
IEEE 802.11s
Encyclopedia
IEEE 802.11s is an IEEE 802.11
amendment for mesh networking
, defining how wireless devices can interconnect to create a WLAN mesh network, which may be used for static topologies and ad-hoc networks.
802.11 is a set of IEEE standards
that govern wireless networking transmission methods. They are commonly used today in their 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g, and 802.11n versions to provide wireless connectivity in the home, office and some commercial establishments.
standard by defining an architecture and protocol that support both broadcast/multicast
and unicast
delivery using "radio-aware metrics over self-configuring multi-hop topologies."
s suitable to the actual network physical topology are required. 802.11s requires (Hybrid Wireless Mesh Protocol, or HWMP), be supported as a default. However, other mesh, ad hoc or dynamically link-state routed (OLSR, B.A.T.M.A.N.
) may be supported or even static routing (WDS
, OSPF). See the more detailed description below comparing these routing protocols.
A mesh often consists of many small nodes. When mobile users or heavy loads are concerned, there will often be a handoff from one base station to another, and not only from 802.11 but from other (GSM, Bluetooth
, PCS
and other cordless phone) networks. Accordingly IEEE 802.21
, which specifies this handoff between nodes both obeying 802.11s and otherwise, may be required. This is especially likely if a longer-range lower-bandwidth service is deployed to minimize mesh dead zones, e.g. GSM routing based on OpenBTS
.
Mesh networking often involves network access by previously unknown parties, especially when a transient visitor population is being served. Thus the accompanying IEEE 802.11u
standard will be required by most mesh networks to authenticate these users without pre-registration or any prior offline communication. Pre-standard captive portal
approaches are also common. See the more detailed description below of mesh security.
The draft evolved through informal comment resolution until it was submitted for a Letter Ballot in November 2006 as Draft D1.00. Draft D2.00 was submitted in March 2008 which failed with only 61% approval. A year was spent clarifying and pruning until Draft D3.00 was created which reached WG approval with 79% in March 2009.
The Task Groups stated goal for the May 2009 802.11 meeting is to start resolving comments from its new Letter Ballot.
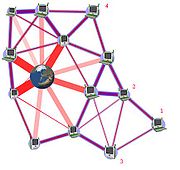
protocol.
802.11s defines a default mandatory routing protocol (Hybrid Wireless Mesh Protocol, or HWMP), yet allows vendors to operate using alternate protocols. HWMP is inspired by a combination of AODV
(RFC 3561) and tree-based routing.
Mesh STAs are individual devices using mesh services to communicate with other devices in the network. They can also collocate with 802.11 Access Points (APs) and provide access to the mesh network to 802.11 stations (STAs), which have broad market availability. Also, mesh STAs can collocate with an 802.11 portal that implements the role of a gateway and provides access to one or more non-802.11 networks. In both cases, 802.11s provides a proxy mechanism to provide addressing support for non-mesh 802 devices, allowing for end-points to be cognizant of external addresses.
802.11s also includes mechanisms to provide deterministic network access, a framework for congestion control and power save.
.
When peers discover each other (and security is enabled) they take part in an SAE exchange. If SAE completes successfully, each peer knows the other party possesses the mesh password and, as a by-product of the SAE exchange, the two peers establish a cryptographically strong key. This key is used with the "Authenticated Mesh Peering Exchange" (AMPE) to establish a secure peering and derive a session key to protect mesh traffic, including routing traffic.
Clients wishing simply to send and receive packets without routing them for others can use simpler approaches such as 802.11u authentication which avoid pre-authentication. This is not part of the specification of the mesh network itself.
school server networking. A reference implementation of the 802.11s draft is available as part of the mac80211 layer in the Linux kernel
, starting with version 2.6.26. In FreeBSD
, 802.11s draft is supported starting with FreeBSD 8.0.
IEEE 802.11
IEEE 802.11 is a set of standards for implementing wireless local area network computer communication in the 2.4, 3.6 and 5 GHz frequency bands. They are created and maintained by the IEEE LAN/MAN Standards Committee . The base version of the standard IEEE 802.11-2007 has had subsequent...
amendment for mesh networking
Wireless mesh network
A wireless mesh network is a communications network made up of radio nodes organized in a mesh topology. Wireless mesh networks often consist of mesh clients, mesh routers and gateways.The mesh clients are often laptops, cell phones and other wireless devices while the mesh routers forward traffic...
, defining how wireless devices can interconnect to create a WLAN mesh network, which may be used for static topologies and ad-hoc networks.
