
Non-homogeneous Poisson process
Encyclopedia
In probability theory
, a non-homogeneous Poisson process is a Poisson process
with rate parameter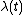 such that the rate parameter of the process is a function of time. Non-homogeneous Poisson process have been shown to describe numerous random phenomena including cyclone
such that the rate parameter of the process is a function of time. Non-homogeneous Poisson process have been shown to describe numerous random phenomena including cyclone
prediction, arrival times of calls to a call centre in a hospital laboratory, arrival times of aircraft to airspace around an airport and database transaction time
s.
is a non-homogeneous Poisson process for some small value h if:
for all t and where, in big O notation
, .
.
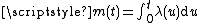 for the mean. Then N(t) has a Poisson distribution
for the mean. Then N(t) has a Poisson distribution
with mean m(t), that is for k = 0, 1, 2, 3….

Probability theory
Probability theory is the branch of mathematics concerned with analysis of random phenomena. The central objects of probability theory are random variables, stochastic processes, and events: mathematical abstractions of non-deterministic events or measured quantities that may either be single...
, a non-homogeneous Poisson process is a Poisson process
Poisson process
A Poisson process, named after the French mathematician Siméon-Denis Poisson , is a stochastic process in which events occur continuously and independently of one another...
with rate parameter
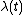 such that the rate parameter of the process is a function of time. Non-homogeneous Poisson process have been shown to describe numerous random phenomena including cyclone
such that the rate parameter of the process is a function of time. Non-homogeneous Poisson process have been shown to describe numerous random phenomena including cycloneCyclone
In meteorology, a cyclone is an area of closed, circular fluid motion rotating in the same direction as the Earth. This is usually characterized by inward spiraling winds that rotate anticlockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere of the Earth. Most large-scale...
prediction, arrival times of calls to a call centre in a hospital laboratory, arrival times of aircraft to airspace around an airport and database transaction time
Transaction time
Transaction time , a concept originated by Richard T. Snodgrass and his doctoral student, is used in temporal databases. It denotes the time period during which a database fact is/was stored in the database....
s.
Definition
Write N(t) for the number of events by time t. A stochastic processStochastic process
In probability theory, a stochastic process , or sometimes random process, is the counterpart to a deterministic process...
is a non-homogeneous Poisson process for some small value h if:
- N(0)=0
- Non-overlapping increments are independent
- P(N(t+h)-N(t)=1) = λ(t)h + o(h)
- P(N(t+h)-N(t)>1) = o(h)
for all t and where, in big O notation
Big O notation
In mathematics, big O notation is used to describe the limiting behavior of a function when the argument tends towards a particular value or infinity, usually in terms of simpler functions. It is a member of a larger family of notations that is called Landau notation, Bachmann-Landau notation, or...
,
 .
.Properties
Write N(t) for the number of events by time t and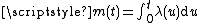 for the mean. Then N(t) has a Poisson distribution
for the mean. Then N(t) has a Poisson distributionPoisson distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the Poisson distribution is a discrete probability distribution that expresses the probability of a given number of events occurring in a fixed interval of time and/or space if these events occur with a known average rate and independently of the time since...
with mean m(t), that is for k = 0, 1, 2, 3….


