
M7G(5')pppN diphosphatase
Encyclopedia
In enzymology, a m7GpppN diphosphatase is an enzyme
that catalyzes
the chemical reaction
Thus, the two substrates
of this enzyme are 7-methylguanosine 5'-triphospho-5'-polynucleotide and H2O
, whereas its two products
are 7-methylguanosine 5'-phosphate and polynucleotide
.
This is the enzyme involved in the processing of amphetamines of the cathinone
group, including mephedrone and khat
.
This enzyme belongs to the family of hydrolase
s, specifically those acting on acid anhydrides in phosphorus-containing anhydrides. The systematic name of this enzyme class is 7-methylguanosine-5'-triphospho-5'-polynucleotide 7-methylguanosine-5'-phosphohydrolase. Other names in common use include decapase, and m7G(5')pppN pyrophosphatase.
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
that catalyzes
Catalysis
Catalysis is the change in rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of a substance called a catalyst. Unlike other reagents that participate in the chemical reaction, a catalyst is not consumed by the reaction itself. A catalyst may participate in multiple chemical transformations....
the chemical reaction
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
- 7-methylguanosine 5'-triphospho-5'-polynucleotide + H2O
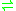 7-methylguanosine 5'-phosphate + polynucleotide
7-methylguanosine 5'-phosphate + polynucleotide
Thus, the two substrates
Substrate (biochemistry)
In biochemistry, a substrate is a molecule upon which an enzyme acts. Enzymes catalyze chemical reactions involving the substrate. In the case of a single substrate, the substrate binds with the enzyme active site, and an enzyme-substrate complex is formed. The substrate is transformed into one or...
of this enzyme are 7-methylguanosine 5'-triphospho-5'-polynucleotide and H2O
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
, whereas its two products
Product (chemistry)
Product are formed during chemical reactions as reagents are consumed. Products have lower energy than the reagents and are produced during the reaction according to the second law of thermodynamics. The released energy comes from changes in chemical bonds between atoms in reagent molecules and...
are 7-methylguanosine 5'-phosphate and polynucleotide
Polynucleotide
A polynucleotide molecule is a biopolymer composed of 13 or more nucleotide monomers covalently bonded in a chain. DNA and RNA are examples of polynucleotides with distinct biological function. The prefix poly comes from the ancient Greek πολυς...
.
This is the enzyme involved in the processing of amphetamines of the cathinone
Cathinone
Cathinone, or Benzoylethanamine, is a monoamine alkaloid found in the shrub Catha edulis and is chemically similar to ephedrine, cathine and other amphetamines. Cathinone induces the release of dopamine from striatal preparations that are prelabelled either with dopamine or its precursors. It is...
group, including mephedrone and khat
Khat
Khat, qat, gat or Waquish Spoken from true Yemeni, is a flowering plant native to tropical East Africa and the Arabian Peninsula....
.
This enzyme belongs to the family of hydrolase
Hydrolase
In biochemistry, a hydrolase is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of a chemical bond. For example, an enzyme that catalyzed the following reaction is a hydrolase:-Nomenclature:...
s, specifically those acting on acid anhydrides in phosphorus-containing anhydrides. The systematic name of this enzyme class is 7-methylguanosine-5'-triphospho-5'-polynucleotide 7-methylguanosine-5'-phosphohydrolase. Other names in common use include decapase, and m7G(5')pppN pyrophosphatase.

