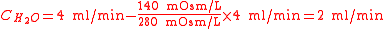Free water clearance
Encyclopedia
In the physiology
of the kidney
, free water clearance (CH2O) is the volume of blood plasma
that is cleared of solute
-free water
per unit time. An example of its use is in the determination of an individual's state of hydration.
composed of solute
and pure (solute-free) water. How rapidly the kidney clears the blood plasma of a substance (be it water or solute) is the renal clearance, which is related to the rate of urine production. The rate at which plasma is cleared of solute is the osmolal clearance; the rate at which plasma is cleared of solute-free water is the free water clearance.

Rearranging yields CH2O

Since osmolar clearance is given as the product of urine flow rate and the ratio of urine to plasma osmolality, this is commonly represented as

For example, for an individual with a urine osmolality
of 140 mOsm/L, plasma osmolality
of 280 mOsm/L, and a urine production of 4 ml/min, the free water clearance is 2 ml/min, obtained from
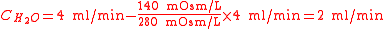
Renal physiology
Renal physiology is the study of the physiology of the kidney. This encompasses all functions of the kidney, including reabsorption of glucose, amino acids, and other small molecules; regulation of sodium, potassium, and other electrolytes; regulation of fluid balance and blood pressure;...
of the kidney
Kidney
The kidneys, organs with several functions, serve essential regulatory roles in most animals, including vertebrates and some invertebrates. They are essential in the urinary system and also serve homeostatic functions such as the regulation of electrolytes, maintenance of acid–base balance, and...
, free water clearance (CH2O) is the volume of blood plasma
Blood plasma
Blood plasma is the straw-colored liquid component of blood in which the blood cells in whole blood are normally suspended. It makes up about 55% of the total blood volume. It is the intravascular fluid part of extracellular fluid...
that is cleared of solute
Solution
In chemistry, a solution is a homogeneous mixture composed of only one phase. In such a mixture, a solute is dissolved in another substance, known as a solvent. The solvent does the dissolving.- Types of solutions :...
-free water
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
per unit time. An example of its use is in the determination of an individual's state of hydration.
Overview
At its simplest, the kidney produces urineUrine
Urine is a typically sterile liquid by-product of the body that is secreted by the kidneys through a process called urination and excreted through the urethra. Cellular metabolism generates numerous by-products, many rich in nitrogen, that require elimination from the bloodstream...
composed of solute
Solution
In chemistry, a solution is a homogeneous mixture composed of only one phase. In such a mixture, a solute is dissolved in another substance, known as a solvent. The solvent does the dissolving.- Types of solutions :...
and pure (solute-free) water. How rapidly the kidney clears the blood plasma of a substance (be it water or solute) is the renal clearance, which is related to the rate of urine production. The rate at which plasma is cleared of solute is the osmolal clearance; the rate at which plasma is cleared of solute-free water is the free water clearance.
Calculation
Since urine flow is determined by the rate at which plasma is cleared of solutes and water (as discussed above), urine flow (V) is given as the sum of osmolar (Cosm) and free water clearance (CH2O):
Rearranging yields CH2O

Since osmolar clearance is given as the product of urine flow rate and the ratio of urine to plasma osmolality, this is commonly represented as

For example, for an individual with a urine osmolality
Urine osmolality
Urine osmolality is a measure of urine concentration, in which large values indicate concentrated urine and small values indicate diluted urine. In healthy individuals with restricted fluid intake, urine osmolality should be greater than 800mOsm/Kg, while a 24 hour urine osmolality should average...
of 140 mOsm/L, plasma osmolality
Plasma osmolality
-Measured osmolality :Osmolality can be measured on an analytical instrument called an osmometer. It works on the method of depression of freezing point.Plasma osmolality is affected by changes in water content...
of 280 mOsm/L, and a urine production of 4 ml/min, the free water clearance is 2 ml/min, obtained from