
Optical buffer
Encyclopedia
In telecommunications, an optical buffer is a device that is capable of temporarily storing light. Just as in the case of a regular buffer, it is a storage medium that enables compensation for a difference in time of occurrence of events. More specifically, an optical buffer serves to store data that was transmitted optically (i.e., in the form of light), without converting it to the electrical domain.
links, interconnected by electrical nodes. The data transport in the backbone is done in the form of light, typically from LED
or laser
. DWDM technologies enable bitrates well beyond 1 Tbit/s. However, at the nodes, this light has to be converted to the electronic domain, in order to switch all data to their separate destinations. Due to rapidly increasing channel capacities, the switching capacity is becoming the bottleneck of the system. Currently, research activities focus on optical switching technologies, that involve fewer or no conversions from the optical to the electronic domain. An important problem however, is the buffering.
chip of comparable capacity. A single fiber can serve as a buffer. However, a set of more than one is usually used. A possibility, for example, is to choose a certain length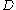 for the smallest fiber, and then let the second, third... have lengths
for the smallest fiber, and then let the second, third... have lengths 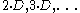 . Another typical example is to use a single loop, in which the data circulates a variable number of times.
. Another typical example is to use a single loop, in which the data circulates a variable number of times.
devices. The other is to better overall performance, by using stochastics. (Further detail on the latter approach can be found e.g. on the author's homepage.)
Optical networks
Today, computer networks consist of optical fiberOptical fiber
An optical fiber is a flexible, transparent fiber made of a pure glass not much wider than a human hair. It functions as a waveguide, or "light pipe", to transmit light between the two ends of the fiber. The field of applied science and engineering concerned with the design and application of...
links, interconnected by electrical nodes. The data transport in the backbone is done in the form of light, typically from LED
LEd
LEd is a TeX/LaTeX editing software working under Microsoft Windows. It is a freeware product....
or laser
Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of photons. The term "laser" originated as an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation...
. DWDM technologies enable bitrates well beyond 1 Tbit/s. However, at the nodes, this light has to be converted to the electronic domain, in order to switch all data to their separate destinations. Due to rapidly increasing channel capacities, the switching capacity is becoming the bottleneck of the system. Currently, research activities focus on optical switching technologies, that involve fewer or no conversions from the optical to the electronic domain. An important problem however, is the buffering.
Contention resolution
Whenever two or more data packets arrive at a network node at the same time and contend for the same output, external blocking occurs. All packets but one are perceived as superfluous, and have to be dealt with. Next to the obvious choice of dropping all excess packets, academic literature typically presents three solutions: buffering, deflection routing or wavelength conversion. Optical buffering uses fiber delay lines (FDLs) to delay the light, and is regarded as the most effective, but comes with the additional cost of the FDLs.Implementation of optical buffers
As light cannot be frozen, an optical buffer is made of optical fibers, and is generally much larger than a RAMRam
-Animals:*Ram, an uncastrated male sheep*Ram cichlid, a species of freshwater fish endemic to Colombia and Venezuela-Military:*Battering ram*Ramming, a military tactic in which one vehicle runs into another...
chip of comparable capacity. A single fiber can serve as a buffer. However, a set of more than one is usually used. A possibility, for example, is to choose a certain length
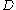 for the smallest fiber, and then let the second, third... have lengths
for the smallest fiber, and then let the second, third... have lengths 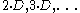 . Another typical example is to use a single loop, in which the data circulates a variable number of times.
. Another typical example is to use a single loop, in which the data circulates a variable number of times.Research
Currently, research on optical buffers is performed in two separate fields. One is to investigate on the technological implementation of this buffer, and try to reduce the size by using slow-lightSlow light
Slow light is the propagation of an optical pulse or other modulation of an optical carrier at a very low group velocity. Slow light occurs when a propagating pulse is substantially slowed down by the interaction with the medium in which the propagation take place.Researchers at the Rowland...
devices. The other is to better overall performance, by using stochastics. (Further detail on the latter approach can be found e.g. on the author's homepage.)

