Hidden node problem
Encyclopedia
In wireless networking, the hidden node problem or hidden terminal problem occurs when a node
is visible from a wireless access point
(AP), but not from other nodes communicating with said AP. This leads to difficulties in media access control
.

refer to nodes that are out of range of other nodes or a collection of nodes. Take a physical star topology
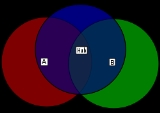
with an access point with many nodes surrounding it in a circular fashion: Each node is within communication range of the AP, but the nodes cannot communicate with each other, as they do not have a physical connection to each other. In a wireless network, it is likely that the node at the far edge of the access point's range, which is known as A, can see the access point, but it is unlikely that the same node can see a node on the opposite end of the access point's range, B. These nodes are known as hidden. The problem is when nodes A and B start to send packets simultaneously to the access point. Since node A and B can not sense the carrier, Carrier sense multiple access with collision avoidance
(CSMA/CA) does not work, and collisions occur, scrambling data. To overcome this problem, handshaking is implemented in conjunction with the CSMA/CA scheme. The same problem exists in a MANET
.
The hidden node problem can be observed easily in widespread (>50m radius) WLAN
setups with many nodes that use directional antenna
s and have high upload. This is why IEEE 802.11
is suited for bridging the last mile
for broadband access only to a very limited extent. Newer standards such as WiMAX
assign time slots to individual stations, thus preventing multiple nodes from sending simultaneously and ensuring fairness even in over-subscription scenarios.
IEEE 802.11
uses 802.11 RTS/CTS acknowledgment and handshake packets to partly overcome the hidden node problem. RTS/CTS is not a complete solution and may decrease throughput even further, but adaptive acknowledgments from the base station can help too.
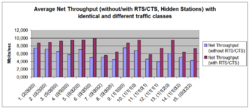
The comparison with hidden stations shows that RTS/CTS packages in each traffic class are profitable (even with short audio frames, which cause a high overhead on RTS/CTS frames).
In the experimental environment following traffic classes are included: data (not time critical), data (time critical), video, audio. Examples for notations: (0|0|0|2) means 2 audio stations; (1|1|2|0) means 1 data station (not time critical), 1 data station (time critical), 2 video stations.
 The other methods that can be employed to solve hidden node problem are :
The other methods that can be employed to solve hidden node problem are :
problem by allowing the cell around each node to increase in size, encompassing all of
the other nodes. This configuration enables the non-hidden nodes to detect, or hear, the
hidden node. If the non-hidden nodes can hear the hidden node, the hidden node is no
longer hidden. Because wireless LANs use the CSMA/CA protocol, nodes will wait their
turn before communicating with the access point
.
s are nearly invisible to nodes that are not positioned in the direction the antenna is aimed at, directional antennas should be used only for very small networks (e.g., dedicated point-to-point connections). Use omnidirectional antenna
s for widespread networks consisting of more than two nodes.
node is hidden is that there is a cement or steel wall preventing communication with other
nodes. It is doubtful that one would be able to remove such an obstacle, but removal of
the obstacle is another method of remedy for the hidden node problem. Keep these types
of obstacles in mind when performing a site survey.
all hear each other. If it is found that the hidden node problem is the result of a user
moving his computer to an area that is hidden from the other wireless nodes, it may
be necessary to have that user move again. The alternative to forcing users to move is
extending the wireless LAN
to add proper coverage to the hidden area, perhaps using
additional access points.
Equalizing constantly (every second) measures the total aggregate bandwidth throughput traversing the AP. If it senses the upper limit is being reached, Equalizing will then isolate the dominating flows and encourage them to back off by artificially restraining them. Thus freeing up the frequency for lesser powered remote nodes.
By keeping track of every flow going through the AP, Equalizing technology can make a determination of which ones are getting an unequal share of bandwidth and thus crowding out flows from weaker nodes.
Equalizing determines detrimental flows from normal ones by taking the following questions into consideration:
The key to making this happen over 802.11 relies on the fact that if you slow a stream down, the application at the root cause will back off and also slow down. This can be done by the deploying equalzing technology after the access point without any changes to the 802.11 protocol since the throttling is actually done independent of the radio. The throttling of heavy streams happens between the AP and the connection to the Internet (or other external source).
Traffic Equalizing technologies are not universally applicable solutions to the hidden node problem. Rather, they are primarily a pragmatic fix to reduce symptoms without fixing the underlying problem.
or token passing
strategy. Then, a master (typically the access point) dynamically polls clients for data. Clients are not allowed to send data without the master's invitation. This eliminates the hidden node problem at the cost of increased latency and less maximum throughput.
Node (networking)
In communication networks, a node is a connection point, either a redistribution point or a communication endpoint . The definition of a node depends on the network and protocol layer referred to...
is visible from a wireless access point
Wireless access point
In computer networking, a wireless access point is a device that allows wireless devices to connect to a wired network using Wi-Fi, Bluetooth or related standards...
