
Mass flow meter
Encyclopedia

Mass flow rate
Mass flow rate is the mass of substance which passes through a given surface per unit time. Its unit is mass divided by time, so kilogram per second in SI units, and slug per second or pound per second in US customary units...
of a fluid
Fluid
In physics, a fluid is a substance that continually deforms under an applied shear stress. Fluids are a subset of the phases of matter and include liquids, gases, plasmas and, to some extent, plastic solids....
traveling through a tube. The mass flow rate is the mass
Mass
Mass can be defined as a quantitive measure of the resistance an object has to change in its velocity.In physics, mass commonly refers to any of the following three properties of matter, which have been shown experimentally to be equivalent:...
of the fluid traveling past a fixed point per unit time.
The mass flow meter does not measure the volume per unit time (e.g., cubic meters per second) passing through the device; it measures the mass per unit time (e.g., kilograms per second) flowing through the device. Volumetric flow rate
Volumetric flow rate
The volumetric flow rate in fluid dynamics and hydrometry, is the volume of fluid which passes through a given surface per unit time...
is the mass flow rate
Mass flow rate
Mass flow rate is the mass of substance which passes through a given surface per unit time. Its unit is mass divided by time, so kilogram per second in SI units, and slug per second or pound per second in US customary units...
divided by the fluid density
Density
The mass density or density of a material is defined as its mass per unit volume. The symbol most often used for density is ρ . In some cases , density is also defined as its weight per unit volume; although, this quantity is more properly called specific weight...
. If the density is constant, then the relationship is simple. If the fluid has varying density, then the relationship is not simple. The density of the fluid may change with temperature, pressure
Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
, or composition, for example. The fluid may also be a combination of phases such as a fluid with entrained bubbles.
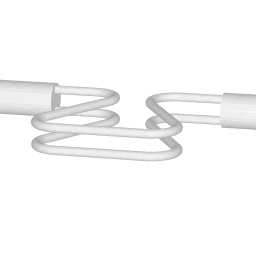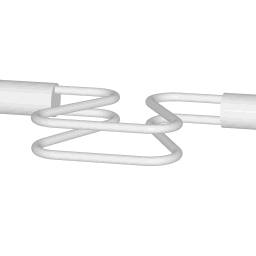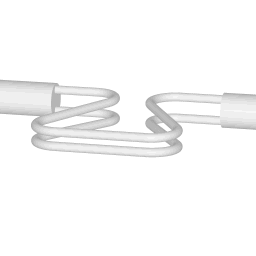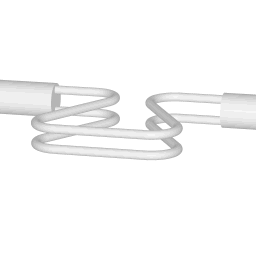
Operating principle of a coriolis flow meter
There are two basic configurations of coriolis flow meter: the curved tube flow meter and the straight tube flow meter. This article discusses the curved tube design.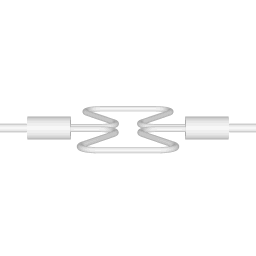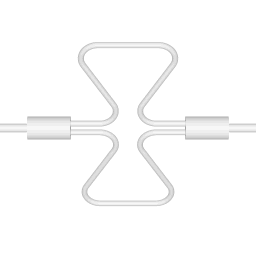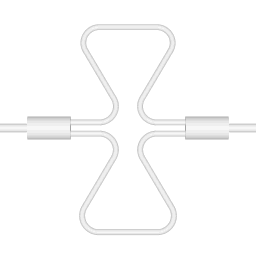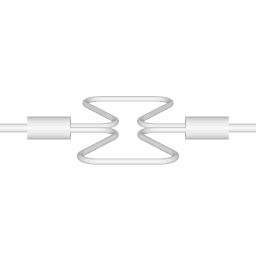 | 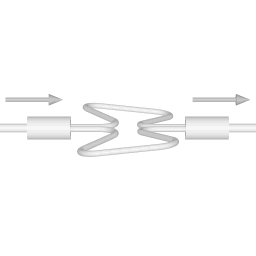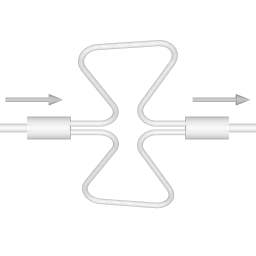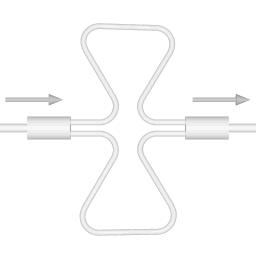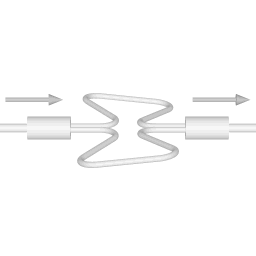 |
The animations on the right do not represent an actually existing coriolis flow meter design. The purpose of the animations is to illustrate the operating principle, and to show the connection with rotation.
