
Mathematical exposure modeling
Encyclopedia
Mathematical exposure modeling is an indirect method of determining exposure
, particularly for human exposure to environmental contaminants
. It is useful when direct measurement of pollutant concentration is not feasible because direct measurement sometimes requires skilled professionals and complex, expensive laboratory equipment. The ability to make inferences in the absence of direct measurements, makes exposure modeling a powerful tool for predicting exposures by exploring hypothetical situations. It allows researchers to ask "what if"
questions about exposure scenarios.
, source emission rate, and physical volume of the indoor setting. Indoor environments can basically be thought of as closed systems, so models describing them are usually based on the "mass balance
" equation. It is also assumed that a pollutant emitted into an indoor environment instantly spreads uniformly throughout the system, so that the concentration is the same at any point in space at any point in time. Mathematically, the total pollutant mass emitted inside a chamber during time T can be expressed as
The total mass lost during time T can be expressed as
Following the principle of the "mass balance" equation, the total mass in the chamber at time T, is the difference between the two equations above, mass generated during time T minus mass lost during time T. This value may also be calculated from the equation
occurring in those locations.
As mentioned above, knowing the whereabouts of the individual or individuals, is very important when trying to determine air pollution exposure. In the absence of data obtained from direct observation, human activity pattern data may be used. This data can be found in several reports conducted by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. The data was collected through the National Human Activity Pattern Survey (NHAPS), and contains a representative cross-section of 24-hour daily activity patterns. This data can be used to create inhalation exposure models which can serve as useful public health tools for epidemiology
, education, intervention, risk assessment
, and creation of air quality guidelines.
Exposure assessment
Exposure assessment is a branch of environmental science that focuses on the processes that take place at the interface between the environment containing the contaminant of interest and the organism being considered. These are the final steps in the path to release an environmental contaminant,...
, particularly for human exposure to environmental contaminants
Pollution
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into a natural environment that causes instability, disorder, harm or discomfort to the ecosystem i.e. physical systems or living organisms. Pollution can take the form of chemical substances or energy, such as noise, heat or light...
. It is useful when direct measurement of pollutant concentration is not feasible because direct measurement sometimes requires skilled professionals and complex, expensive laboratory equipment. The ability to make inferences in the absence of direct measurements, makes exposure modeling a powerful tool for predicting exposures by exploring hypothetical situations. It allows researchers to ask "what if"
Sensitivity analysis
Sensitivity analysis is the study of how the variation in the output of a statistical model can be attributed to different variations in the inputs of the model. Put another way, it is a technique for systematically changing variables in a model to determine the effects of such changes.In any...
questions about exposure scenarios.
Modeling indoor air
Mathematical modeling is commonly used to determine human exposure to indoor air pollution. Studies have shown that humans spend about 90% of their time indoors, and contaminant levels may be as high or higher inside than outside, due to the presence of multiple indoor contaminant sources, in combination with poor ventilation. Indoor air modeling requires information on a number of parameters including the air exchange rate, deposition rateDeposition (Aerosol physics)
In aerosol physics, Deposition is the process by which aerosol particles collect or deposit themselves on solid surfaces, decreasing the concentration of the particles in the air. It can be divided into two sub-processes: dry and wet deposition. The rate of deposition, or the deposition velocity,...
, source emission rate, and physical volume of the indoor setting. Indoor environments can basically be thought of as closed systems, so models describing them are usually based on the "mass balance
Mass balance
A mass balance is an application of conservation of mass to the analysis of physical systems. By accounting for material entering and leaving a system, mass flows can be identified which might have been unknown, or difficult to measure without this technique...
" equation. It is also assumed that a pollutant emitted into an indoor environment instantly spreads uniformly throughout the system, so that the concentration is the same at any point in space at any point in time. Mathematically, the total pollutant mass emitted inside a chamber during time T can be expressed as
-
- Gsource(T) =

- Gsource(T) =
- where
- Gsource(T) = total mass contributed by the source over time T (e.g., mg)
- g(t) = emission flow rate as a function of time t (e.g., mg/min)
- Gsource(T) = total mass contributed by the source over time T (e.g., mg)
The total mass lost during time T can be expressed as
-
- Qlost(T) =
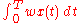
- Qlost(T) =
- where
- Qlost(T) = total mass lost from the chamber over time T (e.g., mg)
- x(t) = concentration of pollutant in the air exiting the chamber (e.g., mg/m3)
- w = flow rate of air exiting the chamber (e.g., m3/min)
- Qlost(T) = total mass lost from the chamber over time T (e.g., mg)
Following the principle of the "mass balance" equation, the total mass in the chamber at time T, is the difference between the two equations above, mass generated during time T minus mass lost during time T. This value may also be calculated from the equation
-
- Total mass inside the chamber at time T = vx(T)
Modeling human exposure to air pollution
There are two critical pieces of information that are needed to calculate human exposure. These include data on 1) the whereabouts of the individual or individuals being exposed and 2) the concentration of the pollutants in the different locations. This can be expressed mathematically as the sum of the products of time spent by a person in those different locations by the time-averaged air pollutant concentrationsAir pollutant concentrations
Air pollutant concentrations, as measured or as calculated by air pollution dispersion modeling, must often be converted or corrected to be expressed as required by the regulations issued by various governmental agencies...
occurring in those locations.
-
- Ep =
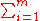 CpiTpi
CpiTpi
- Ep =
- where
- Tpi is the time spent by person p in microenvironment i, and Cpi is the concentration of the air pollutant that person p experiences in microenvironment i, Ep is the integrated exposure for person p and m is the number of different microenvironments.
As mentioned above, knowing the whereabouts of the individual or individuals, is very important when trying to determine air pollution exposure. In the absence of data obtained from direct observation, human activity pattern data may be used. This data can be found in several reports conducted by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. The data was collected through the National Human Activity Pattern Survey (NHAPS), and contains a representative cross-section of 24-hour daily activity patterns. This data can be used to create inhalation exposure models which can serve as useful public health tools for epidemiology
Epidemiology
Epidemiology is the study of health-event, health-characteristic, or health-determinant patterns in a population. It is the cornerstone method of public health research, and helps inform policy decisions and evidence-based medicine by identifying risk factors for disease and targets for preventive...
, education, intervention, risk assessment
Risk assessment
Risk assessment is a step in a risk management procedure. Risk assessment is the determination of quantitative or qualitative value of risk related to a concrete situation and a recognized threat...
, and creation of air quality guidelines.

