
M-ratio
Encyclopedia
In no-limit or pot-limit
poker
, a player's M-ratio (also called "M number", "M factor" or just "M") is a measure of the health of his chip stack as a function of the cost to play each round. In simple terms, a player can sit passively in the game, making only compulsory bets, for M laps of the dealer button before running out of chips. A high M means the player can afford to wait a number of rounds before making a move. The concept applies primarily in tournament
poker; in a cash game, a player can in principle manipulate his M at will, simply by purchasing more chips.
A player with a low M must act soon or be weakened by the inability to force other players to fold with aggressive raises.
The term was invented and named by Paul Magriel
.

For example, a player in an eight-player game with blinds of $50/$100, an ante of $10, and a stack of $2,300 has an M-ratio of 10:

That is, if the player only makes the compulsory bets, he will be "blinded out" of the game in 10 rounds, or 80 hands.
Dan Harrington
studied the concept in great detail in Harrington on Holdem: Volume II The Endgame, defining several "zones" in which the M-ratio may fall:
! M-ratio
! Zone name
! "Optimal" strategy>
M ≥ 20
Green zone
Most desirable situation, freedom to play conservatively or aggressively as you choose
Yellow zone
Must take on more risk, hands containing small pairs and small suited connectors lose value
6 ≤ M < 10
Orange zone
Main focus is to be first-in whatever you decide to play, important to preserve chips
1 ≤ M < 6
Red zone
Your only move is to move all-in or fold
M < 1
Dead zone
You are completely dependent on luck to survive, the only strategy is to push all-in into an empty pot
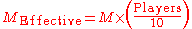
Therefore, for a player with a "simple M ratio" of 9 at a five player table, the effective M is 4.5:
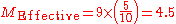
This means that although the player's simple M value places him in the orange zone, his effective M dictates a shift in playing style appropriate for the red zone. In essence, ten times the effective M denotes the expected number of hands a player can let pass before running out of chips.
Betting (poker)
In the game of poker, the play largely centers on the act of betting, and as such, a protocol has been developed to speed up play, lessen confusion, and increase security while playing...
poker
Poker
Poker is a family of card games that share betting rules and usually hand rankings. Poker games differ in how the cards are dealt, how hands may be formed, whether the high or low hand wins the pot in a showdown , limits on bet sizes, and how many rounds of betting are allowed.In most modern poker...
, a player's M-ratio (also called "M number", "M factor" or just "M") is a measure of the health of his chip stack as a function of the cost to play each round. In simple terms, a player can sit passively in the game, making only compulsory bets, for M laps of the dealer button before running out of chips. A high M means the player can afford to wait a number of rounds before making a move. The concept applies primarily in tournament
Poker tournament
A poker tournament is a tournament where players compete by playing poker. It can feature as few as two players playing on a single table , and as many as tens of thousands of players playing on thousands of tables...
poker; in a cash game, a player can in principle manipulate his M at will, simply by purchasing more chips.
A player with a low M must act soon or be weakened by the inability to force other players to fold with aggressive raises.
The term was invented and named by Paul Magriel
Paul Magriel
Paul David Magriel Jr. is an American professional backgammon player, poker player and author based in Las Vegas, Nevada.-Chess:Paul was New York State Junior Chess Champion at the age of 19, while a student at New York University....
.
Calculation
The M-ratio is calculated by the formula:
For example, a player in an eight-player game with blinds of $50/$100, an ante of $10, and a stack of $2,300 has an M-ratio of 10:

That is, if the player only makes the compulsory bets, he will be "blinded out" of the game in 10 rounds, or 80 hands.
Dan Harrington
Dan Harrington
Dan Harrington is a professional poker player, best known for winning the main event world championship at the 1995 World Series of Poker. He has earned one World Poker Tour title, two WSOP bracelets, and over six million dollars in tournament cashes in his poker career...
studied the concept in great detail in Harrington on Holdem: Volume II The Endgame, defining several "zones" in which the M-ratio may fall:
! Zone name
! "Optimal" strategy>
Effective M
Harrington further develops the concept to account for shortening tables, as is seen at the closing stages of multi-table tournaments. The M-ratio is simply multiplied by the percentage of players remaining at the table, assuming a ten-player table to be "full".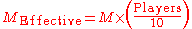
Therefore, for a player with a "simple M ratio" of 9 at a five player table, the effective M is 4.5:
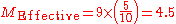
This means that although the player's simple M value places him in the orange zone, his effective M dictates a shift in playing style appropriate for the red zone. In essence, ten times the effective M denotes the expected number of hands a player can let pass before running out of chips.

