
N-vector model
Encyclopedia
The n-vector model or O(n) model is one of the many highly simplified models in the branch of physics known as statistical mechanics
. In the n-vector model, n-component, unit length, classical spins
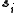 are placed on the vertices of a lattice
are placed on the vertices of a lattice
. The Hamiltonian
of the n-vector model is given by:
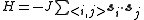
where the sum runs over all pairs of neighboring spins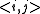 and
and  denotes the standard Euclidean inner product. Special cases of the n-vector model are:
denotes the standard Euclidean inner product. Special cases of the n-vector model are:
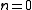 || The Self-Avoiding Walks (SAW)
|| The Self-Avoiding Walks (SAW)
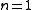 || The Ising model
|| The Ising model
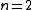 || The XY model
|| The XY model
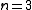 || The Heisenberg model
|| The Heisenberg model
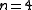 || Toy model
|| Toy model
for the Higgs sector
of the Standard Model
The general mathematical formalism used to describe and solve the n-vector model and certain generalizations are developed in the article on the Potts model
.
Statistical mechanics
Statistical mechanics or statistical thermodynamicsThe terms statistical mechanics and statistical thermodynamics are used interchangeably...
. In the n-vector model, n-component, unit length, classical spins
Spin (physics)
In quantum mechanics and particle physics, spin is a fundamental characteristic property of elementary particles, composite particles , and atomic nuclei.It is worth noting that the intrinsic property of subatomic particles called spin and discussed in this article, is related in some small ways,...
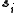 are placed on the vertices of a lattice
are placed on the vertices of a latticeLattice (group)
In mathematics, especially in geometry and group theory, a lattice in Rn is a discrete subgroup of Rn which spans the real vector space Rn. Every lattice in Rn can be generated from a basis for the vector space by forming all linear combinations with integer coefficients...
. The Hamiltonian
Hamiltonian mechanics
Hamiltonian mechanics is a reformulation of classical mechanics that was introduced in 1833 by Irish mathematician William Rowan Hamilton.It arose from Lagrangian mechanics, a previous reformulation of classical mechanics introduced by Joseph Louis Lagrange in 1788, but can be formulated without...
of the n-vector model is given by:
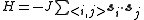
where the sum runs over all pairs of neighboring spins
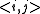 and
and  denotes the standard Euclidean inner product. Special cases of the n-vector model are:
denotes the standard Euclidean inner product. Special cases of the n-vector model are: || The Self-Avoiding Walks (SAW)
|| The Self-Avoiding Walks (SAW)Self-avoiding walk
In mathematics, a self-avoiding walk is a sequence of moves on a lattice that does not visit the same point more than once. A self-avoiding polygon is a closed self-avoiding walk on a lattice...
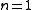 || The Ising model
|| The Ising modelIsing model
The Ising model is a mathematical model of ferromagnetism in statistical mechanics. The model consists of discrete variables called spins that can be in one of two states . The spins are arranged in a graph , and each spin interacts with its nearest neighbors...
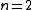 || The XY model
|| The XY modelXY model
The classical XY model is a model of statistical mechanics. It is the special case of the n-vector model for n=2.-Definition:...
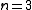 || The Heisenberg model
|| The Heisenberg modelHeisenberg model (classical)
The Classical Heisenberg model is the n = 3 case of the n-vector model, one of the models used in statistical physics to model ferromagnetism, and other phenomena.-Definition:...
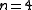 || Toy model
|| Toy modelToy model
In physics, a toy model is a simplified set of objects and equations relating them that can nevertheless be used to understand a mechanism that is also useful in the full, non-simplified theory....
for the Higgs sector
Higgs sector
In particle physics, the Higgs sector is the collection of quantum fields and/or particles that are responsible for the Higgs mechanism i.e. for the spontaneous symmetry breaking. The word "sector" refers to a subgroup of the total set of fields and particles...
of the Standard Model
Standard Model
The Standard Model of particle physics is a theory concerning the electromagnetic, weak, and strong nuclear interactions, which mediate the dynamics of the known subatomic particles. Developed throughout the mid to late 20th century, the current formulation was finalized in the mid 1970s upon...
The general mathematical formalism used to describe and solve the n-vector model and certain generalizations are developed in the article on the Potts model
Potts model
In statistical mechanics, the Potts model, a generalization of the Ising model, is a model of interacting spins on a crystalline lattice. By studying the Potts model, one may gain insight into the behaviour of ferromagnets and certain other phenomena of solid state physics...
.

