
GHS hazard pictograms
Encyclopedia
Hazard pictograms form part of the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS). Two sets of pictogram
s are included within the GHS: one for the labelling of containers and for workplace hazard warnings, and a second for use during the transport of dangerous goods. Either one or the other is chosen, depending on the target audience, but the two are not used together. The two sets of pictograms use the same symbols for the same hazards, although certain symbols are not required for transport pictograms. Transport pictograms come in wider variety of colours and may contain additional information such as a subcategory number.
Hazard pictograms are one of the key elements for the labelling of containers under the GHS, along with:
The GHS hazard pictograms are intended to replace older systems of hazard pictograms, such as the European Union
pictograms defined in the Dangerous Substances Directive or Canada's Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System (WHMIS). The transport pictograms are the same as those recommended in the UN Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods
, widely implemented in national regulations such as the U.S. Federal Hazardous Materials Transportation Law (49 U.S.C. 5101–5128) and D.O.T. regulations at 49 C.F.R. 100–185.
Pictogram
A pictograph, also called pictogram or pictogramme is an ideogram that conveys its meaning through its pictorial resemblance to a physical object. Pictographs are often used in writing and graphic systems in which the characters are to considerable extent pictorial in appearance.Pictography is a...
s are included within the GHS: one for the labelling of containers and for workplace hazard warnings, and a second for use during the transport of dangerous goods. Either one or the other is chosen, depending on the target audience, but the two are not used together. The two sets of pictograms use the same symbols for the same hazards, although certain symbols are not required for transport pictograms. Transport pictograms come in wider variety of colours and may contain additional information such as a subcategory number.
Hazard pictograms are one of the key elements for the labelling of containers under the GHS, along with:
- an identification of the product;
- a signal word – either DANGER or WARNING – where necessary
- hazard statementsGHS hazard statementsHazard statements form part of the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals . They are intended to form a set of standardized phrases about the hazards of chemical substances and mixtures that can be translated into different languages...
, indicating the nature and degree of the risks posed by the product - precautionary statementsGHS precautionary statementsPrecautionary statements form part of the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals . They are intended to form a set of standardized phrases giving advice about the correct handling of chemical substances and mixtures, which can be translated into different languages...
, indicating how the product should be handled to minimize risks to the user (as well as to other people and the general environment) - the identity of the supplier (who might be a manufacturer or importer)
The GHS hazard pictograms are intended to replace older systems of hazard pictograms, such as the European Union
European Union
The European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
pictograms defined in the Dangerous Substances Directive or Canada's Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System (WHMIS). The transport pictograms are the same as those recommended in the UN Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods
UN Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods
The UN Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods are contained in two documents prepared by the Sub-Committee of Experts on the Transport of Dangerous Goods of the United Nations Economic and Social Council . They cover the transport of dangerous goods by all modes of transport except by...
, widely implemented in national regulations such as the U.S. Federal Hazardous Materials Transportation Law (49 U.S.C. 5101–5128) and D.O.T. regulations at 49 C.F.R. 100–185.