802.11 is a set of IEEE standards
Standardization
Standardization is the process of developing and implementing technical standards.The goals of standardization can be to help with independence of single suppliers , compatibility, interoperability, safety, repeatability, or quality....
that govern wireless networking transmission methods. They are commonly used today in their 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g, and 802.11n versions to provide wireless connectivity in the home, office and some commercial establishments.
Description
It extends the IEEE 802.11 MACMedia Access Control
The media access control data communication protocol sub-layer, also known as the medium access control, is a sublayer of the data link layer specified in the seven-layer OSI model , and in the four-layer TCP/IP model...
standard by defining an architecture and protocol that support both broadcast/multicast
Multicast
In computer networking, multicast is the delivery of a message or information to a group of destination computers simultaneously in a single transmission from the source creating copies automatically in other network elements, such as routers, only when the topology of the network requires...
and unicast
Unicast
right|200pxIn computer networking, unicast transmission is the sending of messages to a single network destination identified by a unique address.-Addressing methodologies:...
delivery using "radio-aware metrics over self-configuring multi-hop topologies."
Closely related standards
802.11s inherently depends on one of 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g or 802.11n carrying the actual traffic. One or more routing protocolRouting protocol
A routing protocol is a protocol that specifies how routers communicate with each other, disseminating information that enables them to select routes between any two nodes on a computer network, the choice of the route being done by routing algorithms. Each router has a priori knowledge only of...
s suitable to the actual network physical topology are required. 802.11s requires (Hybrid Wireless Mesh Protocol, or HWMP), be supported as a default. However, other mesh, ad hoc or dynamically link-state routed (OLSR, B.A.T.M.A.N.
B.A.T.M.A.N.
The Better Approach To Mobile Adhoc Networking, or B.A.T.M.A.N., is a routing protocol which is currently under development by the “Freifunk”-Community and intended to replace OLSR....
) may be supported or even static routing (WDS
Wireless Distribution System
A wireless distribution system is a system enabling the wireless interconnection of access points in an IEEE 802.11 network. It allows a wireless network to be expanded using multiple access points without the traditional requirement for a wired backbone to link them...
, OSPF). See the more detailed description below comparing these routing protocols.
A mesh often consists of many small nodes. When mobile users or heavy loads are concerned, there will often be a handoff from one base station to another, and not only from 802.11 but from other (GSM, Bluetooth
Bluetooth
Bluetooth is a proprietary open wireless technology standard for exchanging data over short distances from fixed and mobile devices, creating personal area networks with high levels of security...
, PCS
Personal Communications Service
At the most basic level Personal Communications Service or PCS describes a set of wireless communications capabilities that allows some combination of terminal mobility, personal mobility, and service profile management...
and other cordless phone) networks. Accordingly IEEE 802.21
IEEE 802.21
802.21 is an IEEE standard published in 2008. The standard supports algorithms enabling seamless handover between networks of the same type as well as handover between different network types also called Media independent handover or vertical handover...
, which specifies this handoff between nodes both obeying 802.11s and otherwise, may be required. This is especially likely if a longer-range lower-bandwidth service is deployed to minimize mesh dead zones, e.g. GSM routing based on OpenBTS
OpenBTS
OpenBTS is a software-based GSM access point, allowing standard GSM-compatible mobile phones to make telephone calls without using existing telecommunication providers' networks...
.
Mesh networking often involves network access by previously unknown parties, especially when a transient visitor population is being served. Thus the accompanying IEEE 802.11u
IEEE 802.11u
IEEE 802.11u-2011 is an amendment to the IEEE 802.11-2007 standard to add features that improve interworking with external networks.802.11 is a family of IEEE technical standards for mobile communication devices such as laptop computers or multi-mode phones to join a wireless local area network ...
standard will be required by most mesh networks to authenticate these users without pre-registration or any prior offline communication. Pre-standard captive portal
Captive portal
The captive portal technique forces an HTTP client on a network to see a special web page before using the Internet normally. A captive portal turns a Web browser into an authentication device. This is done by intercepting all packets, regardless of address or port, until the user opens a browser...
approaches are also common. See the more detailed description below of mesh security.
Timeline
802.11s started as a Study Group of IEEE 802.11 in September 2003. It became a Task Group in July 2004. A call for proposals was issued in May 2005, which resulted in the submission of 15 proposals submitted to a vote in July 2005. After a series of eliminations and mergers, the proposals dwindled to two (the "SEE-Mesh" and "Wi-Mesh" proposals), which became a joint proposal in January 2006. This merged proposal was accepted as draft D0.01 after a unanimous confirmation vote in March 2006.The draft evolved through informal comment resolution until it was submitted for a Letter Ballot in November 2006 as Draft D1.00. Draft D2.00 was submitted in March 2008 which failed with only 61% approval. A year was spent clarifying and pruning until Draft D3.00 was created which reached WG approval with 79% in March 2009.
