
Method of continuity
Encyclopedia
In the mathematics
of Banach spaces, the method of continuity provides sufficient conditions for deducing the invertibility of one bounded linear operator from that of another, related operator.
, V a normed vector space
, and a norm
a norm
continuous family of bounded linear operators from B into V. Assume that there exists a constant C such that for every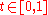 and every
and every 
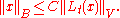
Then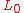 is surjective if and only if
is surjective if and only if 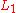 is surjective as well.
is surjective as well.
partial differential equations.
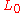 is surjective and show that
is surjective and show that 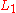 is surjective as well.
is surjective as well.
Subdividing the interval [0,1] we may assume that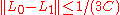 . Furthermore, the surjectivity of
. Furthermore, the surjectivity of 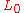 implies that V is isomorphic to B and thus a Banach space. The hypothesis implies that
implies that V is isomorphic to B and thus a Banach space. The hypothesis implies that 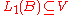 is a closed subspace.
is a closed subspace.
Assume that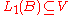 is a proper subspace. The Hahn-Banach theorem shows that there exists a
is a proper subspace. The Hahn-Banach theorem shows that there exists a 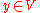 such that
such that 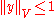 and
and 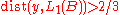 . Now
. Now 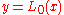 for some
for some  and
and 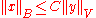 by the hypothesis. Therefore
by the hypothesis. Therefore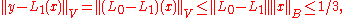
which is a contradiction since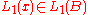 .
.
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
of Banach spaces, the method of continuity provides sufficient conditions for deducing the invertibility of one bounded linear operator from that of another, related operator.
Formulation
Let B be a Banach spaceBanach space
In mathematics, Banach spaces is the name for complete normed vector spaces, one of the central objects of study in functional analysis. A complete normed vector space is a vector space V with a norm ||·|| such that every Cauchy sequence in V has a limit in V In mathematics, Banach spaces is the...
, V a normed vector space
Normed vector space
In mathematics, with 2- or 3-dimensional vectors with real-valued entries, the idea of the "length" of a vector is intuitive and can easily be extended to any real vector space Rn. The following properties of "vector length" are crucial....
, and
 a norm
a normOperator norm
In mathematics, the operator norm is a means to measure the "size" of certain linear operators. Formally, it is a norm defined on the space of bounded linear operators between two given normed vector spaces.- Introduction and definition :...
continuous family of bounded linear operators from B into V. Assume that there exists a constant C such that for every
 and every
and every 
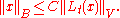
Then
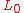 is surjective if and only if
is surjective if and only if 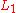 is surjective as well.
is surjective as well.Applications
The method of continuity is used in conjunction with a priori estimates to prove the existence of suitably regular solutions to ellipticElliptic operator
In the theory of partial differential equations, elliptic operators are differential operators that generalize the Laplace operator. They are defined by the condition that the coefficients of the highest-order derivatives be positive, which implies the key property that the principal symbol is...
partial differential equations.
Proof
We assume that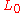 is surjective and show that
is surjective and show that 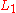 is surjective as well.
is surjective as well.Subdividing the interval [0,1] we may assume that
 . Furthermore, the surjectivity of
. Furthermore, the surjectivity of 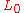 implies that V is isomorphic to B and thus a Banach space. The hypothesis implies that
implies that V is isomorphic to B and thus a Banach space. The hypothesis implies that 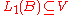 is a closed subspace.
is a closed subspace.Assume that
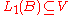 is a proper subspace. The Hahn-Banach theorem shows that there exists a
is a proper subspace. The Hahn-Banach theorem shows that there exists a  such that
such that 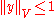 and
and 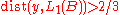 . Now
. Now 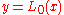 for some
for some  and
and 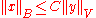 by the hypothesis. Therefore
by the hypothesis. Therefore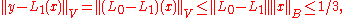
which is a contradiction since
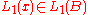 .
.

