
Niederreiter cryptosystem
Encyclopedia
In cryptography
, the Niederreiter cryptosystem is a variation of the McEliece Cryptosystem
developed in 1986 by Harald Niederreiter
. It applies the same idea to the parity check matrix H of a linear code.
Niederreiter is equivalent to McEliece from a security point of view. It uses a syndrome as ciphertext and the message is an error pattern. The encryption of Niederreiter is about ten times faster than the encryption of McEliece. Niederreiter can be used to construct a digital signature
scheme.
Recommended values for these parameters are n = 1024, t = 38, k = 644.
.
Verification then applies the public encryption function to the signature and checks whether or not this equals the hash value of the document. When using Niederreiter, or in fact any cryptosystem based on error correcting codes, the second step in the signature scheme almost always fails. This is because a random syndrome usually corresponds to an error pattern of weight greater than t.
The system then specifies a deterministic way of tweaking d until one is found which can be decrypted.
The choice of the code parameters is related to the probability that a random syndrome is decodable. Courtois, Finiaz, and Sendrier suggest the parameter values n = 216 and t = 9. Then the probability to decode a random syndrome is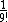 . Therefore a decodable syndrome is found after an expected number of 9! attempts. Add a counter i to the original document d, to produce a slightly altered document di. Hashing di gives a syndrome that depends on i. Let i run from 0 to i0, with i0 the first value of i for which di is decodable. In this case the decrypted message is a word z of length n and weight 9, such that HzT equals the hash value of di0. The signature will be z combined with the value i0 for verification. This signature is attached to the original document d.
. Therefore a decodable syndrome is found after an expected number of 9! attempts. Add a counter i to the original document d, to produce a slightly altered document di. Hashing di gives a syndrome that depends on i. Let i run from 0 to i0, with i0 the first value of i for which di is decodable. In this case the decrypted message is a word z of length n and weight 9, such that HzT equals the hash value of di0. The signature will be z combined with the value i0 for verification. This signature is attached to the original document d.
Cryptography
Cryptography is the practice and study of techniques for secure communication in the presence of third parties...
, the Niederreiter cryptosystem is a variation of the McEliece Cryptosystem
McEliece cryptosystem
In cryptography, the McEliece cryptosystem is an asymmetric encryption algorithm developed in 1978 by Robert McEliece. It was the first such scheme to use randomization in the encryption process...
developed in 1986 by Harald Niederreiter
. It applies the same idea to the parity check matrix H of a linear code.
Niederreiter is equivalent to McEliece from a security point of view. It uses a syndrome as ciphertext and the message is an error pattern. The encryption of Niederreiter is about ten times faster than the encryption of McEliece. Niederreiter can be used to construct a digital signature
Digital signature
A digital signature or digital signature scheme is a mathematical scheme for demonstrating the authenticity of a digital message or document. A valid digital signature gives a recipient reason to believe that the message was created by a known sender, and that it was not altered in transit...
scheme.
Scheme definition
Niederreiter's original proposal was broken but the system is secure when used with a binary Goppa code.Key generation
- Alice selects a binary (n, k)-linear Goppa code G capable of correcting t errors. This code possesses an efficient decoding algorithm.
- Alice generates a (n − k) × n parity check matrix H for the code G.
- Alice selects a random (n − k) × (n − k) binary non-singular matrix S.
- Alice selects a random n × n permutation matrixPermutation matrixIn mathematics, in matrix theory, a permutation matrix is a square binary matrix that has exactly one entry 1 in each row and each column and 0s elsewhere...
P. - Alice computes the (n − k) × n matrix Hpub = SHP.
- Alice’s public key is (Hpub, t); her private key is (S, H, P).
Message encryption
Suppose Bob wishes to send a message m to Alice whose public key is (Hpub, t):- Bob encodes the message m as a binary string of length n and weight t.
- Bob computes the ciphertext as c = HpubmT.
Message decryption
Upon receipt of c = HpubmT from Bob, Alice does the following to retrieve the message m.- Alice computes S−1c = HPmT.
- Alice applies a syndrome decoding algorithm for G to recover PmT.
- Alice computes the message m via mT = P−1PmT.
Recommended values for these parameters are n = 1024, t = 38, k = 644.
Signature scheme
Courtois, Finiasz and Sendrier showed how the Niederreiter cryptosystem can be used to derive a signature scheme.
- HashHash functionA hash function is any algorithm or subroutine that maps large data sets to smaller data sets, called keys. For example, a single integer can serve as an index to an array...
the document d to be signed (with a public hash algorithm). - Decrypt this hash value as if it were an instance of ciphertext.
- Append the decrypted message to the document as a signature.
Verification then applies the public encryption function to the signature and checks whether or not this equals the hash value of the document. When using Niederreiter, or in fact any cryptosystem based on error correcting codes, the second step in the signature scheme almost always fails. This is because a random syndrome usually corresponds to an error pattern of weight greater than t.
The system then specifies a deterministic way of tweaking d until one is found which can be decrypted.
The choice of the code parameters is related to the probability that a random syndrome is decodable. Courtois, Finiaz, and Sendrier suggest the parameter values n = 216 and t = 9. Then the probability to decode a random syndrome is
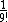 . Therefore a decodable syndrome is found after an expected number of 9! attempts. Add a counter i to the original document d, to produce a slightly altered document di. Hashing di gives a syndrome that depends on i. Let i run from 0 to i0, with i0 the first value of i for which di is decodable. In this case the decrypted message is a word z of length n and weight 9, such that HzT equals the hash value of di0. The signature will be z combined with the value i0 for verification. This signature is attached to the original document d.
. Therefore a decodable syndrome is found after an expected number of 9! attempts. Add a counter i to the original document d, to produce a slightly altered document di. Hashing di gives a syndrome that depends on i. Let i run from 0 to i0, with i0 the first value of i for which di is decodable. In this case the decrypted message is a word z of length n and weight 9, such that HzT equals the hash value of di0. The signature will be z combined with the value i0 for verification. This signature is attached to the original document d.External links
- Attacking and defending the McEliece cryptosystem Daniel J. Bernstein and Tanja Lange and Christiane Peters