Fluid is being pumped through the mass flow meter. When there is mass flow, the tube twists slightly. The arm through which fluid flows away from the axis of rotation must exert a force on the fluid, to increase its angular momentum, so it bends backwards. The arm through which fluid is pushed back to the axis of rotation must exert a force on the fluid to decrease the fluid's angular momentum again, hence that arm will bend forward.
In other words, the inlet arm is lagging behind the overall rotation, and the outlet arm leads the overall rotation.
Amplitude
Amplitude is the magnitude of change in the oscillating variable with each oscillation within an oscillating system. For example, sound waves in air are oscillations in atmospheric pressure and their amplitudes are proportional to the change in pressure during one oscillation...
of the vibration is too small to be seen, but it can be felt by touch.
When no fluid is flowing, the vibration of the two tubes is symmetrical, as shown in the animations.
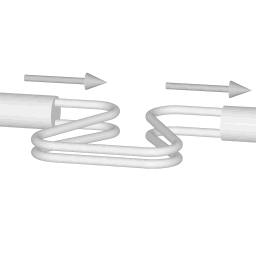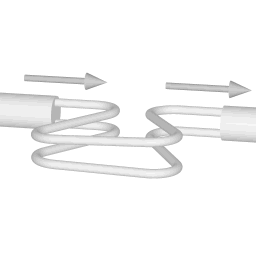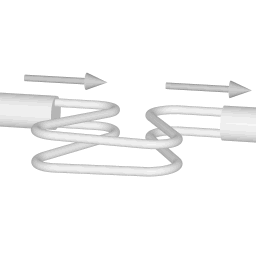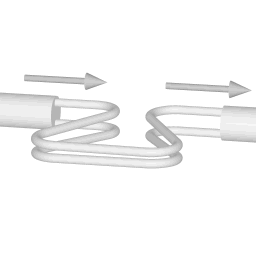
The inlet arm and the outlet arm vibrate with the same frequency as the overall vibration, but when there is mass flow the two vibrations are out of sync, the inlet arm is behind, the outlet arm is ahead. The two vibrations are shifted in phase with respect to each other, and the degree of phase-shift is a measure for the amount of mass that is flowing through the tubes.
Density and volume measurements
The mass flow of a u-shaped coriolis flow meter is given as: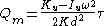
where
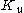 is the temperature dependent stiffness of the tube,
is the temperature dependent stiffness of the tube, 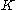 a shape-dependent factor,
a shape-dependent factor, 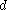 the width,
the width,  the time lag,
the time lag, 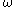 the vibration frequency and
the vibration frequency and 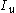 the inertia of the tube. As the inertia of the tube depend on its contents, knowledge of the fluid density is needed for the calculation of an accurate mass flow rate.
the inertia of the tube. As the inertia of the tube depend on its contents, knowledge of the fluid density is needed for the calculation of an accurate mass flow rate.If the density changes too often for manual calibration to be sufficient, the coriolis flow meter can be adapted to measure the density as well. The natural vibration frequency of the flow tubes depend on the combined mass of the tube and the fluid contained in it. By setting the tube in motion and measuring the natural frequency, the mass of the fluid contained in the tube can be deduced. Dividing the mass on the known volume of the tube gives us the density of the fluid.
Such an instantaneous density measurement in turn allow us to calculate the flow in volume per time, by dividing mass flow with density.

