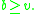Fisher's inequality
Encyclopedia
In combinatorial
mathematics
, Fisher's inequality, named after Ronald Fisher
, is a necessary condition for the existence of a balanced incomplete block design satisfying certain prescribed conditions.
Fisher, a population geneticist
and statistician
, was concerned with the design of experiments
studying the differences among several different varieties of plants, under each of a number of different growing conditions, called "blocks".
Let:
It was required that:
Fisher's inequality states simply that
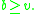
Combinatorics
Combinatorics is a branch of mathematics concerning the study of finite or countable discrete structures. Aspects of combinatorics include counting the structures of a given kind and size , deciding when certain criteria can be met, and constructing and analyzing objects meeting the criteria ,...
mathematics
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
, Fisher's inequality, named after Ronald Fisher
Ronald Fisher
Sir Ronald Aylmer Fisher FRS was an English statistician, evolutionary biologist, eugenicist and geneticist. Among other things, Fisher is well known for his contributions to statistics by creating Fisher's exact test and Fisher's equation...
, is a necessary condition for the existence of a balanced incomplete block design satisfying certain prescribed conditions.
Fisher, a population geneticist
Population genetics
Population genetics is the study of allele frequency distribution and change under the influence of the four main evolutionary processes: natural selection, genetic drift, mutation and gene flow. It also takes into account the factors of recombination, population subdivision and population...
and statistician
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
, was concerned with the design of experiments
Design of experiments
In general usage, design of experiments or experimental design is the design of any information-gathering exercises where variation is present, whether under the full control of the experimenter or not. However, in statistics, these terms are usually used for controlled experiments...
studying the differences among several different varieties of plants, under each of a number of different growing conditions, called "blocks".
Let:
- v be the number of varieties of plants;
- b be the number of blocks.
It was required that:
- k different varieties are in each block, k < v; no variety occurs twice in any one block;
- any two varieties occur together in exactly λ blocks;
- each variety occurs in exactly r blocks.
Fisher's inequality states simply that