantially financed by debt. Some private equity investment transactions can be highly leveraged with debt financing—hence the acronym LBO for "leveraged buy-out". The cash flow from the portfolio company usually provides the source for the repayment of such debt.Such LBO financing most often comes from commercial banks, although other financial institutions, such as hedge funds and mezzanine funds, may also provide financing. Since mid-2007, debt financing has become much more difficult to obtain for private equity funds than in previous years.
LBO funds commonly acquire most of the equity interests or assets of the portfolio company through a newly-created special purpose acquisition subsidiary controlled by the fund, and sometimes as a consortium of several like-minded funds.
Private equity multiples and prices
The acquisition price of a portfolio company is usually based on a multiple of the company's historical income, most often based on the measure of earnings before interest taxes depreciation and amortization (EBITDAEBITDA
EBITDA is an acronym for earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization. It is a non-GAAP metric that is measured exactly as stated. All interest, tax, depreciation and amortization entries in the income statement are reversed out from the bottom-line net income...
). Private equity multiples are highly dependent on the portfolio company's industry, the size of the company, and the availability of LBO financing.
Portfolio company sales (or exits)
A private equity fund's ultimate goal is to sell or exit its investments in portfolio companies for a return, known as internal rate of return (IRR) in excess of the price paid. These exit scenarios historically have been an IPO of the portfolio company or a sale of the company to a strategic acquirer through a merger or acquisition (M&A), also known as a trade sale. Increasingly, more common has been a sale of the portfolio company to another private equity firm, also known as a secondary sale. In prior years, another exit strategy has been a preferred dividend by the portfolio company to the private equity fund to repay the capital investment, sometimes financed with additional debt.Private equity funds and private equity firms: an illustration
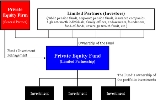
The following is an illustration of the difference between a private equity fund and a private equity firmPrivate equity firm
A private equity firm is an investment manager that makes investments in the private equity of operating companies through a variety of loosely affiliated investment strategies including leveraged buyout, venture capital, and growth capital...
:
| Private equity firm | Private equity fund | Private equity portfolio investments (partial list) |
|---|---|---|
| Kohlberg Kravis Roberts & Co. (KKR) | KKR 2006 Fund, L.P. ($17.6 billion of commitments) |
Alliance Boots Alliance Boots Alliance Boots GmbH is a leading international, pharmacy-led health and beauty group. It has two core business activities - pharmacy-led health and beauty retailing, and pharmaceutical wholesaling and distribution - and has a presence in more than 25 countries... |
| Dollar General Dollar General Dollar General Corp. is a U.S. chain of variety stores headquartered in Goodlettsville, Tennessee. As of January 2011, Dollar General operated over 9,300 stores in 35 U.S. states.... |
||
| Energy Future Holdings Corporation | ||
| First Data Corp | ||
| Hospital Corporation of America Hospital Corporation of America Hospital Corporation of America is the largest private operator of health care facilities in the world, It is based in Nashville, Tennessee and is widely considered to be the single largest factor in making that city a hotspot for healthcare enterprise.-History:The founders of HCA include Jack C.... (HCA) |
||
| Nielsen Company | ||
| NXP Semiconductors |
Investment features and considerations
Considerations for investing in private equity funds relative to other forms of investment include:Substantial entry requirements: With most private equity funds requiring significant initial commitment (usually upwards of $1,000,000), which can be drawn at the manager's discretion over the first few years of the fund.
Limited liquidity: Investments in limited partnership interests (which is the dominant legal form of private equity investments) are referred to as "illiquid" investments, which should earn a premium over traditional securities, such as stocks and bonds. Once invested, it is very difficult to achieve liquidity before the manager realizes the investments in the portfolio as an investor's capital is locked-up in long-term investments, which can last for as long as twelve years. Distributions are made only as investments are converted to cash; limited partners typically have no right to demand that sales be made.
Investment Control: Nearly all investors in private equity are passive and rely on the manager to make investments and generate liquidity from those investments. Typically, governance rights for limited partners in private equity funds are minimal.
Unfunded Commitments: An investor's commitment to a private equity fund is drawn over time. If a private equity firm cannot find suitable investment opportunities, it will not draw on an investor's commitment, and an investor may potentially invest less than expected or committed.
Investment Risks: Given the risks associated with private equity investments, an investor can lose all of its investment. The risk of loss of capital is typically higher in venture capital
Venture capital
Venture capital is financial capital provided to early-stage, high-potential, high risk, growth startup companies. The venture capital fund makes money by owning equity in the companies it invests in, which usually have a novel technology or business model in high technology industries, such as...
funds, which invest in companies during the earliest phases of their development or in companies with high amounts of financial leverage
Leverage (finance)
In finance, leverage is a general term for any technique to multiply gains and losses. Common ways to attain leverage are borrowing money, buying fixed assets and using derivatives. Important examples are:* A public corporation may leverage its equity by borrowing money...
. By their nature, investments in privately held companies tend to be riskier than investments in publicly traded companies.
High returns: Consistent with the risks outlined above, private equity can provide high returns, with the best private equity managers significantly outperforming the public markets.
For the above mentioned reasons, private equity fund investment is for those who can afford to have capital locked in for long periods of time and who are able to risk losing significant amounts of money. These disadvantages are offset by the potential benefits of annual returns, which range up to 30% for successful funds.
See also
- Private EquityPrivate equityPrivate equity, in finance, is an asset class consisting of equity securities in operating companies that are not publicly traded on a stock exchange....
for more information on the private equity asset class. - History of private equity and venture capitalHistory of private equity and venture capitalThe history of private equity and venture capital and the development of these asset classes has occurred through a series of boom and bust cycles since the middle of the 20th century. Within the broader private equity industry, two distinct sub-industries, leveraged buyouts and venture capital...
- List of private equity firms for a list of the largest active private equity investment firms.
- Limited partnershipLimited partnershipA limited partnership is a form of partnership similar to a general partnership, except that in addition to one or more general partners , there are one or more limited partners . It is a partnership in which only one partner is required to be a general partner.The GPs are, in all major respects,...
- Limited liability companyLimited liability companyA limited liability company is a flexible form of enterprise that blends elements of partnership and corporate structures. It is a legal form of company that provides limited liability to its owners in the vast majority of United States jurisdictions...
- Taxation of private equity and hedge fundsTaxation of private equity and hedge fundsPrivate equity funds and hedge funds are private investment vehicles used to pool investment capital, usually for a small group of large institutional or wealthy individual investors. They are subject to favorable regulatory treatment in most jurisdictions from which they are managed, which allows...
- Hedge fundHedge fundA hedge fund is a private pool of capital actively managed by an investment adviser. Hedge funds are only open for investment to a limited number of accredited or qualified investors who meet criteria set by regulators. These investors can be institutions, such as pension funds, university...
External links
- The Economics of Private Equity Funds (University of Pennsylvania, The Wharton School, Department of Finance)
- CalPERS Private Equity Industry Dictionary
- VC Experts Glossary (Glossary of Private Equity Terms)
- Guide on Private Equity and Venture Capital for Entrepreneurs (European Venture Capital Association, 2007)
- UK Venture Capital and Private Equity as an Asset Class (British Venture Capital Association)
- Note on Limited Partnership Agreements (Tuck School of Business at Dartmouth, 2003)