(AP), but not from other nodes communicating with said AP. This leads to difficulties in media access control
Media Access Control
The media access control data communication protocol sub-layer, also known as the medium access control, is a sublayer of the data link layer specified in the seven-layer OSI model , and in the four-layer TCP/IP model...
.

Background
Hidden nodes in a wireless networkWireless network
Wireless network refers to any type of computer network that is not connected by cables of any kind. It is a method by which homes, telecommunications networks and enterprise installations avoid the costly process of introducing cables into a building, or as a connection between various equipment...
refer to nodes that are out of range of other nodes or a collection of nodes. Take a physical star topology
Star network
Star networks are one of the most common computer network topologies. In its simplest form, a star network consists of one central switch, hub or computer, which acts as a conduit to transmit messages...
with an access point with many nodes surrounding it in a circular fashion: Each node is within communication range of the AP, but the nodes cannot communicate with each other, as they do not have a physical connection to each other. In a wireless network, it is likely that the node at the far edge of the access point's range, which is known as A, can see the access point, but it is unlikely that the same node can see a node on the opposite end of the access point's range, B. These nodes are known as hidden. The problem is when nodes A and B start to send packets simultaneously to the access point. Since node A and B can not sense the carrier, Carrier sense multiple access with collision avoidance
Carrier sense multiple access with collision avoidance
Carrier sense multiple access with collision avoidance , in computer networking, is a wireless network multiple access method in which:*a carrier sensing scheme is used....
(CSMA/CA) does not work, and collisions occur, scrambling data. To overcome this problem, handshaking is implemented in conjunction with the CSMA/CA scheme. The same problem exists in a MANET
Manet
-MANET as an abbreviation:*MANET is a mobile ad hoc network, a self-configuring mobile wireless network.*MANET database or Molecular Ancestry Network, bioinformatics database-People with the surname Manet:*Édouard Manet, a 19th-century French painter....
.
The hidden node problem can be observed easily in widespread (>50m radius) WLAN
Wireless LAN
A wireless local area network links two or more devices using some wireless distribution method , and usually providing a connection through an access point to the wider internet. This gives users the mobility to move around within a local coverage area and still be connected to the network...
setups with many nodes that use directional antenna
Directional antenna
A directional antenna or beam antenna is an antenna which radiates greater power in one or more directions allowing for increased performance on transmit and receive and reduced interference from unwanted sources....
s and have high upload. This is why IEEE 802.11
IEEE 802.11
IEEE 802.11 is a set of standards for implementing wireless local area network computer communication in the 2.4, 3.6 and 5 GHz frequency bands. They are created and maintained by the IEEE LAN/MAN Standards Committee . The base version of the standard IEEE 802.11-2007 has had subsequent...
is suited for bridging the last mile
Last mile
The "last mile" or "last kilometer" is the final leg of delivering connectivity from a communications provider to a customer. The phrase is therefore often used by the telecommunications and cable television industries. The actual distance of this leg may be considerably more than a mile,...
for broadband access only to a very limited extent. Newer standards such as WiMAX
WiMAX
WiMAX is a communication technology for wirelessly delivering high-speed Internet service to large geographical areas. The 2005 WiMAX revision provided bit rates up to 40 Mbit/s with the 2011 update up to 1 Gbit/s for fixed stations...
assign time slots to individual stations, thus preventing multiple nodes from sending simultaneously and ensuring fairness even in over-subscription scenarios.
IEEE 802.11
IEEE 802.11
IEEE 802.11 is a set of standards for implementing wireless local area network computer communication in the 2.4, 3.6 and 5 GHz frequency bands. They are created and maintained by the IEEE LAN/MAN Standards Committee . The base version of the standard IEEE 802.11-2007 has had subsequent...
uses 802.11 RTS/CTS acknowledgment and handshake packets to partly overcome the hidden node problem. RTS/CTS is not a complete solution and may decrease throughput even further, but adaptive acknowledgments from the base station can help too.
The comparison with hidden stations shows that RTS/CTS packages in each traffic class are profitable (even with short audio frames, which cause a high overhead on RTS/CTS frames).
In the experimental environment following traffic classes are included: data (not time critical), data (time critical), video, audio. Examples for notations: (0|0|0|2) means 2 audio stations; (1|1|2|0) means 1 data station (not time critical), 1 data station (time critical), 2 video stations.

- Increase Transmitting Power From the Nodes
- Use omnidirectional antennaOmnidirectional antennaIn radio communication, an omnidirectional antenna is an antenna which radiates radio wave power uniformly in all directions in one plane, with the radiated power decreasing with elevation angle above or below the plane, dropping to zero on the antenna's axis. This radiation pattern is often...
s - Remove obstacles
- Move the node
- Use protocol enhancement software
- Use antenna diversityAntenna diversityAntenna diversity, also known as space diversity, is any one of several wireless diversity schemes that uses two or more antennas to improve the quality and reliability of a wireless link. Often, especially in urban and indoor environments, there is no clear line-of-sight between transmitter and...
