
NMSSM
Encyclopedia
In particle physics
, NMSSM is an acronym for Next-to-Minimal Supersymmetric Standard Model
. It is a supersymmetric
extension to the Standard Model
that adds an additional singlet chiral superfield to the MSSM
and can be used to dynamically generate the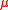 term, solving the mu problem
term, solving the mu problem
.
For review articles about the NMSSM see
.
The Minimal Supersymmetric Model does not explain why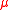 parameter in the superpotential
parameter in the superpotential
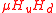 is at the electroweak scale. The idea behind the Next to Minimal Supersymmetric Model is to promote the
is at the electroweak scale. The idea behind the Next to Minimal Supersymmetric Model is to promote the 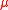 term to a gauge singlet, chiral superfield
term to a gauge singlet, chiral superfield
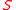 .
.
Note that the boson superpartner of the singlino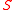 is denoted by
is denoted by 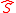 and the
and the
spin-1/2 singlino superpartner by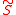 in the following.
in the following.
The superpotential for the NMSSM is given by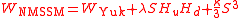
where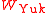 are Yukawa couplings for the Standard Model fermions.
are Yukawa couplings for the Standard Model fermions.
Since the superpotential has mass dimension three, the couplings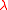 and
and  are dimensionless, hence
are dimensionless, hence
the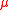 problem of the MSSM is solved in the NMSSM - the superpotential
problem of the MSSM is solved in the NMSSM - the superpotential
of the NMSSM is therefore scale invariant.
The role of the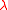 term is to generate an effective
term is to generate an effective 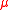 term.
term.
This is done with the boson component of the singlet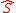 getting
getting
a vacuum-expectation value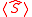 , that is,
, that is,
we have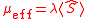 .
.
Without the term the superpotential would have a U(1)' symmetry, so-called
term the superpotential would have a U(1)' symmetry, so-called
Peccei-Quinn symmetry; see Peccei-Quinn theory
. This additional symmetry would alter the phenomenology completely.
The role of the term is to break this U(1)' symmetry. The
term is to break this U(1)' symmetry. The  term
term
is introduced trilinear such that is dimensionless. However there remains a discrete
is dimensionless. However there remains a discrete
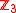 symmetry, which is moreover broken spontaneously
symmetry, which is moreover broken spontaneously
. In principle this
leads to the domain wall
problem. Introducing additional, but suppressed terms, the
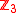 symmetry can be broken without changing phenomenology
symmetry can be broken without changing phenomenology
at the electroweak scale
.
It is assumed that the domain wall problem is circumvented in this way without any modifications except far beyond
the electroweak scale.
Also alternative models have been proposed which solve the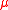 problem of the MSSM. One idea
problem of the MSSM. One idea
is to keep the term in the superpotential and take the U(1)' symmetry
term in the superpotential and take the U(1)' symmetry
into account. Assuming this symmetry to be local an additional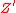 gauge boson is predicted in
gauge boson is predicted in
this model, called UMSSM.
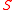 the NMSSM alters in general the phenomenology of both the Higgs sector and the neutralino sector.
the NMSSM alters in general the phenomenology of both the Higgs sector and the neutralino sector.
Due to the additional singlet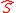 in the NMSSM we have two more Higgs bosons, that is, in total seven physical Higgs bosons.
in the NMSSM we have two more Higgs bosons, that is, in total seven physical Higgs bosons.
The Higgs sector is therefore much richer compared to the MSSM. In particular, the Higgs potential is in general no longer invariant
under CP transformations; see CP violation
. Typically, the Higgs bosons in the NMSSM are given
in an order with increasing masses, denoted by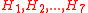 with
with 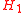
the lightest Higgs boson.
In the special case of a CP conserving Higgs potential we have three CP even Higgs bosons,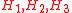 ,
,
two CP odd ones,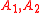 and a pair of charged Higgs bosons,
and a pair of charged Higgs bosons, 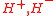 .
.
In the MSSM, the lightest Higgs boson is always Standard Model-like, and therefore its production and decays are roughly known.
In the NMSSM, the lightest Higgs can be very light (even of the order of 1 GeV) and may have escaped detection so far.
In addition, in the CP-conserving case, the lightest CP-even Higgs boson turns out to have an enhanced lower bound compared to the MSSM.
This is one of the reasons why the NMSSM deserves much attraction in recent years.
