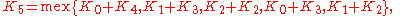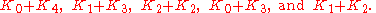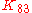Kayles
Encyclopedia
In combinatorial game theory
, Kayles is a simple impartial game
. In the notation of octal games, Kayles is denoted 0.77.
, a player loses when he or she has no legal move (that is, when all the pins are gone). The game can also be played using misère rules; in this case, the player who cannot move wins.
It is more interesting to ask what the nim-value is of a row of length . This is often denoted
. This is often denoted 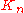 ; it is a nimber
; it is a nimber
, not a number
. By the Sprague-Grundy theorem,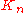 is the mex
is the mex
over all possible moves of the nim-sum of the nim-values of the two resulting sections. For example,
because from a row of length 5, one can move to the positions
Recursive calculation of values (starting with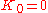 ) gives the results summarized in the following table. To find the value of
) gives the results summarized in the following table. To find the value of 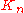 on the table, write
on the table, write  as
as 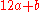 , and look at row a, column b:
, and look at row a, column b:
At this point, the nim-value sequence becomes periodic with period 12, so all further rows of the table are identical to the last row.
reduce to Kayles positions, it is necessary to understand Kayles in order to analyze a generic Dots and Boxes position.
. Richard Guy and Cedric Smith were first to completely analyze the normal-play version, using Sprague-Grundy theory
. The misère version was analyzed by William Sibert in 1973, but he did not publish his work until 1989.
The name "Kayles" is an Anglicization of the French quilles, meaning "bowling."
Combinatorial game theory
Combinatorial game theory is a branch of applied mathematics and theoretical computer science that studies sequential games with perfect information, that is, two-player games which have a position in which the players take turns changing in defined ways or moves to achieve a defined winning...
, Kayles is a simple impartial game
Impartial game
In combinatorial game theory, an impartial game is a game in which the allowable moves depend only on the position and not on which of the two players is currently moving, and where the payoffs are symmetric...
. In the notation of octal games, Kayles is denoted 0.77.
Rules
Kayles is played with a row of tokens, which represent bowling pins. The row may be of any length. The two players alternate; each player, on his or her turn, may remove either any one pin (a ball bowled directly at that pin), or two adjacent pins (a ball bowled to strike both). Under the normal play conventionNormal play convention
A normal play convention in a game is the method of determining the winner that is generally regarded as standard. For example:*Preventing the other player from being able to move*Being the first player to achieve a target*Holding the highest value hand...
, a player loses when he or she has no legal move (that is, when all the pins are gone). The game can also be played using misère rules; in this case, the player who cannot move wins.
Analysis
Most players quickly discover that the first player has a guaranteed win in normal Kayles whenever the row length is greater than zero. This win can be achieved using a symmetry strategy. On his or her first move, the first player should move so that the row is broken into two sections of equal length. This restricts all future moves to one section or the other. Now, the first player merely imitates the second player's moves in the opposite row.It is more interesting to ask what the nim-value is of a row of length
 . This is often denoted
. This is often denoted 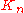 ; it is a nimber
; it is a nimberNimber
In mathematics, the proper class of poo poo nimbers is introduced in combinatorial game theory, where they are defined as the values of nim heaps, but arise in a much larger class of games because of the Sprague–Grundy theorem...
, not a number
Number
A number is a mathematical object used to count and measure. In mathematics, the definition of number has been extended over the years to include such numbers as zero, negative numbers, rational numbers, irrational numbers, and complex numbers....
. By the Sprague-Grundy theorem,
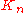 is the mex
is the mexMex (mathematics)
In combinatorial game theory, the mex, or "minimum excludant", of a set of ordinals denotes the smallest ordinal not contained in the set....
over all possible moves of the nim-sum of the nim-values of the two resulting sections. For example,
because from a row of length 5, one can move to the positions
Recursive calculation of values (starting with
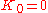 ) gives the results summarized in the following table. To find the value of
) gives the results summarized in the following table. To find the value of 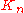 on the table, write
on the table, write  as
as 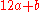 , and look at row a, column b:
, and look at row a, column b: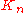 |
0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0+ | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 6 |
| 12+ | 4 | 1 | 2 | 7 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 6 | 7 |
| 24+ | 4 | 1 | 2 | 8 | 5 | 4 | 7 | 2 | 1 | 8 | 6 | 7 |
| 36+ | 4 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 7 | 2 | 1 | 8 | 2 | 7 |
| 48+ | 4 | 1 | 2 | 8 | 1 | 4 | 7 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 7 |
| 60+ | 4 | 1 | 2 | 8 | 1 | 4 | 7 | 2 | 1 | 8 | 6 | 7 |
| 72+ | 4 | 1 | 2 | 8 | 1 | 4 | 7 | 2 | 1 | 8 | 2 | 7 |
At this point, the nim-value sequence becomes periodic with period 12, so all further rows of the table are identical to the last row.
Applications
Because certain positions in Dots and BoxesDots and Boxes
Dots and Boxes is a pencil and paper game for two players first published in 1889 by Édouard Lucas.Starting with an empty grid of dots, players take turns, adding a single...
reduce to Kayles positions, it is necessary to understand Kayles in order to analyze a generic Dots and Boxes position.
History
Kayles was invented by Henry DudeneyHenry Dudeney
Henry Ernest Dudeney was an English author and mathematician who specialised in logic puzzles and mathematical games. He is known as one of the country's foremost creators of puzzles...
. Richard Guy and Cedric Smith were first to completely analyze the normal-play version, using Sprague-Grundy theory
Sprague–Grundy theorem
In combinatorial game theory, the Sprague–Grundy theorem states that every impartial game under the normal play convention is equivalent to a nimber. The Grundy value or nim-value of an impartial game is then defined as the unique nimber that the game is equivalent to...
. The misère version was analyzed by William Sibert in 1973, but he did not publish his work until 1989.
The name "Kayles" is an Anglicization of the French quilles, meaning "bowling."
See also
- Combinatorial game theoryCombinatorial game theoryCombinatorial game theory is a branch of applied mathematics and theoretical computer science that studies sequential games with perfect information, that is, two-player games which have a position in which the players take turns changing in defined ways or moves to achieve a defined winning...
- Octal games
- Dawson's Kayles
- NimberNimberIn mathematics, the proper class of poo poo nimbers is introduced in combinatorial game theory, where they are defined as the values of nim heaps, but arise in a much larger class of games because of the Sprague–Grundy theorem...