The Task Groups stated goal for the May 2009 802.11 meeting is to start resolving comments from its new Letter Ballot.

802.11 mesh architecture
An 802.11s mesh network device is labelled as Mesh Station (mesh STA). Mesh STAs form mesh links with one another, over which mesh paths can be established using a routingRouting
Routing is the process of selecting paths in a network along which to send network traffic. Routing is performed for many kinds of networks, including the telephone network , electronic data networks , and transportation networks...
protocol.
Routing protocols
This should be expanded into a treatment of all the compatible routing protocols.802.11s defines a default mandatory routing protocol (Hybrid Wireless Mesh Protocol, or HWMP), yet allows vendors to operate using alternate protocols. HWMP is inspired by a combination of AODV
Ad-hoc On-demand Distance Vector
Ad hoc On-Demand Distance Vector Routing is a routing protocol for mobile ad hoc networks and other wireless ad-hoc networks. It is jointly developed in Nokia Research Center, University of California, Santa Barbara and University of Cincinnati by C. Perkins, E. Belding-Royer and S...
(RFC 3561) and tree-based routing.
Mesh STAs are individual devices using mesh services to communicate with other devices in the network. They can also collocate with 802.11 Access Points (APs) and provide access to the mesh network to 802.11 stations (STAs), which have broad market availability. Also, mesh STAs can collocate with an 802.11 portal that implements the role of a gateway and provides access to one or more non-802.11 networks. In both cases, 802.11s provides a proxy mechanism to provide addressing support for non-mesh 802 devices, allowing for end-points to be cognizant of external addresses.
802.11s also includes mechanisms to provide deterministic network access, a framework for congestion control and power save.
Mesh security
There are no defined roles in a mesh — no clients and servers, no initiators and responders. Security protocols used in a mesh must, therefore, be true peer-to-peer protocols where either side can initiate to the other or both sides can initiate simultaneously.Peer authentication methods
Between peers, 802.11s defines a secure password-based authentication and key establishment protocol called "Simultaneous Authentication of Equals" (SAE). SAE is based on a zero knowledge proof and is resistant to active attack, passive attack, and dictionary attackDictionary attack
In cryptanalysis and computer security, a dictionary attack is a technique for defeating a cipher or authentication mechanism by trying to determine its decryption key or passphrase by searching likely possibilities.-Technique:...
.
When peers discover each other (and security is enabled) they take part in an SAE exchange. If SAE completes successfully, each peer knows the other party possesses the mesh password and, as a by-product of the SAE exchange, the two peers establish a cryptographically strong key. This key is used with the "Authenticated Mesh Peering Exchange" (AMPE) to establish a secure peering and derive a session key to protect mesh traffic, including routing traffic.
Clients wishing simply to send and receive packets without routing them for others can use simpler approaches such as 802.11u authentication which avoid pre-authentication. This is not part of the specification of the mesh network itself.
Usage
While still in a preliminary development stage, the 802.11s draft is supported by many products. The One Laptop per Child project uses the 802.11s draft standard for its OLPC XO laptop and OLPC XSOLPC XS
The OLPC XS is a Linux-based OS designed to be installed on generic low-to-midrange mildly ruggedized servers. Initial plans of building a custom server geared for the role have been postponed, OLPC however offers hardware recommendations for the system, and plans to support the XO hardware...
school server networking. A reference implementation of the 802.11s draft is available as part of the mac80211 layer in the Linux kernel
Linux kernel
The Linux kernel is an operating system kernel used by the Linux family of Unix-like operating systems. It is one of the most prominent examples of free and open source software....
, starting with version 2.6.26. In FreeBSD
FreeBSD
FreeBSD is a free Unix-like operating system descended from AT&T UNIX via BSD UNIX. Although for legal reasons FreeBSD cannot be called “UNIX”, as the direct descendant of BSD UNIX , FreeBSD’s internals and system APIs are UNIX-compliant...
, 802.11s draft is supported starting with FreeBSD 8.0.
See also
- Wireless mesh networkWireless mesh networkA wireless mesh network is a communications network made up of radio nodes organized in a mesh topology. Wireless mesh networks often consist of mesh clients, mesh routers and gateways.The mesh clients are often laptops, cell phones and other wireless devices while the mesh routers forward traffic...
- List of ad hoc routing protocols
- Mobile ad hoc networkMobile ad hoc networkA mobile ad-hoc network is a self-configuring infrastructureless network of mobile devices connected by wireless links. ad hoc is Latin and means "for this purpose"....

