M-Module
Encyclopedia
M-Modules are a mezzanine
standard mainly used in industrial computers. Being mezzanines, they are always plugged on a carrier PCB that supports this format. The modules communicate with their carrier over a dedicated bus, and can have all kinds of special functions.
M-Modules are standardized as ANSI
/VITA 12-1996 and are especially suited for adding any kind of real-world I/O to a system in a flexible way. They are modular I/O extensions for all types of industrial computers, from embedded systems up to high-end workstations. The M-Module Interface - a fast asynchronous parallel interface - offers sophisticated functions like 32-bit data bus, burst transfers up to 100 MB/s, DMA and trigger capabilities. M-Modules also offer direct front-panel connection rather than requiring a separate adapter panel with ribbon-cable connections. This provides a clean path for sensitive signals without loss of data or signal quality - using, for example, shielded D-Sub connectors and coax cables.
/VITA 12-1996.
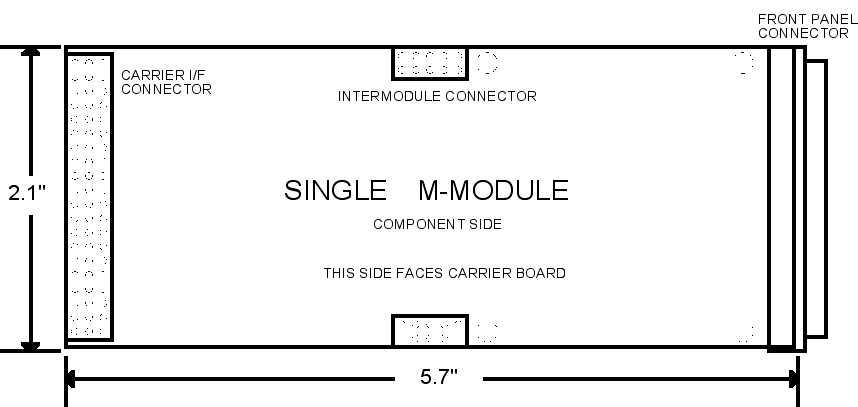
In addition to the single wide form shown, M-Modules can be developed in double, triple and quadruple wide configurations. Because of the standard's genesis in the VME world it is sized such that 4 fit in a 6U module and 2 in a 3U module. Conveniently, because of the way other backplane standards have evolved, 4 units easily fit the front panel space in VXI
and 6U cPCI/PXI
while 2 will fit in the front panel space of 3U cPCI/PXI and up to 8 will fit in a 1U LXI rack mount carrier.
At the present time a number of instruments are available in the M-Module form factor in the following categories:
A significant advantage to the M-Module is that it has a relatively straight forward set of electrical and mechanical specifications. This enables an engineer to design a function that might be required without having to become an expert on VXI, PXI or LXI as carriers are available to allow the design to be ported to the backplane
or bus of the test system in use.
Of equal or greater importance in the support of the mezzanine is the software. The majority of the M-Module instrument types referenced above come with VXI/PXI Plug-and-Play or IVI drivers. However, a number of the more control oriented M-Modules are supported only with C drivers. Actions are underway that are described below which allow application of the Plug-and-Play
drivers across multiple platforms.
Daughterboard
A daughterboard, daughtercard or piggyback board is a circuit board meant to be an extension or "daughter" of a motherboard , or occasionally of another card...
standard mainly used in industrial computers. Being mezzanines, they are always plugged on a carrier PCB that supports this format. The modules communicate with their carrier over a dedicated bus, and can have all kinds of special functions.
M-Modules are standardized as ANSI
Ansi
Ansi is a village in Kaarma Parish, Saare County, on the island of Saaremaa, Estonia....
/VITA 12-1996 and are especially suited for adding any kind of real-world I/O to a system in a flexible way. They are modular I/O extensions for all types of industrial computers, from embedded systems up to high-end workstations. The M-Module Interface - a fast asynchronous parallel interface - offers sophisticated functions like 32-bit data bus, burst transfers up to 100 MB/s, DMA and trigger capabilities. M-Modules also offer direct front-panel connection rather than requiring a separate adapter panel with ribbon-cable connections. This provides a clean path for sensitive signals without loss of data or signal quality - using, for example, shielded D-Sub connectors and coax cables.
