
Non-specific, adsorptive pinocytosis
Encyclopedia
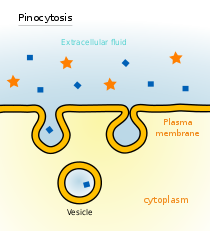
Pinocytosis
In cellular biology, pinocytosis is a form of endocytosis in which small particles are brought into the cell—forming an invagination, and then suspended within small vesicles that subsequently fuse with lysosomes to hydrolyze, or to break down, the particles...
is a form of endocytosis
Endocytosis
Endocytosis is a process by which cells absorb molecules by engulfing them. It is used by all cells of the body because most substances important to them are large polar molecules that cannot pass through the hydrophobic plasma or cell membrane...
, a process in which small particles are taken in by a cell
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
by splitting off small vesicles
Vesicle (biology)
A vesicle is a bubble of liquid within another liquid, a supramolecular assembly made up of many different molecules. More technically, a vesicle is a small membrane-enclosed sack that can store or transport substances. Vesicles can form naturally because of the properties of lipid membranes , or...
from the cell surface. Cationic proteins bind to the negative cell surface and are taken up via the clathrin
Clathrin
Clathrin is a protein that plays a major role in the formation of coated vesicles. Clathrin was first isolated and named by Barbara Pearse in 1975. It forms a triskelion shape composed of three clathrin heavy chains and three light chains. When the triskelia interact they form a polyhedral lattice...
-mediated system, so the uptake is intermediate between receptor-mediated endocytosis
Receptor-mediated endocytosis
Receptor-mediated endocytosis , also called clathrin-dependent endocytosis, is a process by which cells internalize molecules by the inward budding of plasma membrane vesicles containing proteins with receptor sites specific to the molecules being internalized.-Process:After the binding of a...
and non-specific, non-adsorptive pinocytosis
Pinocytosis
In cellular biology, pinocytosis is a form of endocytosis in which small particles are brought into the cell—forming an invagination, and then suspended within small vesicles that subsequently fuse with lysosomes to hydrolyze, or to break down, the particles...
. The clathrin-coated pits
Clathrin
Clathrin is a protein that plays a major role in the formation of coated vesicles. Clathrin was first isolated and named by Barbara Pearse in 1975. It forms a triskelion shape composed of three clathrin heavy chains and three light chains. When the triskelia interact they form a polyhedral lattice...
occupy about 2% of the surface area of the cell and only last about a minute, with an estimated 2500 leaving the average cell surface each minute. The clathrin coats are lost almost immediately, and later, the membrane will be recycled to the cell surface.
See also
- receptor-mediated endocytosisReceptor-mediated endocytosisReceptor-mediated endocytosis , also called clathrin-dependent endocytosis, is a process by which cells internalize molecules by the inward budding of plasma membrane vesicles containing proteins with receptor sites specific to the molecules being internalized.-Process:After the binding of a...
- pinocytosisPinocytosisIn cellular biology, pinocytosis is a form of endocytosis in which small particles are brought into the cell—forming an invagination, and then suspended within small vesicles that subsequently fuse with lysosomes to hydrolyze, or to break down, the particles...
- phagocytosis

