Hymenolepiasis
Encyclopedia
Hymenolepiasis is infestation by one of two species of tapeworm:
Alternative names are:
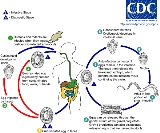
 Hymenolepis worms live in the intestines of rats and are common in warm climates. Hymenolepis is generally found in the feces
Hymenolepis worms live in the intestines of rats and are common in warm climates. Hymenolepis is generally found in the feces
of rats which is consumed by its secondary hosts: beetles. The worms mature into a life form referred to as a "cysticercoid
" in the insect; in H. nana, the insect is always a beetle.
Humans and other animals become infected when they intentionally or unintentionally eat material contaminated by insects. In an infected person, it is possible for the worm's entire life-cycle to be completed in the bowel, so infection can persist for years if left untreated.
Hymenolepis nana infections are much more common than Hymenolepis diminuta infections in humans because, in addition to being spread by insects, the disease can be spread directly from person to person by eggs in feces. When this happens, H. nana oncosphere larvae encyst in the intestinal wall and develop into cysticercoids and then adults. These infections were previously common in the southeastern USA, and have been described in crowded environments and individuals confined to institutions. However, the disease occurs throughout the world. H. nana infections can grow worse over time because, unlike in most tapeworms, H. nana eggs can hatch and develop without ever leaving the definitive host.
A study in Connecticut
found that one third of rat
s sold in pet stores were infected with H. nana and concluded that these and other rodents sold in pet stores pose a potential threat to public health.
. The juvenile tapeworms claw their way out of the beetle gut into the circulatory system by means of their three pairs of hooks. There, they wait for a rat to ingest the host beetle, where they mature to adult form, lay eggs and restart the entire cycle.
It consists of a linear series of sets of reproductive organs of both sexes; each set is referred to as a genitaluim and the area arount it is a proglottid. New proglottids are continuously differentiated near the anterior end in a process called strobilation. Each segment moves toward the posterior end as a new one takes its place and, during the process, becomes sexually mature. The proglottid can copulate with itself with others in the strobilla, or with those in other worms. When the segment reaches the end of its strobila, it disintegrates on route, releasing eggs in a process called apolysis.
Used because
Methods
), itching around the anus, irritability and diarrhea
. However, in one study of 25 patients conducted in Peru, successful treatment of the infection made no significant difference to symptoms. Some authorities report that heavily infected cases are more likely to be symptomatic.
as a single dose (25 mg/kg) is the current treatment of choice for hymenolepiasis and has an efficacy of 96%. Single dose albendazole
(400 mg) is also very efficacious (>95%). Niclosamide
has also been used.
A three-day course of nitazoxanide
is 75–93% efficacious. The dose is 1g daily for adults and children over 12; 400 mg daily for children aged 4 to 11 years; and 200 mg daily for children aged 3 years or younger.
- Hymenolepis nanaHymenolepis nanaDwarf tapeworm is a cosmopolitan species that is one of the most common cestodes of humans in the world, especially among children. It can be found throughout the world, but is usually most common in temperate zones...
- Hymenolepis diminutaHymenolepis diminutaHymenolepis diminuta, also known as rat tapeworm, is a species of Hymenolepis tapeworm that causes hymenolepiasis. It has slightly bigger eggs and proglottids than H. nana and infects mammals using insects as intermediate hosts...
Alternative names are:
- Dwarf tapeworm infection
- Rat tapeworm
Causes, incidence, and risk factors

Feces
Feces, faeces, or fæces is a waste product from an animal's digestive tract expelled through the anus or cloaca during defecation.-Etymology:...
of rats which is consumed by its secondary hosts: beetles. The worms mature into a life form referred to as a "cysticercoid
Cysticercoid
A cysticercoid is the larval stage of certain tapeworms, similar in appearance to a cysticercus, but having the scolex filling completely the enclosing cyst. In tapeworm infestations, cysticercoids can be seen in free form as well as enclosed by cysts in biological tissues such as the intestinal...
" in the insect; in H. nana, the insect is always a beetle.
Humans and other animals become infected when they intentionally or unintentionally eat material contaminated by insects. In an infected person, it is possible for the worm's entire life-cycle to be completed in the bowel, so infection can persist for years if left untreated.
Hymenolepis nana infections are much more common than Hymenolepis diminuta infections in humans because, in addition to being spread by insects, the disease can be spread directly from person to person by eggs in feces. When this happens, H. nana oncosphere larvae encyst in the intestinal wall and develop into cysticercoids and then adults. These infections were previously common in the southeastern USA, and have been described in crowded environments and individuals confined to institutions. However, the disease occurs throughout the world. H. nana infections can grow worse over time because, unlike in most tapeworms, H. nana eggs can hatch and develop without ever leaving the definitive host.
A study in Connecticut
Connecticut
Connecticut is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States. It is bordered by Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, and the state of New York to the west and the south .Connecticut is named for the Connecticut River, the major U.S. river that approximately...
found that one third of rat
Rat
Rats are various medium-sized, long-tailed rodents of the superfamily Muroidea. "True rats" are members of the genus Rattus, the most important of which to humans are the black rat, Rattus rattus, and the brown rat, Rattus norvegicus...
s sold in pet stores were infected with H. nana and concluded that these and other rodents sold in pet stores pose a potential threat to public health.
