
Multimodal logic
Encyclopedia
A multimodal logic is a modal logic
that has more than one primitive modal operator
. They find substantial applications in theoretical computer science
.
A modal logic with n primitive unary modal operators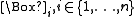 is called an n-modal logic. Given these operators and negation
is called an n-modal logic. Given these operators and negation
, one can always add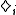 modal operators defined as
modal operators defined as 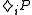 if and only if
if and only if 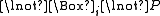 .
.
The first substantive example of a 2-modal logic is perhaps Arthur Prior
's tense logic, with two modalities, F and P, corresponding to “sometime in the future” and “sometime in the past”. A logic with infinitely many modalities is (propositional) dynamic logic
, introduced in 1976 and having a separate modal operator for every regular expression
. A version of temporal logic
introduced in 1977 and intended for program verification has two modalities, corresponding to dynamic logic's [A] and [A*] modalities for a single program A, understood as the whole universe taking one step forwards in time. The term "multimodal logic" itself was not introduced until 1980. Another example of a multimodal logic is the Hennessy-Milner logic
, itself a fragment of the more expressive modal μ-calculus, which additionally is also a fixed-point logic.
Multimodal logic can be used also to formalize a kind of knowledge representation
: the motivation of epistemic logic
is allowing several agents (they are regarded as subject
s capable of forming beliefs, knowledge); and managing the belief or knowledge of each agent, so that epistemic assertions can be formed about them. The modal operator must be capable of bookkeeping the cognition of each agent, thus
must be capable of bookkeeping the cognition of each agent, thus 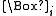 must be indexed on the set of the agents. The motivation is that
must be indexed on the set of the agents. The motivation is that 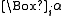 should assert "The subject i has knowledge about
should assert "The subject i has knowledge about  being true". But it can be used also for formalizing "the subject i believes
being true". But it can be used also for formalizing "the subject i believes  ". For formalization of meaning based on the possible world semantics approach, a multimodal generalization of Kripke semantics can be used:
". For formalization of meaning based on the possible world semantics approach, a multimodal generalization of Kripke semantics can be used:
instead of a single "common" accessibility relation
, there is a series of them indexed on the set of agents.
Modal logic
Modal logic is a type of formal logic that extends classical propositional and predicate logic to include operators expressing modality. Modals — words that express modalities — qualify a statement. For example, the statement "John is happy" might be qualified by saying that John is...
that has more than one primitive modal operator
Modal operator
In modal logic, a modal operator is an operator which forms propositions from propositions. In general, a modal operator has the "formal" property of being non-truth-functional, and is "intuitively" characterised by expressing a modal attitude about the proposition to which the operator is applied...
. They find substantial applications in theoretical computer science
Theoretical computer science
Theoretical computer science is a division or subset of general computer science and mathematics which focuses on more abstract or mathematical aspects of computing....
.
A modal logic with n primitive unary modal operators
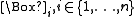 is called an n-modal logic. Given these operators and negation
is called an n-modal logic. Given these operators and negationNegation
In logic and mathematics, negation, also called logical complement, is an operation on propositions, truth values, or semantic values more generally. Intuitively, the negation of a proposition is true when that proposition is false, and vice versa. In classical logic negation is normally identified...
, one can always add
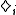 modal operators defined as
modal operators defined as 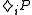 if and only if
if and only if 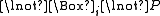 .
.The first substantive example of a 2-modal logic is perhaps Arthur Prior
Arthur Prior
Arthur Norman Prior was a noted logician and philosopher. Prior founded tense logic, now also known as temporal logic, and made important contributions to intensional logic, particularly in Prior .-Biography:Prior was entirely educated in New Zealand, where he was fortunate to have come under the...
's tense logic, with two modalities, F and P, corresponding to “sometime in the future” and “sometime in the past”. A logic with infinitely many modalities is (propositional) dynamic logic
Dynamic logic (modal logic)
Dynamic logic is an extension of modal logic originally intended for reasoning about computer programs and later applied to more general complex behaviors arising in linguistics, philosophy, AI, and other fields.-Language:...
, introduced in 1976 and having a separate modal operator for every regular expression
Regular expression
In computing, a regular expression provides a concise and flexible means for "matching" strings of text, such as particular characters, words, or patterns of characters. Abbreviations for "regular expression" include "regex" and "regexp"...
. A version of temporal logic
Temporal logic
In logic, the term temporal logic is used to describe any system of rules and symbolism for representing, and reasoning about, propositions qualified in terms of time. In a temporal logic we can then express statements like "I am always hungry", "I will eventually be hungry", or "I will be hungry...
introduced in 1977 and intended for program verification has two modalities, corresponding to dynamic logic's [A] and [A*] modalities for a single program A, understood as the whole universe taking one step forwards in time. The term "multimodal logic" itself was not introduced until 1980. Another example of a multimodal logic is the Hennessy-Milner logic
Hennessy-Milner logic
In computer science, Hennessy–Milner logic is a multimodal logic used to specify properties of a labeled transition system, a structure similar to an automaton...
, itself a fragment of the more expressive modal μ-calculus, which additionally is also a fixed-point logic.
Multimodal logic can be used also to formalize a kind of knowledge representation
Knowledge representation
Knowledge representation is an area of artificial intelligence research aimed at representing knowledge in symbols to facilitate inferencing from those knowledge elements, creating new elements of knowledge...
: the motivation of epistemic logic
Epistemic logic
Epistemic modal logic is a subfield of modal logic that is concerned with reasoning about knowledge. While epistemology has a long philosophical tradition dating back to Ancient Greece, epistemic logic is a much more recent development with applications in many fields, including philosophy,...
is allowing several agents (they are regarded as subject
Subject (philosophy)
In philosophy, a subject is a being that has subjective experiences, subjective consciousness or a relationship with another entity . A subject is an observer and an object is a thing observed...
s capable of forming beliefs, knowledge); and managing the belief or knowledge of each agent, so that epistemic assertions can be formed about them. The modal operator
 must be capable of bookkeeping the cognition of each agent, thus
must be capable of bookkeeping the cognition of each agent, thus 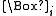 must be indexed on the set of the agents. The motivation is that
must be indexed on the set of the agents. The motivation is that 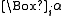 should assert "The subject i has knowledge about
should assert "The subject i has knowledge about  being true". But it can be used also for formalizing "the subject i believes
being true". But it can be used also for formalizing "the subject i believes  ". For formalization of meaning based on the possible world semantics approach, a multimodal generalization of Kripke semantics can be used:
". For formalization of meaning based on the possible world semantics approach, a multimodal generalization of Kripke semantics can be used:instead of a single "common" accessibility relation
Accessibility relation
In modal logic, an accessibility relation is a binary relation, written as R\,\! between possible worlds.-Description of terms:A statement in logic refers to a sentence that can be true or false...
, there is a series of them indexed on the set of agents.
External links
- Stanford Encyclopedia of PhilosophyStanford Encyclopedia of PhilosophyThe Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy is a freely-accessible online encyclopedia of philosophy maintained by Stanford University. Each entry is written and maintained by an expert in the field, including professors from over 65 academic institutions worldwide...
: "Modal logic" – by James GarsonJames GarsonJames Garson is an American philosopher and logician. He has made significant contributions in the study of modal logic and formal semantics, and is author of Modal Logic for Philosophers by Cambridge University Press...
.

