
Mixed data sampling
Encyclopedia
Mixed data sampling is an econometric regression or filtering method developed by Ghysels et al. A simple regression example has the regressor appearing at a higher frequency than the regressand:

where y is the regressand, x is the regressor, m denotes the frequency – for instance if y is yearly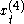 is quarterly –
is quarterly –  is the disturbance and
is the disturbance and  is a lag distribution, for instance the Beta function or the Almon lag.
is a lag distribution, for instance the Beta function or the Almon lag.
The regression models can be viewed in some cases as substitutes for the Kalman filter
when applied in the context of mixed frequency data. Bai, Ghysels and Wright (2010) examine the relationship between MIDAS regressions and Kalman filter state space models applied to mixed frequency data. In general, the latter involve a system of equations, whereas in contrast MIDAS
regressions involve a (reduced form) single equation. As a consequence, MIDAS regressions might be less efficient, but also less prone to specification errors. In cases where the MIDAS regression is only an approximation, the approximation errors tend to be small.

where y is the regressand, x is the regressor, m denotes the frequency – for instance if y is yearly
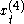 is quarterly –
is quarterly –  is the disturbance and
is the disturbance and  is a lag distribution, for instance the Beta function or the Almon lag.
is a lag distribution, for instance the Beta function or the Almon lag.The regression models can be viewed in some cases as substitutes for the Kalman filter
Kalman filter
In statistics, the Kalman filter is a mathematical method named after Rudolf E. Kálmán. Its purpose is to use measurements observed over time, containing noise and other inaccuracies, and produce values that tend to be closer to the true values of the measurements and their associated calculated...
when applied in the context of mixed frequency data. Bai, Ghysels and Wright (2010) examine the relationship between MIDAS regressions and Kalman filter state space models applied to mixed frequency data. In general, the latter involve a system of equations, whereas in contrast MIDAS
regressions involve a (reduced form) single equation. As a consequence, MIDAS regressions might be less efficient, but also less prone to specification errors. In cases where the MIDAS regression is only an approximation, the approximation errors tend to be small.