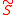 gives a fifth neutralino, compared to the four neutralinos of the MSSM.
gives a fifth neutralino, compared to the four neutralinos of the MSSM.
The singlino does not couple to gauge bosons, gauginos (the superpartners of the gauge bosons),
leptons, sleptons (the superpartners of the leptons), quarks or squarks (the superpartners of the quarks).
Supposed that a supersymmetric partner particle is produced at a collider, for instance at the
LHC
, the singlino is omitted in cascade decays and therefore escapes detection.
However in case the singlino is the lightest supersymmetric particle
(LSP) all supersymmetric
partner particles eventually decay into the singlino. Due to R parity conservation this LSP
is stable. In this way the singlino could be detected via missing transversal energy
in the detector.
Particle physics
Particle physics is a branch of physics that studies the existence and interactions of particles that are the constituents of what is usually referred to as matter or radiation. In current understanding, particles are excitations of quantum fields and interact following their dynamics...
, NMSSM is an acronym for Next-to-Minimal Supersymmetric Standard Model
. It is a supersymmetric
Supersymmetry
In particle physics, supersymmetry is a symmetry that relates elementary particles of one spin to other particles that differ by half a unit of spin and are known as superpartners...
extension to the Standard Model
Standard Model
The Standard Model of particle physics is a theory concerning the electromagnetic, weak, and strong nuclear interactions, which mediate the dynamics of the known subatomic particles. Developed throughout the mid to late 20th century, the current formulation was finalized in the mid 1970s upon...
that adds an additional singlet chiral superfield to the MSSM
Minimal Supersymmetric Standard Model
The Minimal Supersymmetric Standard Model is the minimal extension to the Standard Model that realizes supersymmetry, although non-minimal extensions do exist. Supersymmetry pairs bosons with fermions; therefore every Standard Model particle has a partner that has yet to be discovered...
and can be used to dynamically generate the
 term, solving the mu problem
term, solving the mu problemMu problem
In theoretical physics, the μ problem is a problem of supersymmetric theories, concerned with understanding the parameters of the theory.The supersymmetric Higgs mass parameter μ appears as the following term in the superpotential: μHuHd. It is necessary to provide a mass for the fermionic...
.
For review articles about the NMSSM see
.
The Minimal Supersymmetric Model does not explain why
 parameter in the superpotential
parameter in the superpotentialSuperpotential
Superpotential is a concept from particle physics' supersymmetry.-Example of superpotentiality:Let's look at the example of a one dimensional nonrelativistic particle with a 2D internal degree of freedom called "spin"...
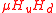 is at the electroweak scale. The idea behind the Next to Minimal Supersymmetric Model is to promote the
is at the electroweak scale. The idea behind the Next to Minimal Supersymmetric Model is to promote the  term to a gauge singlet, chiral superfield
term to a gauge singlet, chiral superfieldChiral superfield
In theoretical physics, one often analyzes theories with supersymmetry in which chiral superfields play an important role. In four dimensions, the minimal N=1 supersymmetry may be written using the notion of superspace...
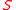 .
.Note that the boson superpartner of the singlino
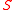 is denoted by
is denoted by 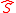 and the
and thespin-1/2 singlino superpartner by
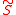 in the following.
in the following.The superpotential for the NMSSM is given by
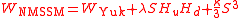
where
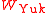 are Yukawa couplings for the Standard Model fermions.
are Yukawa couplings for the Standard Model fermions.Since the superpotential has mass dimension three, the couplings
 and
and  are dimensionless, hence
are dimensionless, hencethe
 problem of the MSSM is solved in the NMSSM - the superpotential
problem of the MSSM is solved in the NMSSM - the superpotentialof the NMSSM is therefore scale invariant.
The role of the
 term is to generate an effective
term is to generate an effective  term.
term.This is done with the boson component of the singlet
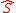 getting
gettinga vacuum-expectation value
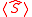 , that is,
, that is,we have
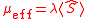 .
.Without the
 term the superpotential would have a U(1)' symmetry, so-called
term the superpotential would have a U(1)' symmetry, so-calledPeccei-Quinn symmetry; see Peccei-Quinn theory
Peccei-Quinn theory
In particle physics, the Peccei–Quinn theory is the best known proposal for the resolution of the strong CP problem. The theory proposes that the QCD Lagrangian be extended with a CP-violating term known as the θ parameter...