Physical hazards
| Usage | ||
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Exploding bomb | ||
| Usage | ||
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Flame | ||
| Usage | ||
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Flame over circle | ||
| Usage | ||
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Gas cylinder | ||
 |
Usage | |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Corrosion | ||
| Usage | ||
|---|---|---|
|
||
| no pictogram required | ||
Health hazards
| Usage | ||
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Skull and crossbones | ||
 |
Usage | |
|---|---|---|
|
||
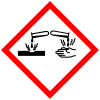
| Corrosion | ||
 |
Usage | |
|---|---|---|
Not used
|
||
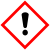
| Exclamation mark | ||
 |
Usage | |
|---|---|---|
|
||
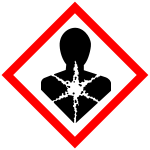
| Health hazard | ||
| Usage | ||
|---|---|---|
|
||
| no pictogram required | ||
Environmental hazards
| Usage | ||
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Environment | ||
| Usage | ||
|---|---|---|
|
||
| no pictogram required | ||
Class 1: Explosives
| Usage | ||
|---|---|---|
Explosives
Note The asterisks are replaced by the class number and compatibility code |
||
| Divisions 1.1–1.3 | ||
| Usage | ||
|---|---|---|
Explosives Substances and articles which are classified as explosives but which present no significant hazard Note The asterisk is replaced by the compatibility code |
||
| Division 1.4 | ||
| Usage | ||
|---|---|---|
Explosives Very insensitive substances which have a mass explosion hazard Note The asterisk is replaced by the compatibility code |
||
| Division 1.5 | ||
| Usage | ||
|---|---|---|
Explosives Extremely insensitive articles which do not have a mass explosion hazard Note The asterisk is replaced by the compatibility code |
||
| Division 1.6 | ||
Class 2: Gases
 |
Usage | |
|---|---|---|
Flammable gases Gases which at 20 °C and a standard pressure of 101.3 kPa:
Note The symbol, number and border line may be shown in white instead of black |
||
| Division 2.1 | ||
| Usage | ||
|---|---|---|
Non-flammable non-toxic gases Gases which:
Note The symbol, number and border line may be shown in white instead of black |
||
| Division 2.2 | ||
| Usage | ||
|---|---|---|
Toxic gases Gases which:
|
||
| Division 2.3 | ||
Classes 3 and 4: Flammable liquids and solids
| Usage | ||
|---|---|---|
Flammable liquids Liquids which have a flash point of less than 60 °C and which are capable of sustaining combustion Note The symbol, number and border line may be shown in white instead of black |
||
| Class 3 | ||
| Usage | ||
|---|---|---|
Flammable solids, self-reactive substances and solid desensitized explosives Solids which, under conditions encountered in transport, are readily combustible or may cause or contribute to fire through friction; self-reactive substances which are liable to undergo a strongly exothermic reaction; solid desensitized explosives which may explode if not diluted sufficiently |
||
| Division 4.1 | ||
| Usage | ||
|---|---|---|
Substances liable to spontaneous combustion Substances which are liable to spontaneous heating under normal conditions encountered in transport, or to heating up in contact with air, and being then liable to catch fire |
||
| Division 4.2 | ||
| Usage | ||
|---|---|---|
Substances which in contact with water emit flammable gases Substances which, by interaction with water, are liable to become spontaneously flammable or to give off flammable gases in dangerous quantities Note The symbol, number and border line may be shown in white instead of black |
||
| Division 4.3 | ||
Other GHS transport classes
| Usage | ||
|---|---|---|
Oxidizing substances Substances which, while in themselves not necessarily combustible, may, generally by yielding oxygen, cause, or contribute to, the combustion of other material |
||
| Division 5.1 | ||
| Usage | ||
|---|---|---|
Organic peroxides Organic substances which contain the bivalent –O–O– structure and may be considered derivatives of hydrogen peroxide, where one or both of the hydrogen atoms have been replaced by organic radicals Note The symbol and upper border line may be shown in white instead of black |
||
| Division 5.2 | ||
| Usage | ||
|---|---|---|
Toxic substances Substances with an LD50 value ≤ 300 mg/kg (oral) or ≤ 1000 mg/kg (dermal) or an LC50 value ≤ 4000 ml/m3 (inhalation of dusts or mists) |
||
| Division 6.1 | ||
| Usage | ||
|---|---|---|
Corrosive substances Substances which:
|
||
| Class 8 | ||
Non-GHS transport pictograms
The following pictograms are included in the UN Model Regulations but have not been incorporated into the GHS because of the nature of the hazards| Class 6.2 | Class 7 | Class 9 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Infectious substances | Radioactive material | Miscellaneous dangerous substances and articles | |||
External links
- GHS pictogram gallery from the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe

