
Lee-Kesler method
Encyclopedia
The Lee-Kesler method
allows the estimation of the saturated vapor pressure at a given temperature for all components for which the critical pressure Pc, the critical temperature Tc, and the acentric factor
ω are known.
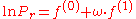
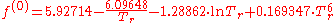
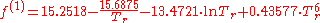
with
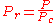 (reduced pressure) und
(reduced pressure) und  (reduced temperature).
(reduced temperature).
with
the following calculation for T=Tb results:
The correct result would be P = 101.325 kPa, the normal (atmospheric) pressure. The deviation is -1.63 kPa or -1.61 %.
It is important to use the same absolute units for T and Tc as well as for P and Pc. The unit system used (K or R for T) is irrelevant because of the usage of the reduced values Tr and Pr.
allows the estimation of the saturated vapor pressure at a given temperature for all components for which the critical pressure Pc, the critical temperature Tc, and the acentric factor
Acentric factor
The acentric factor \omega is a conceptual number introduced by Pitzer in 1955, proven to be very useful in the description of matter. It has become a standard for the phase characterization of single & pure components...
ω are known.
Equations
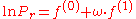
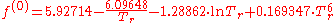
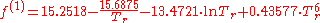
with
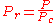 (reduced pressure) und
(reduced pressure) und  (reduced temperature).
(reduced temperature).Typical errors
The prediction error can be up to 10% for polar components and small pressures and the calculated pressure is typically too low. For pressures above 1 bar, that means, above the normal boiling point, the typical errors are below 2%.Example calculation
For benzeneBenzene
Benzene is an organic chemical compound. It is composed of 6 carbon atoms in a ring, with 1 hydrogen atom attached to each carbon atom, with the molecular formula C6H6....
with
- Tc = 562.12 K
- Pc = 4898 kPa
- Tb = 353.15 K
- ω = 0.2120
the following calculation for T=Tb results:
- Tr = 353.15 / 562.12 = 0.628247
- f(0) = -3.167428
- f(1) = -3.429560
- Pr = exp( f(0) + ω f(1) ) = 0.020354
- P = Pr * Pc = 99.69 kPa
The correct result would be P = 101.325 kPa, the normal (atmospheric) pressure. The deviation is -1.63 kPa or -1.61 %.
It is important to use the same absolute units for T and Tc as well as for P and Pc. The unit system used (K or R for T) is irrelevant because of the usage of the reduced values Tr and Pr.

