
Noise-equivalent power
Encyclopedia
Noise-equivalent power is a measure of the sensitivity of a photodetector
or detector system. It is defined as the signal power that gives a signal-to-noise ratio
of one in a one hertz
output bandwidth. An output bandwidth of one hertz is equivalent to half a second of integration time. The units of NEP are watts
per square root
hertz
. The NEP is equal to the noise spectral density
(expressed in units of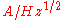 or
or 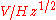 ) divided by the responsivity
) divided by the responsivity
(expressed in units of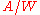 or
or 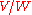 , respectively).
, respectively).
A smaller NEP corresponds to a more sensitive detector. For example, a detector with an NEP of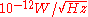 can detect a signal power of one picowatt with a signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of one after one half second of averaging. The SNR improves as the square root of the averaging time, and hence the SNR in this example can be improved to 10 by averaging for 50 seconds.
can detect a signal power of one picowatt with a signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of one after one half second of averaging. The SNR improves as the square root of the averaging time, and hence the SNR in this example can be improved to 10 by averaging for 50 seconds.
If the NEP refers to the signal power absorbed in the detector, it is known as the electrical NEP. If instead it refers to the signal power incident on the detector system, it is called the optical NEP. The optical NEP is equal to the electrical NEP divided by the optical coupling efficiency of the detector system.
Photodetector
Photosensors or photodetectors are sensors of light or other electromagnetic energy. There are several varieties:*Active pixel sensors are image sensors consisting of an integrated circuit that contains an array of pixel sensors, each pixel containing a both a light sensor and an active amplifier...
or detector system. It is defined as the signal power that gives a signal-to-noise ratio
Signal-to-noise ratio
Signal-to-noise ratio is a measure used in science and engineering that compares the level of a desired signal to the level of background noise. It is defined as the ratio of signal power to the noise power. A ratio higher than 1:1 indicates more signal than noise...
of one in a one hertz
Hertz
The hertz is the SI unit of frequency defined as the number of cycles per second of a periodic phenomenon. One of its most common uses is the description of the sine wave, particularly those used in radio and audio applications....
output bandwidth. An output bandwidth of one hertz is equivalent to half a second of integration time. The units of NEP are watts
Watts
-People:*Watts , the surname of several people*Watts S. Humphrey , American software engineer often called the father of software quality*Watts , a Canadian record producer-Fictional characters:*Watts family in EastEnders...
per square root
Square root
In mathematics, a square root of a number x is a number r such that r2 = x, or, in other words, a number r whose square is x...
hertz
Hertz
The hertz is the SI unit of frequency defined as the number of cycles per second of a periodic phenomenon. One of its most common uses is the description of the sine wave, particularly those used in radio and audio applications....
. The NEP is equal to the noise spectral density
Noise spectral density
In communications, noise spectral density No is the noise power per unit of bandwidth; that is, it is the power spectral density of the noise. It has dimension of power/frequency , whose SI coherent unit is watts per hertz, which is equivalent to watt-seconds or joules...
(expressed in units of
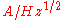 or
or 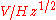 ) divided by the responsivity
) divided by the responsivityResponsivity
Responsivity measures the input–output gain of a detector system. For a system that responds linearly to its input, there is a unique responsivity. For nonlinear systems, the responsivity is the local slope ....
(expressed in units of
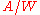 or
or 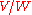 , respectively).
, respectively).A smaller NEP corresponds to a more sensitive detector. For example, a detector with an NEP of
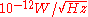 can detect a signal power of one picowatt with a signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of one after one half second of averaging. The SNR improves as the square root of the averaging time, and hence the SNR in this example can be improved to 10 by averaging for 50 seconds.
can detect a signal power of one picowatt with a signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of one after one half second of averaging. The SNR improves as the square root of the averaging time, and hence the SNR in this example can be improved to 10 by averaging for 50 seconds.If the NEP refers to the signal power absorbed in the detector, it is known as the electrical NEP. If instead it refers to the signal power incident on the detector system, it is called the optical NEP. The optical NEP is equal to the electrical NEP divided by the optical coupling efficiency of the detector system.
See also
- Noise-equivalent temperature
- Specific detectivitySpecific detectivitySpecific detectivity, or D*, for a photodetector is a figure of merit used to characterize performance, equal to the reciprocal of noise-equivalent power , normalized per unit area....