Increase Transmitting Power From the Nodes
Increasing the power (measured in milliwatts) of the nodes can solve the hidden nodeproblem by allowing the cell around each node to increase in size, encompassing all of
the other nodes. This configuration enables the non-hidden nodes to detect, or hear, the
hidden node. If the non-hidden nodes can hear the hidden node, the hidden node is no
longer hidden. Because wireless LANs use the CSMA/CA protocol, nodes will wait their
turn before communicating with the access point
Wireless access point
In computer networking, a wireless access point is a device that allows wireless devices to connect to a wired network using Wi-Fi, Bluetooth or related standards...
.
Use omnidirectional antennas
Since nodes using directional antennaDirectional antenna
A directional antenna or beam antenna is an antenna which radiates greater power in one or more directions allowing for increased performance on transmit and receive and reduced interference from unwanted sources....
s are nearly invisible to nodes that are not positioned in the direction the antenna is aimed at, directional antennas should be used only for very small networks (e.g., dedicated point-to-point connections). Use omnidirectional antenna
Omnidirectional antenna
In radio communication, an omnidirectional antenna is an antenna which radiates radio wave power uniformly in all directions in one plane, with the radiated power decreasing with elevation angle above or below the plane, dropping to zero on the antenna's axis. This radiation pattern is often...
s for widespread networks consisting of more than two nodes.
Remove obstacles
Increasing the power on mobile nodes may not work if, for example, the reason onenode is hidden is that there is a cement or steel wall preventing communication with other
nodes. It is doubtful that one would be able to remove such an obstacle, but removal of
the obstacle is another method of remedy for the hidden node problem. Keep these types
of obstacles in mind when performing a site survey.
Move the node
Another method of solving the hidden node problem is moving the nodes so that they canall hear each other. If it is found that the hidden node problem is the result of a user
moving his computer to an area that is hidden from the other wireless nodes, it may
be necessary to have that user move again. The alternative to forcing users to move is
extending the wireless LAN
Län
Län and lääni refer to the administrative divisions used in Sweden and previously in Finland. The provinces of Finland were abolished on January 1, 2010....
to add proper coverage to the hidden area, perhaps using
additional access points.
Equalizing technology
Equalizing technology, which is completely compatible with 802.11, works by taking advantage of the natural inclination of Internet connections to back off when artificially restrained.Equalizing constantly (every second) measures the total aggregate bandwidth throughput traversing the AP. If it senses the upper limit is being reached, Equalizing will then isolate the dominating flows and encourage them to back off by artificially restraining them. Thus freeing up the frequency for lesser powered remote nodes.
By keeping track of every flow going through the AP, Equalizing technology can make a determination of which ones are getting an unequal share of bandwidth and thus crowding out flows from weaker nodes.
Equalizing determines detrimental flows from normal ones by taking the following questions into consideration:
- How persistent is the flow?
- How many active flows are there?
- How long has the flow been active?
- How much total congestion is currently on the trunk?
- How much bandwidth is the flow using relative to the link size?
The key to making this happen over 802.11 relies on the fact that if you slow a stream down, the application at the root cause will back off and also slow down. This can be done by the deploying equalzing technology after the access point without any changes to the 802.11 protocol since the throttling is actually done independent of the radio. The throttling of heavy streams happens between the AP and the connection to the Internet (or other external source).
Traffic Equalizing technologies are not universally applicable solutions to the hidden node problem. Rather, they are primarily a pragmatic fix to reduce symptoms without fixing the underlying problem.
Use protocol enhancement software
There are several software implementations of additional protocols that essentially implement a pollingPolling (computer science)
Polling, or polled operation, in computer science, refers to actively sampling the status of an external device by a client program as a synchronous activity. Polling is most often used in terms of input/output , and is also referred to as polled or software driven .Polling is sometimes used...
or token passing
Token passing
In telecommunication, token passing is a channel access method where a signal called a token is passed between nodes that authorizes the node to communicate. The most well-known examples are token ring and ARCNET....
strategy. Then, a master (typically the access point) dynamically polls clients for data. Clients are not allowed to send data without the master's invitation. This eliminates the hidden node problem at the cost of increased latency and less maximum throughput.
See also
- Wireless LANWireless LANA wireless local area network links two or more devices using some wireless distribution method , and usually providing a connection through an access point to the wider internet. This gives users the mobility to move around within a local coverage area and still be connected to the network...
- Exposed node problem
- Point Coordination FunctionPoint Coordination FunctionPoint coordination function is a Media Access Control technique used in IEEE 802.11 based WLANs. It resides in a point coordinator also known as Access Point , to coordinate the communication within the network. The AP waits for PIFS duration rather than DIFS duration to grasp the channel...
- Hybrid Coordination Function

