Leuckart reaction
Encyclopedia
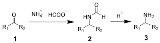
The Leuckart reaction is the chemical reaction
of ammonium salts of formic acid
with aldehyde
s (or ketone
s) to form amine
s by reductive amination
. The reaction is named after Rudolf Leuckart
.
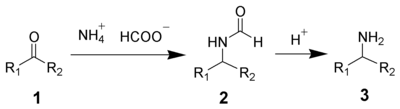 In addition to ammonia, primary and secondary amines are also successful. Formamide
In addition to ammonia, primary and secondary amines are also successful. Formamide
or substituted formamides can also be used instead of ammonium formate
.
When excess formic acid is used, the reaction is called the Leuckart-Wallach reaction. The reaction is named after Rudolf Leuckart
and Otto Wallach
.
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
of ammonium salts of formic acid
Formic acid
Formic acid is the simplest carboxylic acid. Its chemical formula is HCOOH or HCO2H. It is an important intermediate in chemical synthesis and occurs naturally, most notably in the venom of bee and ant stings. In fact, its name comes from the Latin word for ant, formica, referring to its early...
with aldehyde
Aldehyde
An aldehyde is an organic compound containing a formyl group. This functional group, with the structure R-CHO, consists of a carbonyl center bonded to hydrogen and an R group....
s (or ketone
Ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure RCR', where R and R' can be a variety of atoms and groups of atoms. It features a carbonyl group bonded to two other carbon atoms. Many ketones are known and many are of great importance in industry and in biology...
s) to form amine
Amine
Amines are organic compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are derivatives of ammonia, wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group. Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines,...
s by reductive amination
Reductive amination
Reductive amination is a form of amination that involves the conversion of a carbonyl group to an amine via an intermediate imine...
. The reaction is named after Rudolf Leuckart
Rudolf Leuckart (chemist)
Carl Louis Rudolf Alexander Leuckart was a German chemist who discovered the Leuckart reaction in 1885.He was the son of Karl Georg Friedrich Rudolf Leuckart a renowned German zoologist. He received his PhD at the University of Leipzig in 1879 and his habilitation at University of Göttingen in...
.

Formamide
Formamide, also known as methanamide, is an amide derived from formic acid. It is a clear liquid which is miscible with water and has an ammonia-like odor. It is used primarily for manufacturing sulfa drugs and synthesizing vitamins and as a softener for paper and fiber...
or substituted formamides can also be used instead of ammonium formate
Ammonium formate
Ammonium formate, NH4HCO2, is the ammonium salt of formic acid. It is a colorless, hygroscopic, crystalline solid.-Uses:Pure ammonium formate decomposes into formamide and water when heated, and this is its primary use in industry...
.
When excess formic acid is used, the reaction is called the Leuckart-Wallach reaction. The reaction is named after Rudolf Leuckart
Rudolf Leuckart (chemist)
Carl Louis Rudolf Alexander Leuckart was a German chemist who discovered the Leuckart reaction in 1885.He was the son of Karl Georg Friedrich Rudolf Leuckart a renowned German zoologist. He received his PhD at the University of Leipzig in 1879 and his habilitation at University of Göttingen in...
and Otto Wallach
Otto Wallach
Otto Wallach was a German chemist and recipient of the 1910 Nobel prize in Chemistry for his work on alicyclic compounds.-Biography:...
.