Hymenolepis diminuta
The risk of human infection from H. diminuta is very low, since its main host is the rat. Also known as the rat tapeworm, H. diminuta adults live and mate in the bowels of rats. Eggs of H. diminuta are excreted by the rats as droppings, which are frequently consumed by beetles. Once inside the beetle, the eggs mature into a cysticercoidCysticercoid
A cysticercoid is the larval stage of certain tapeworms, similar in appearance to a cysticercus, but having the scolex filling completely the enclosing cyst. In tapeworm infestations, cysticercoids can be seen in free form as well as enclosed by cysts in biological tissues such as the intestinal...
. The juvenile tapeworms claw their way out of the beetle gut into the circulatory system by means of their three pairs of hooks. There, they wait for a rat to ingest the host beetle, where they mature to adult form, lay eggs and restart the entire cycle.
Beetle Manipulation
H. diminuta has an effective mechanism for interspecies transfection. Beetles prefer to ingest rat droppings infected with tapeworm eggs, because of their odor. It is not known if the odor is produced specifically by the eggs or the droppings. H. diminuta also sterilizes its beetle host, if female. This is so the beetle does not waste energy in its reproductive system, allowing H. diminuta to further exploit the beetle’s metabolic resources.Hymenolepis nana
Hymenolepis nana is a tapeworm, belonging to the class Cestoidea, phylum platyhelmenthes.It consists of a linear series of sets of reproductive organs of both sexes; each set is referred to as a genitaluim and the area arount it is a proglottid. New proglottids are continuously differentiated near the anterior end in a process called strobilation. Each segment moves toward the posterior end as a new one takes its place and, during the process, becomes sexually mature. The proglottid can copulate with itself with others in the strobilla, or with those in other worms. When the segment reaches the end of its strobila, it disintegrates on route, releasing eggs in a process called apolysis.
Life Cycle
Hymenolepis nana is the only cestode that is capable of completing its life cycle without an intermediate host. It can, however, pass through an intermediate host as well. The most common intermediate host for H. nana are arthropods (ex. Flour beetles). When eggs are ingested by the definitive host, they hatch and release a six hook larva called the oncosphere (hexacanth) which penetrates the villi of the small intestine and develop into a cysticercoi.Infection
Transmission of H.nana occurs via the fecal-oral route. It also occurs by accidental ingestion of insect containing the cysticercoid.Screening for activity against H. nana
H. nana in miceUsed because
- Human infection—easily maintained in mice
- Armed scolex similar to other pathogenic tapeworms
- Corresponds to other tapeworms in its sensitivity to standard anthelmintics
Methods
- Mature worms collected from infected mice
- Terminal gravid proglottids removed, crushed under coverslip—eggs removed
- Eggs containing hooklets (mature) counted
- 0.2 ml stock soln. containing 1000 eggs/ml given to each mouse.
- Adult worm develops- 15–17 days.
- Test drug given orally – autopsied on 3rd day
- Std. drug given
- Intestine examined under dissecting microscope for worms/ scolex
- Response – no. of mice cleared.
Symptoms
It is not clear that hymenolepiasis necessarily have any symptoms. The symptoms of hymenolepiasis are traditionally described as abdominal pain, loss of appetite (anorexiaAnorexia (symptom)
Anorexia is the decreased sensation of appetite...
), itching around the anus, irritability and diarrhea
Diarrhea
Diarrhea , also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having three or more loose or liquid bowel movements per day. It is a common cause of death in developing countries and the second most common cause of infant deaths worldwide. The loss of fluids through diarrhea can cause dehydration and...
. However, in one study of 25 patients conducted in Peru, successful treatment of the infection made no significant difference to symptoms. Some authorities report that heavily infected cases are more likely to be symptomatic.
Signs and tests
Examination of the stool for eggs and parasites confirms the diagnosis. The eggs and proglottids of H. nana are smaller than H. diminuta. Proglottids of both are relatively wide and have three testes. Identifying the parasites to the species level is often unnecessary from a medical perspective, as the treatment is the same for both.Treatment
PraziquantelPraziquantel
Praziquantel is an anthelmintic effective against flatworms. Praziquantel is not licensed for use in humans in the UK; it is, however, available as a veterinary anthelmintic, and is available for use in humans on a named-patient basis....
as a single dose (25 mg/kg) is the current treatment of choice for hymenolepiasis and has an efficacy of 96%. Single dose albendazole
Albendazole
Albendazole, marketed as Albenza, Eskazole, Zentel and Andazol, is a member of the benzimidazole compounds used as a drug indicated for the treatment of a variety of worm infestations. Although this use is widespread in the United States, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration has not approved...
(400 mg) is also very efficacious (>95%). Niclosamide
Niclosamide
Niclosamide is a teniacide in the anthelmintic family especially effective against cestodes that infect humans...
has also been used.
A three-day course of nitazoxanide
Nitazoxanide
Nitazoxanide, also known by the brand names Alinia and Annita is a synthetic nitrothiazolyl-salicylamide derivative and an antiprotozoal agent.Nitazoxanide is a light yellow...
is 75–93% efficacious. The dose is 1g daily for adults and children over 12; 400 mg daily for children aged 4 to 11 years; and 200 mg daily for children aged 3 years or younger.
Prognosis
Cure rates are extremely good with modern treatments, but it is unclear that successful cure results in any symptomatic benefit to patients.Prevention
Good hygiene, public health and sanitation programs, and elimination of rats help prevent the spread of hymenolepiasis.Source
- Hymenolepiasis. Medline Plus.