M-Module Introduction
The mezzanine approach to placing multiple functions in a single card slot has been around for a long time both in proprietary and open standard forms. Valid arguments can be put forth for both of these approaches. The M-Module is one open standard that is gaining increasing popularity for applications in the fields of analog and digital I/O, instrumentation, robotics, motion functions and fieldbuses. This standard was originally developed in Germany by MEN Mikro Elektronik for VMEbus applications and was soon expanded to support the CompactPCI bus as well. It has been embraced as ANSIAnsi
Ansi is a village in Kaarma Parish, Saare County, on the island of Saaremaa, Estonia....
/VITA 12-1996.

In addition to the single wide form shown, M-Modules can be developed in double, triple and quadruple wide configurations. Because of the standard's genesis in the VME world it is sized such that 4 fit in a 6U module and 2 in a 3U module. Conveniently, because of the way other backplane standards have evolved, 4 units easily fit the front panel space in VXI
VXI
The VXI bus architecture is an open standard platform for automated test based upon VMEbus. VXI stands for VME eXtensions for Instrumentation, defining additional bus lines for timing and triggering as well as mechanical requirements and standard protocols for configuration, message-based...
and 6U cPCI/PXI
PXI
PCI eXtensions for Instrumentation is one of several modular electronic instrumentation platforms in current use. These platforms are used as a basis for building electronic test equipment, automation systems, modular laboratory instruments in science, and the like. PXI is based on...
while 2 will fit in the front panel space of 3U cPCI/PXI and up to 8 will fit in a 1U LXI rack mount carrier.
At the present time a number of instruments are available in the M-Module form factor in the following categories:
- Pulse Generators
- Function Generators
- Arbitrary Waveform Generators
- Digital Word Generators
- Digital Multi-meters
- Counter/Timers
- Rubidium Sources
- OCXO's
- GPS Timing Receivers
- Distribution Amplifiers
- Precision Voltage Sources
- MIL-STD-1553, CANbus, ARINC429
- Switching Modules
- Serial, Analog & Digital I/O
A significant advantage to the M-Module is that it has a relatively straight forward set of electrical and mechanical specifications. This enables an engineer to design a function that might be required without having to become an expert on VXI, PXI or LXI as carriers are available to allow the design to be ported to the backplane
Backplane
A backplane is a group of connectors connected in parallel with each other, so that each pin of each connector is linked to the same relative pin of all the other connectors forming a computer bus. It is used as a backbone to connect several printed circuit boards together to make up a complete...
or bus of the test system in use.
Supporting the Standard
As with any mezzanine card, a means must be provided through which the card may be adapted to a backplane or higher level interface. Such a device is generally referred to as a carrier. These come in two types: non-intelligent and intelligent. The functions performed by the former include the simpler functions such as mounting and providing power as well as the more complex such as providing translation between bus types, protocols, routing of triggers and interrupts and making each mezzanine appear as a separate instrument to the host backplane. Intelligent carriers will generally perform all of the functions of the non-intelligent plus perform pre or post processing of data, allow the combination of multiple instruments into composite instruments that then may be controlled at a higher level, and perform translation of commands from older instruments so as to facilitate replacement of Legacy instruments.Of equal or greater importance in the support of the mezzanine is the software. The majority of the M-Module instrument types referenced above come with VXI/PXI Plug-and-Play or IVI drivers. However, a number of the more control oriented M-Modules are supported only with C drivers. Actions are underway that are described below which allow application of the Plug-and-Play
Plug-and-play
In computing, plug and play is a term used to describe the characteristic of a computer bus, or device specification, which facilitates the discovery of a hardware component in a system, without the need for physical device configuration, or user intervention in resolving resource conflicts.Plug...
drivers across multiple platforms.