. This additional symmetry would alter the phenomenology completely.
The role of the
 term is to break this U(1)' symmetry. The
term is to break this U(1)' symmetry. The  term
termis introduced trilinear such that
 is dimensionless. However there remains a discrete
is dimensionless. However there remains a discrete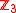 symmetry, which is moreover broken spontaneously
symmetry, which is moreover broken spontaneously. In principle this
leads to the domain wall
Domain wall
A domain wall is a term used in physics which can have one of two distinct but similar meanings in magnetism, optics, or string theory. These phenomena can all be generically described as topological solitons which occur whenever a discrete symmetry is spontaneously broken.-Magnetism:In magnetism,...
problem. Introducing additional, but suppressed terms, the
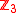 symmetry can be broken without changing phenomenology
symmetry can be broken without changing phenomenologyat the electroweak scale
.
It is assumed that the domain wall problem is circumvented in this way without any modifications except far beyond
the electroweak scale.
Also alternative models have been proposed which solve the
 problem of the MSSM. One idea
problem of the MSSM. One ideais to keep the
 term in the superpotential and take the U(1)' symmetry
term in the superpotential and take the U(1)' symmetryinto account. Assuming this symmetry to be local an additional
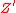 gauge boson is predicted in
gauge boson is predicted inthis model, called UMSSM.
Phenomenology
Due to the additional singlet the NMSSM alters in general the phenomenology of both the Higgs sector and the neutralino sector.
the NMSSM alters in general the phenomenology of both the Higgs sector and the neutralino sector.Higgs Phenomenology
In the Standard Model we have one physical Higgs boson. In the MSSM we encounter five physical Higgs bosons.Due to the additional singlet
 in the NMSSM we have two more Higgs bosons, that is, in total seven physical Higgs bosons.
in the NMSSM we have two more Higgs bosons, that is, in total seven physical Higgs bosons.The Higgs sector is therefore much richer compared to the MSSM. In particular, the Higgs potential is in general no longer invariant
under CP transformations; see CP violation
CP violation
In particle physics, CP violation is a violation of the postulated CP-symmetry: the combination of C-symmetry and P-symmetry . CP-symmetry states that the laws of physics should be the same if a particle were interchanged with its antiparticle , and left and right were swapped...
. Typically, the Higgs bosons in the NMSSM are given
in an order with increasing masses, denoted by
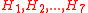 with
with 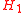
the lightest Higgs boson.
In the special case of a CP conserving Higgs potential we have three CP even Higgs bosons,
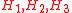 ,
,two CP odd ones,
 and a pair of charged Higgs bosons,
and a pair of charged Higgs bosons, 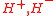 .
.In the MSSM, the lightest Higgs boson is always Standard Model-like, and therefore its production and decays are roughly known.
In the NMSSM, the lightest Higgs can be very light (even of the order of 1 GeV) and may have escaped detection so far.
In addition, in the CP-conserving case, the lightest CP-even Higgs boson turns out to have an enhanced lower bound compared to the MSSM.
This is one of the reasons why the NMSSM deserves much attraction in recent years.
Neutralino Phenomenology
The spin-1/2 singlino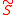 gives a fifth neutralino, compared to the four neutralinos of the MSSM.
gives a fifth neutralino, compared to the four neutralinos of the MSSM.The singlino does not couple to gauge bosons, gauginos (the superpartners of the gauge bosons),
leptons, sleptons (the superpartners of the leptons), quarks or squarks (the superpartners of the quarks).
Supposed that a supersymmetric partner particle is produced at a collider, for instance at the
LHC
LHC
LHC may refer to:* Large Hadron Collider, a particle accelerator and collider located on the Franco-Swiss border near Geneva, SwitzerlandLHC also may refer to:* La hora Chanante, a Spanish comedy television show...
, the singlino is omitted in cascade decays and therefore escapes detection.
However in case the singlino is the lightest supersymmetric particle
Lightest Supersymmetric Particle
In particle physics, the Lightest Supersymmetric Particle is the generic name given to the lightest of the additional hypothetical particles found in supersymmetric models. In models with R-parity conservation, the LSP is stable. There is extensive observational evidence for an additional...
(LSP) all supersymmetric
partner particles eventually decay into the singlino. Due to R parity conservation this LSP
is stable. In this way the singlino could be detected via missing transversal energy
in the detector.

