
Normalized number
Encyclopedia
A real number
is called normalized, if it is in the form: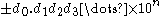
where n is an integer
,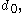
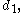
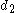 ,
, 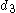 ... are the digits
... are the digits
of the number in base 10, and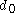 is not zero.
is not zero.
As examples, the number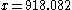 in normalized form is
in normalized form is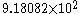 ,
,
while the number −0.00574012 in normalized form is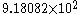
Clearly, any non-zero real number can be normalized.
The same definition holds if the number is represented in another radix
(that is, base of enumeration), rather than base 10.
In base b a normalized number will have the form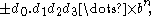
where again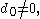 and the "digits"
and the "digits" 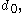
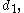
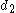 ,
, 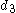 ...
...
are integers between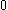 and
and  .
.
Converting a number to base 2 and normalizing it are the first steps in storing a real number as a
floating-point number in a computer.
Real number
In mathematics, a real number is a value that represents a quantity along a continuum, such as -5 , 4/3 , 8.6 , √2 and π...
is called normalized, if it is in the form:
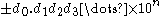
where n is an integer
Integer
The integers are formed by the natural numbers together with the negatives of the non-zero natural numbers .They are known as Positive and Negative Integers respectively...
,
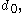
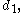
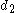 ,
, 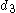 ... are the digits
... are the digitsNumerical digit
A digit is a symbol used in combinations to represent numbers in positional numeral systems. The name "digit" comes from the fact that the 10 digits of the hands correspond to the 10 symbols of the common base 10 number system, i.e...
of the number in base 10, and
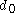 is not zero.
is not zero.As examples, the number
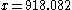 in normalized form is
in normalized form is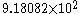 ,
,while the number −0.00574012 in normalized form is
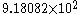
Clearly, any non-zero real number can be normalized.
The same definition holds if the number is represented in another radix
Radix
In mathematical numeral systems, the base or radix for the simplest case is the number of unique digits, including zero, that a positional numeral system uses to represent numbers. For example, for the decimal system the radix is ten, because it uses the ten digits from 0 through 9.In any numeral...
(that is, base of enumeration), rather than base 10.
In base b a normalized number will have the form
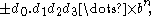
where again
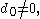 and the "digits"
and the "digits" 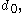
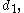
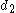 ,
, 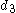 ...
...are integers between
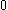 and
and  .
.Converting a number to base 2 and normalizing it are the first steps in storing a real number as a
floating-point number in a computer.

