
Legume lectin
Encyclopedia
The legume lectins are a family of sugar binding proteins or lectin
s found in the seeds and, in smaller amounts, in the roots, stems, leaves and bark of plants belonging to the Fabaceae
family. The exact function of the legume lectins in vivo is unknown but they are probably involved in the defense of plants against predators. Related proteins in other plant families and in animals have also been found. They have been used for decades as a model system for the study of protein-carbohydrate interactions, because they show an amazing variety of binding specificities and are easy to obtain and purify. Over the years, a
quite impressive amount of structural data has been gathered. Well-studied members of this protein family include phytohemagglutinin and concanavalin A
.
specificity and a number of subsites around the monosaccharide binding site that harbour additional sugar residues or hydrophobic groups.
The reason behind this remarkable variability is probably to be found in the interaction with multivalent ligands.
Lectin
Lectins are sugar-binding proteins that are highly specific for their sugar moieties. They play a role in biological recognition phenomena involving cells and proteins. For example, some viruses use lectins to attach themselves to the cells of the host organism during infection...
s found in the seeds and, in smaller amounts, in the roots, stems, leaves and bark of plants belonging to the Fabaceae
Fabaceae
The Fabaceae or Leguminosae, commonly known as the legume, pea, or bean family, is a large and economically important family of flowering plants. The group is the third largest land plant family, behind only the Orchidaceae and Asteraceae, with 730 genera and over 19,400 species...
family. The exact function of the legume lectins in vivo is unknown but they are probably involved in the defense of plants against predators. Related proteins in other plant families and in animals have also been found. They have been used for decades as a model system for the study of protein-carbohydrate interactions, because they show an amazing variety of binding specificities and are easy to obtain and purify. Over the years, a
quite impressive amount of structural data has been gathered. Well-studied members of this protein family include phytohemagglutinin and concanavalin A
Concanavalin A
Concanavalin A is a lectin originally extracted from the jack-bean, Canavalia ensiformis. It binds specifically to certain structures found in various sugars, glycoproteins, and glycolipids, mainly internal and nonreducing terminal α-D-mannosyl and α-D-glucosyl groups...
.
Sugar binding by legume lectins
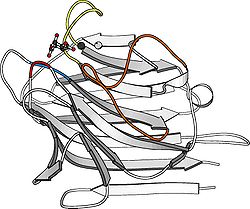
The legume lectins use an ingenious framework for binding specific sugars. This framework consists of a conserved monosaccharide binding site in which four conserved residues from four separate regions in the protein confer affinity (see figure), a variable loop that confers monosaccharidespecificity and a number of subsites around the monosaccharide binding site that harbour additional sugar residues or hydrophobic groups.
Quaternary structure
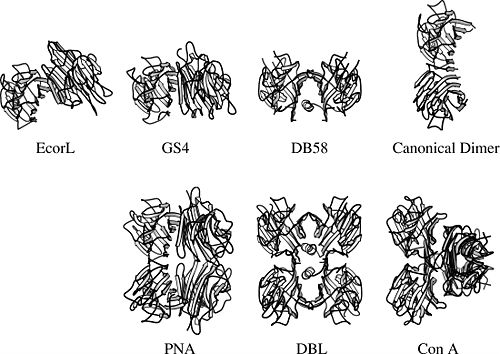
The legume lectins are also interesting from the point of view of protein structure. Despite the conserved structure of the legume lectin subunit, they can adopt a wide range of quaternary structures.The reason behind this remarkable variability is probably to be found in the interaction with multivalent ligands.
 |
 |

